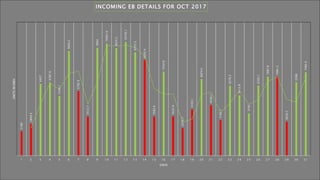
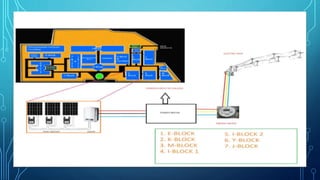
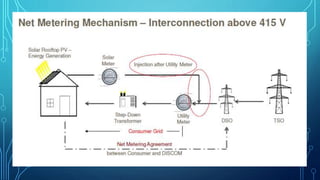
The document describes a project aimed at designing a reverse power relay to manage power flow from rooftop solar PV systems when connected to the grid. By monitoring the load consumed and solar output, the relay disconnects panels to prevent reverse power flow, particularly during times of low demand. The system utilizes a microcontroller for control signals, and a simulation is presented to demonstrate its effectiveness in real-time scenarios.