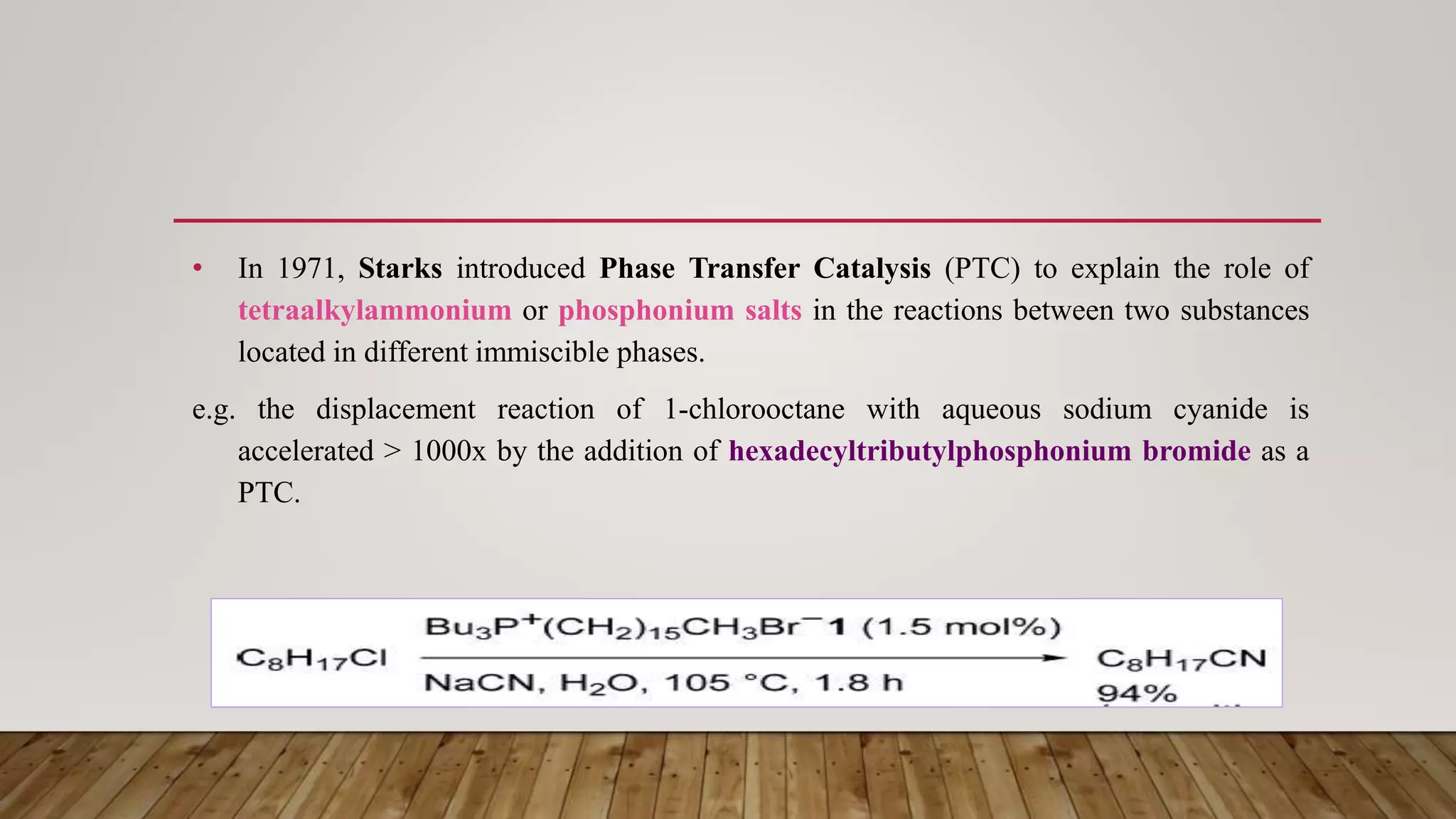
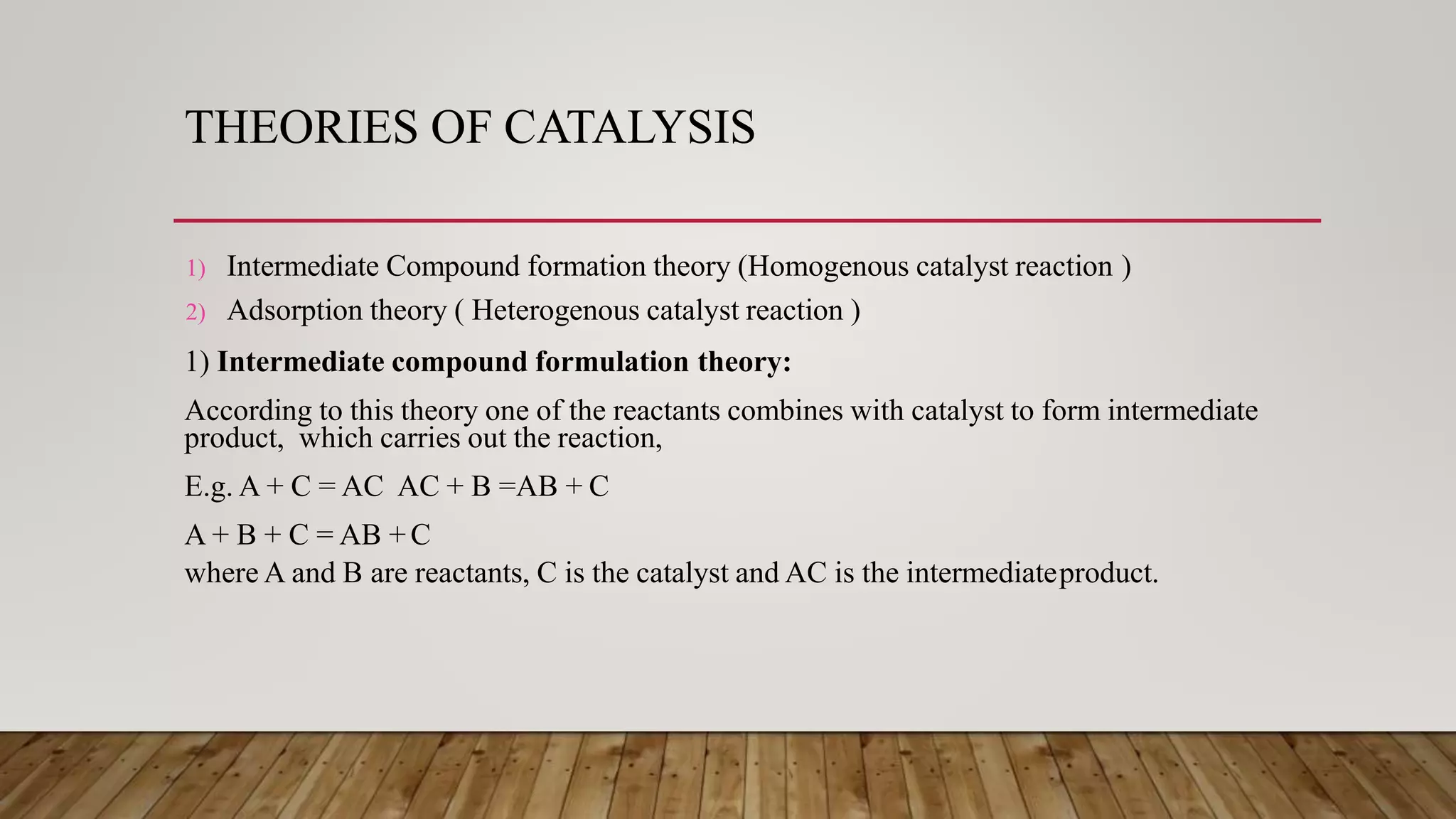
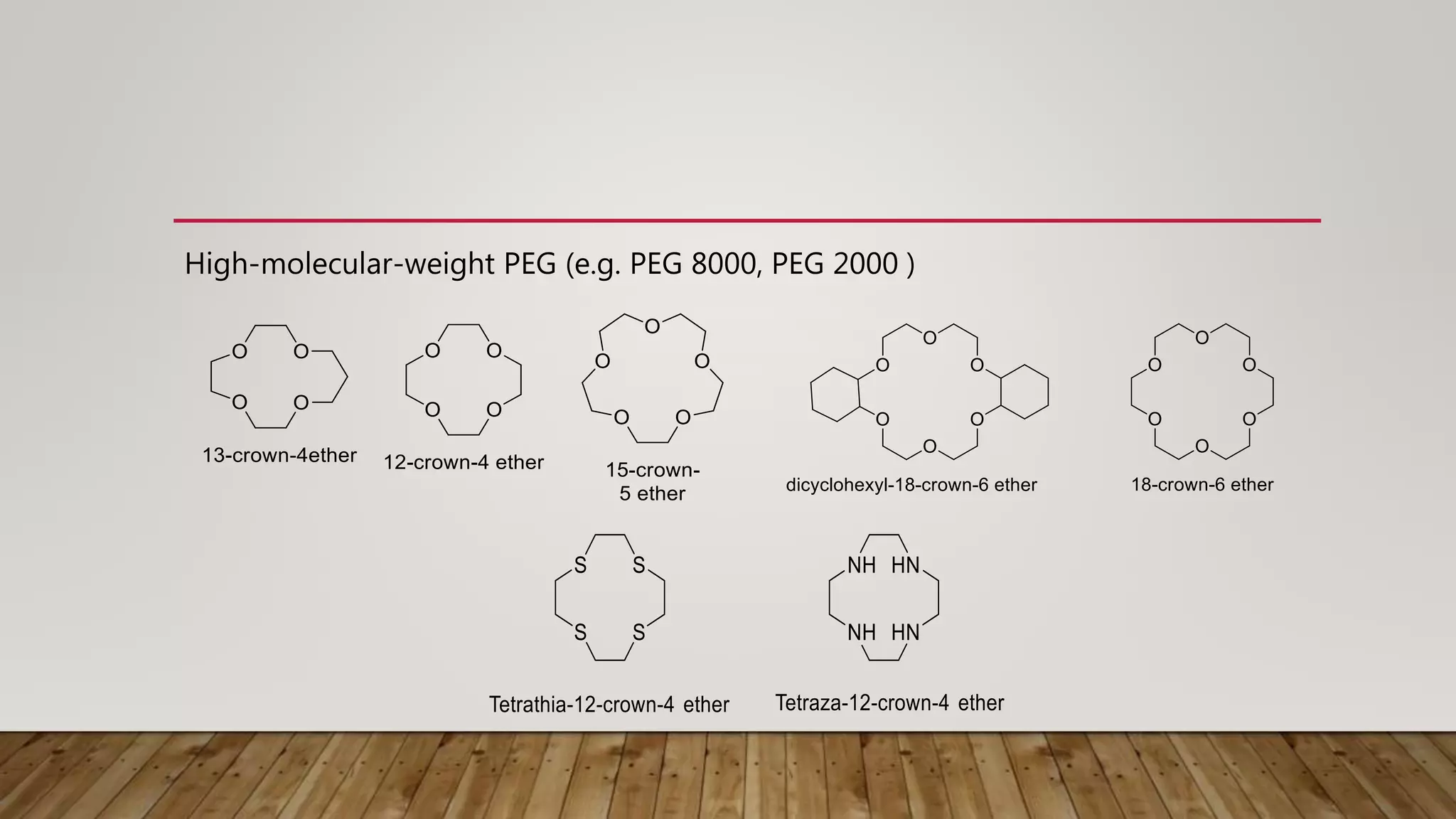
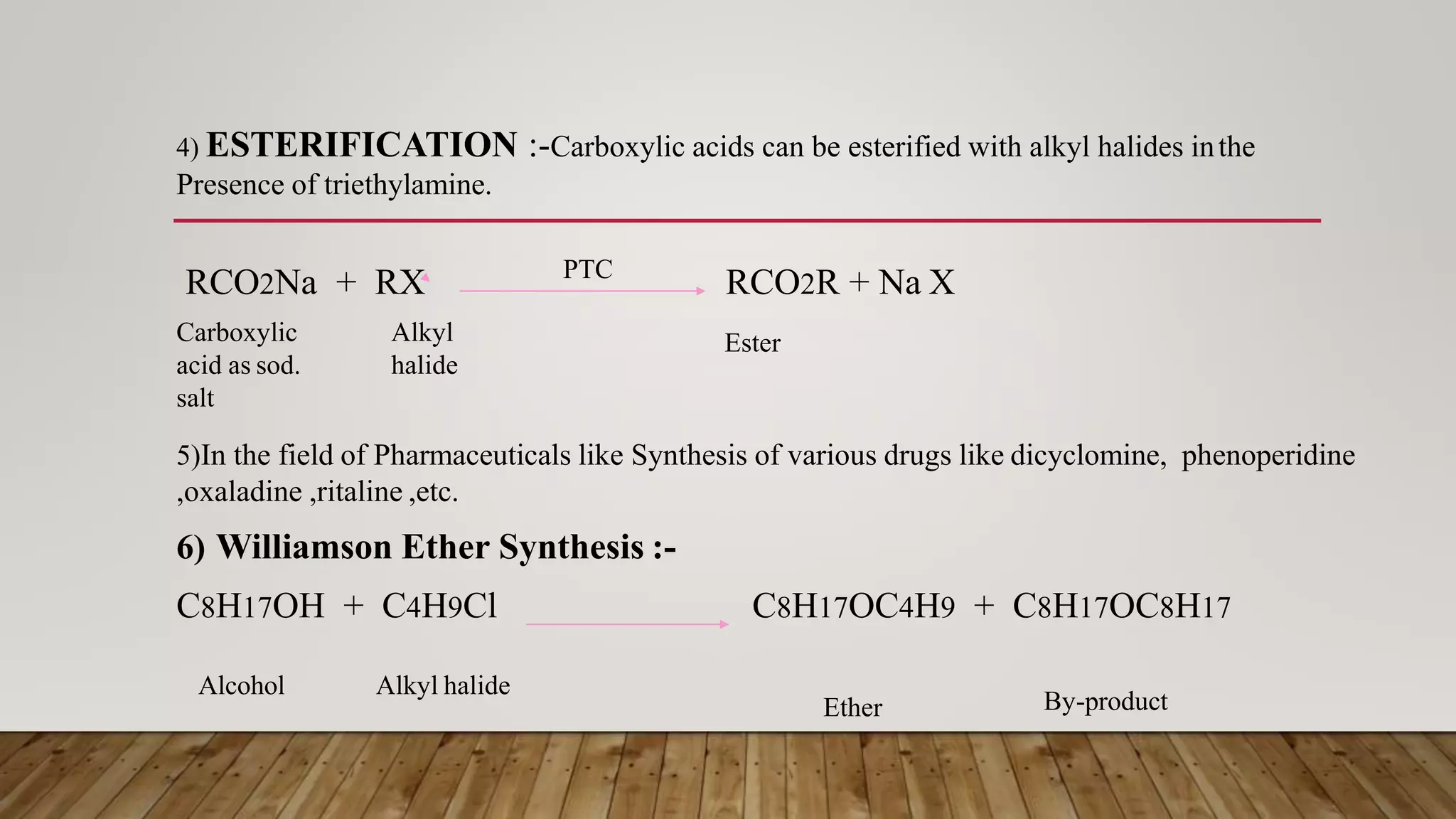
Phase transfer catalysis involves using a catalyst to transfer a reactant from one immiscible liquid phase to another where the reaction takes place. Common phase transfer catalysts are quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. The catalyst forms an ion pair with the reactant anion, transporting it into the organic phase where it undergoes nucleophilic substitution or other reactions. Phase transfer catalysis allows reactions between ions and organic molecules that would otherwise not interact due to being in separate phases. It has many applications in organic synthesis and pharmaceutical manufacturing.