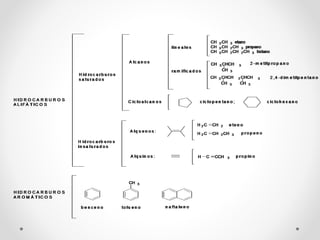
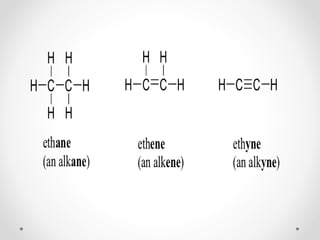
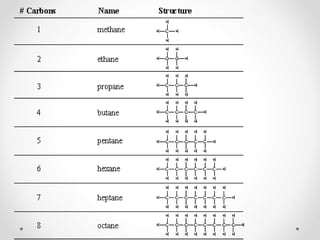
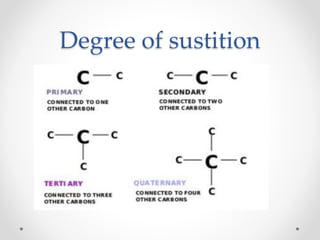
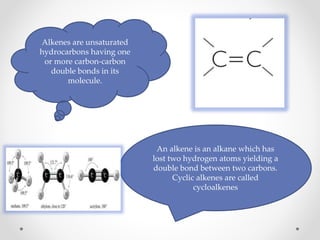
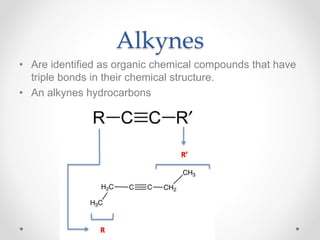
The document discusses aliphatic hydrocarbons, which are organic compounds formed by carbon and hydrogen in open chains, and categorizes them into alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes based on their bond types. Alkanes, with the general formula CnH2n+2, are saturated hydrocarbons characterized by single bonds, while alkenes and alkynes contain double and triple bonds respectively. Cyclic forms are also described, along with traditional naming conventions for these hydrocarbons.