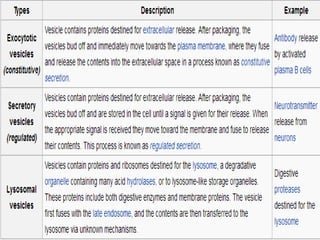
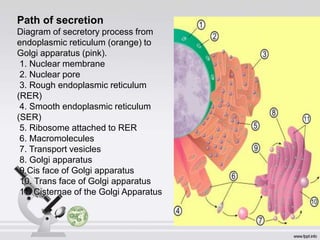
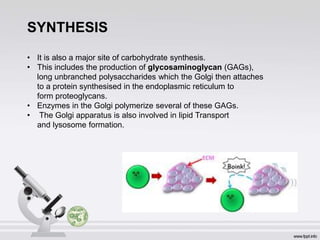
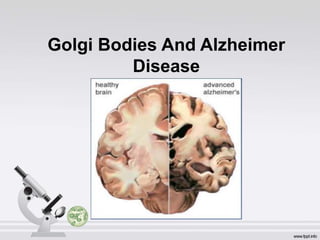
The Golgi apparatus, discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1898, is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells, playing a crucial role in processing and transporting proteins and lipids. It consists of a stack of cisternae and is involved in various cellular functions including secretion, synthesis, sulfation, and phosphorylation. The Golgi apparatus is essential for proper functioning, and its dysfunction is linked to conditions such as Alzheimer's disease.