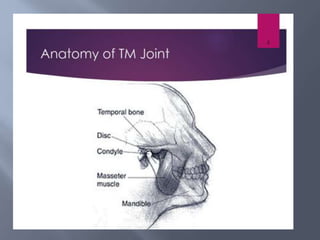
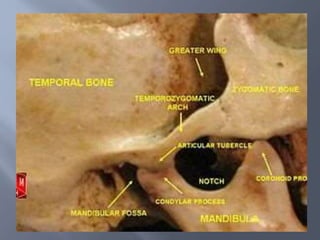
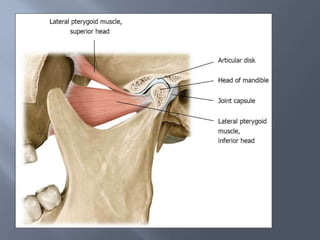
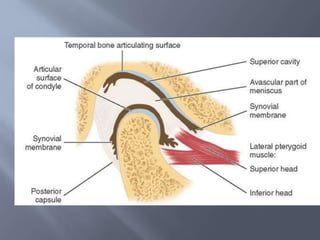
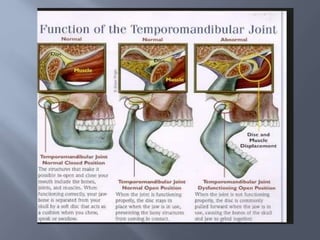
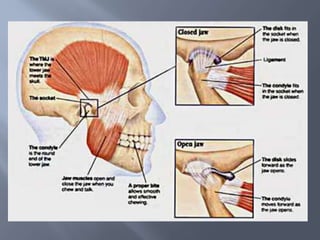
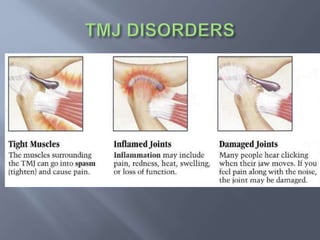
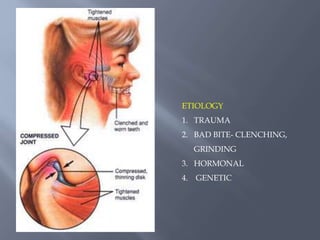
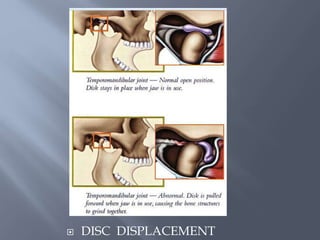
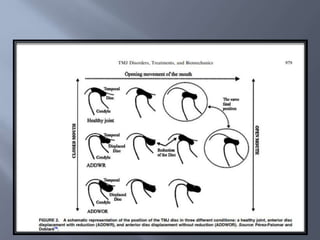
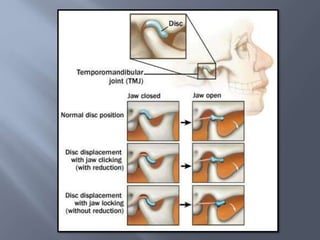
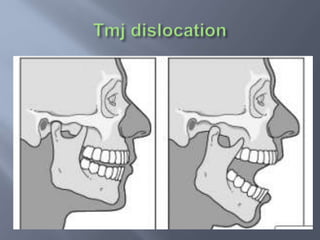
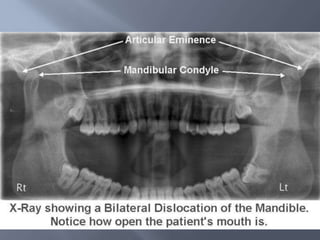
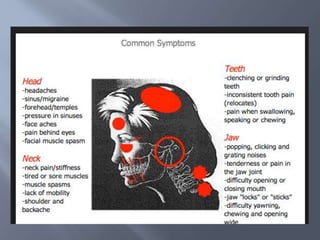
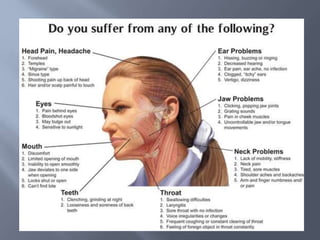
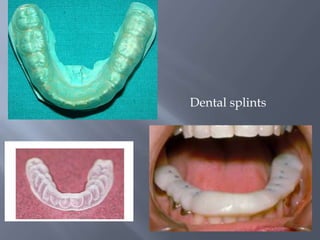
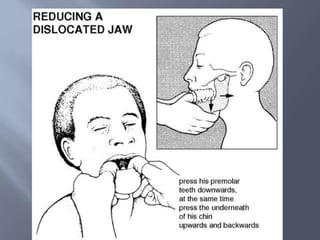
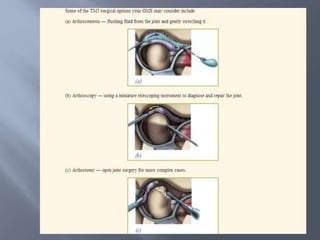
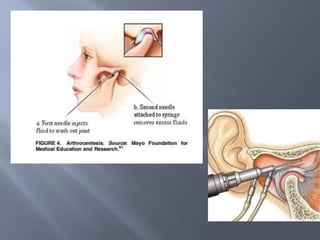
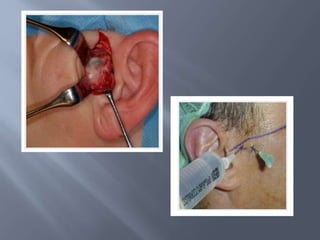
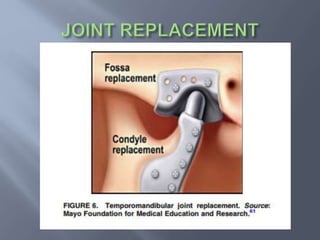
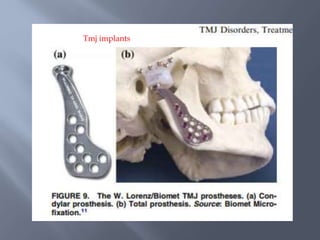
Temporomandibular joint and muscle disorders (TMJ) cause jaw pain and dysfunction. There are three main types: myofascial pain involving jaw muscles, internal derangement involving a displaced disc or joint injury, and arthritis. Causes include trauma, teeth grinding, hormones, genetics, and stress. Treatment involves heat/ice, soft diet, jaw exercises, relaxation techniques, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs. More severe cases may require physical therapy, splints, injections, or surgery like arthrocentesis, arthroscopy, or disc removal.