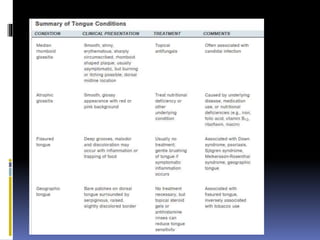
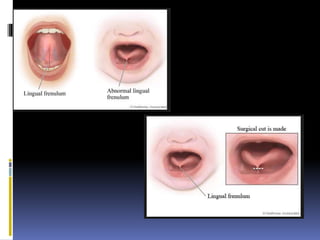
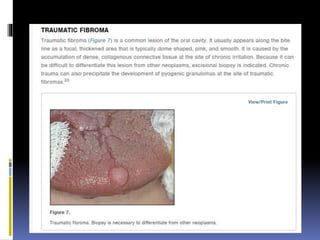
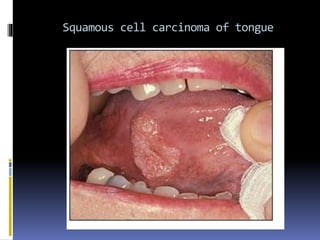
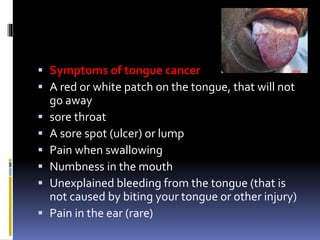
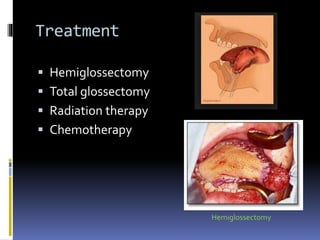
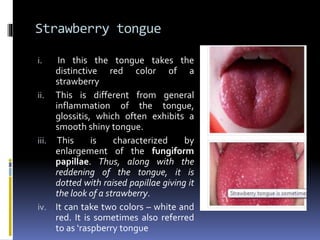
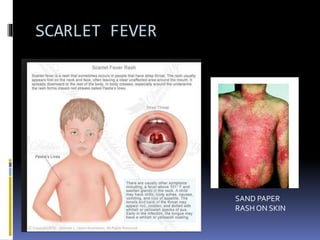
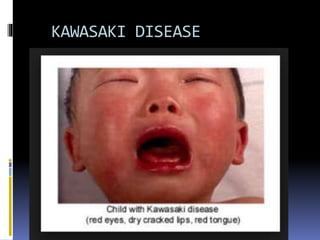
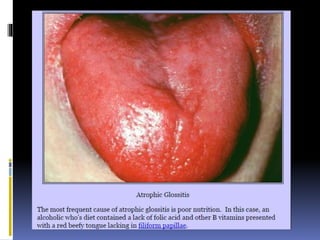
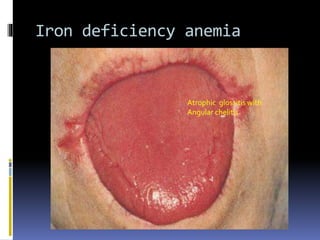
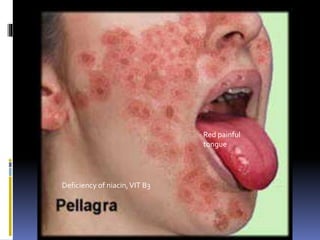
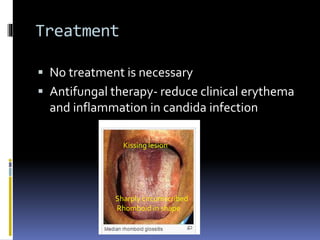
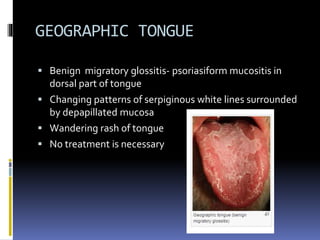
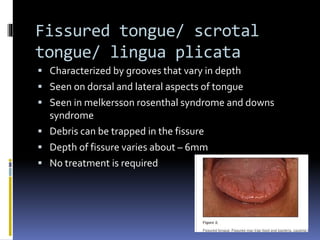
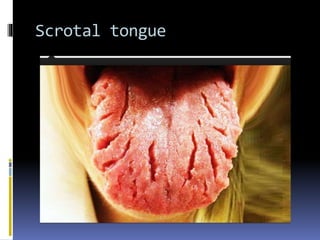
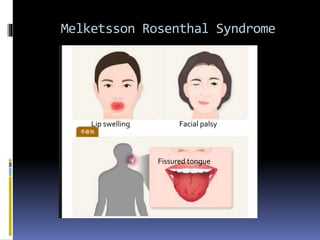
The document discusses several disorders of the tongue including oral hairy leukoplakia, hairy tongue, ankyloglossia, squamous cell carcinoma, strawberry tongue, pernicious anemia, median rhomboid glossitis, geographic tongue, fissured tongue, and burning mouth syndrome. It provides details on symptoms, causes, and treatments for each condition. Key information includes that oral hairy leukoplakia is associated with HIV, hairy tongue results from poor oral hygiene, ankyloglossia restricts tongue movement, smoking increases risk of squamous cell carcinoma, and strawberry tongue reflects underlying diseases like scarlet fever or Kawasaki disease.












![BMS
Burning Mouth Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome (also called oral dysesthesia) occurs most
commonly in women after menopause.
The most commonly affected part of the mouth is the tongue (pain
in the tongue is termed glossodynia)
. A painful burning sensation may affect the entire mouth
(particularly the tongue, lips, and roof of the mouth [palate]) or just
the tongue
The sensation may be continuous or intermittent and may gradually
increase throughout the day.
Symptoms that commonly accompany the burning sensation
include a dry mouth, thirst, and altered taste
Possible consequences include changes in eating habits, irritability,
depression, and avoidance of other people.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tonguedisorders-150616104030-lva1-app6892/85/Tongue-disorders-32-320.jpg)