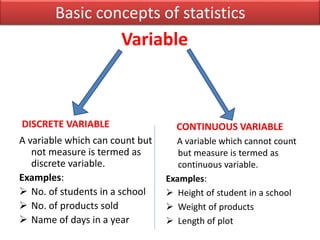
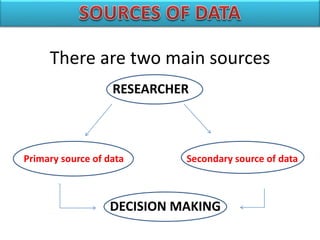
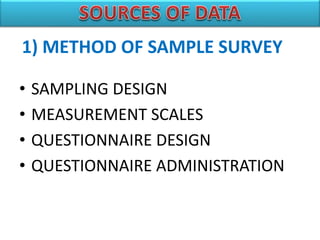
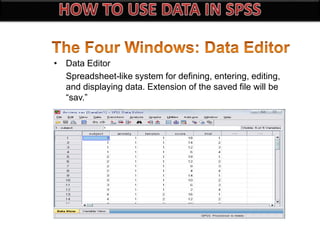
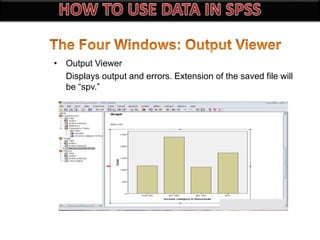
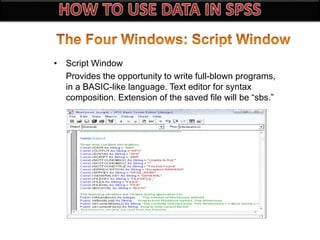
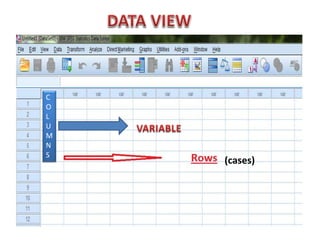
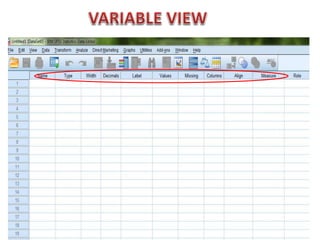
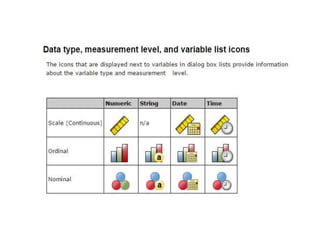
The document introduces SPSS as a powerful statistical package for social sciences that streamlines data analysis and manipulation. It covers basic statistical concepts, types of data, sources of data, and the functionalities of SPSS including data entry, editing, and various statistical techniques like correlation and hypothesis testing. Additionally, it discusses levels of measurement and provides insights into questionnaire design and data output features in SPSS.