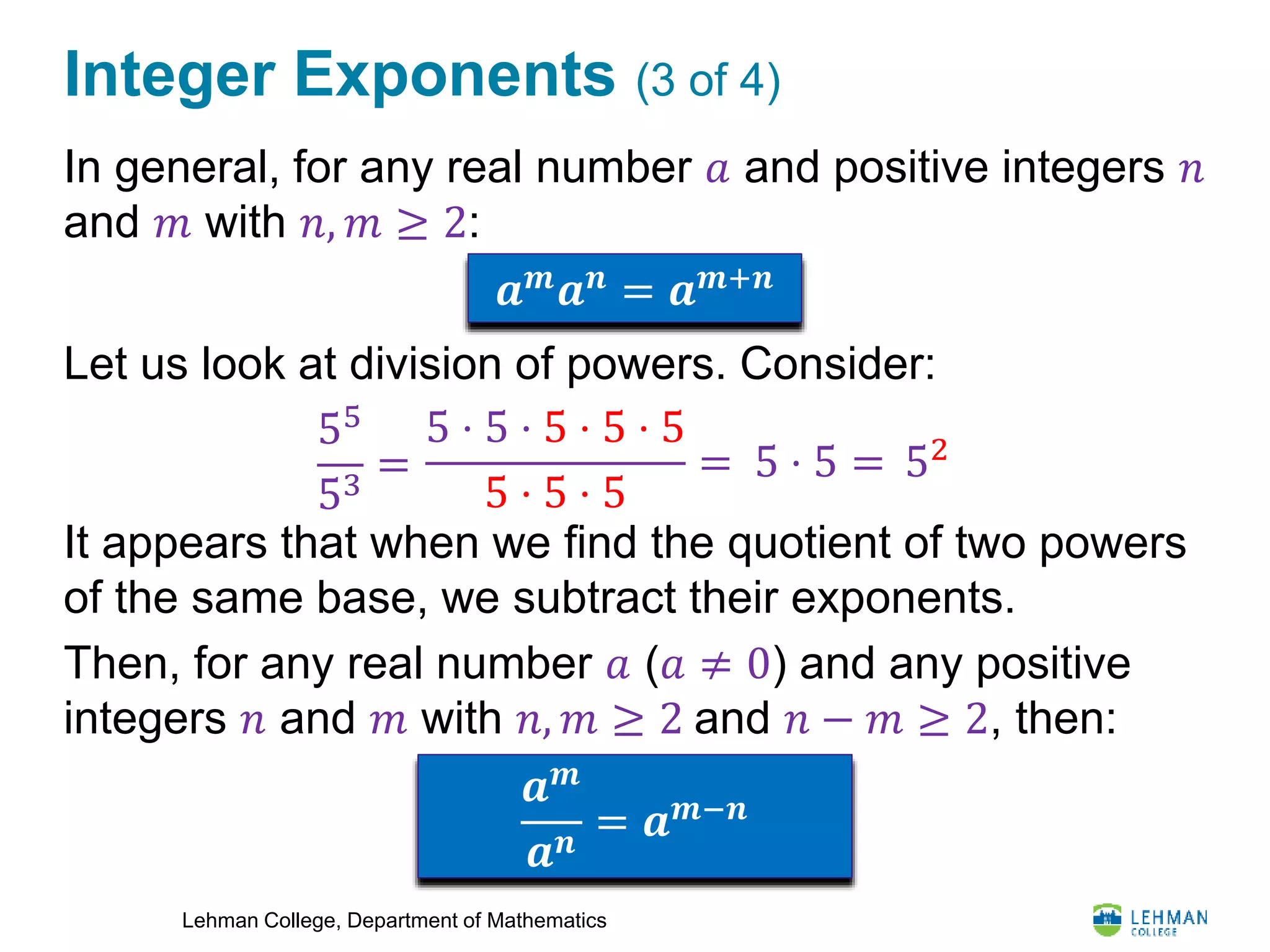
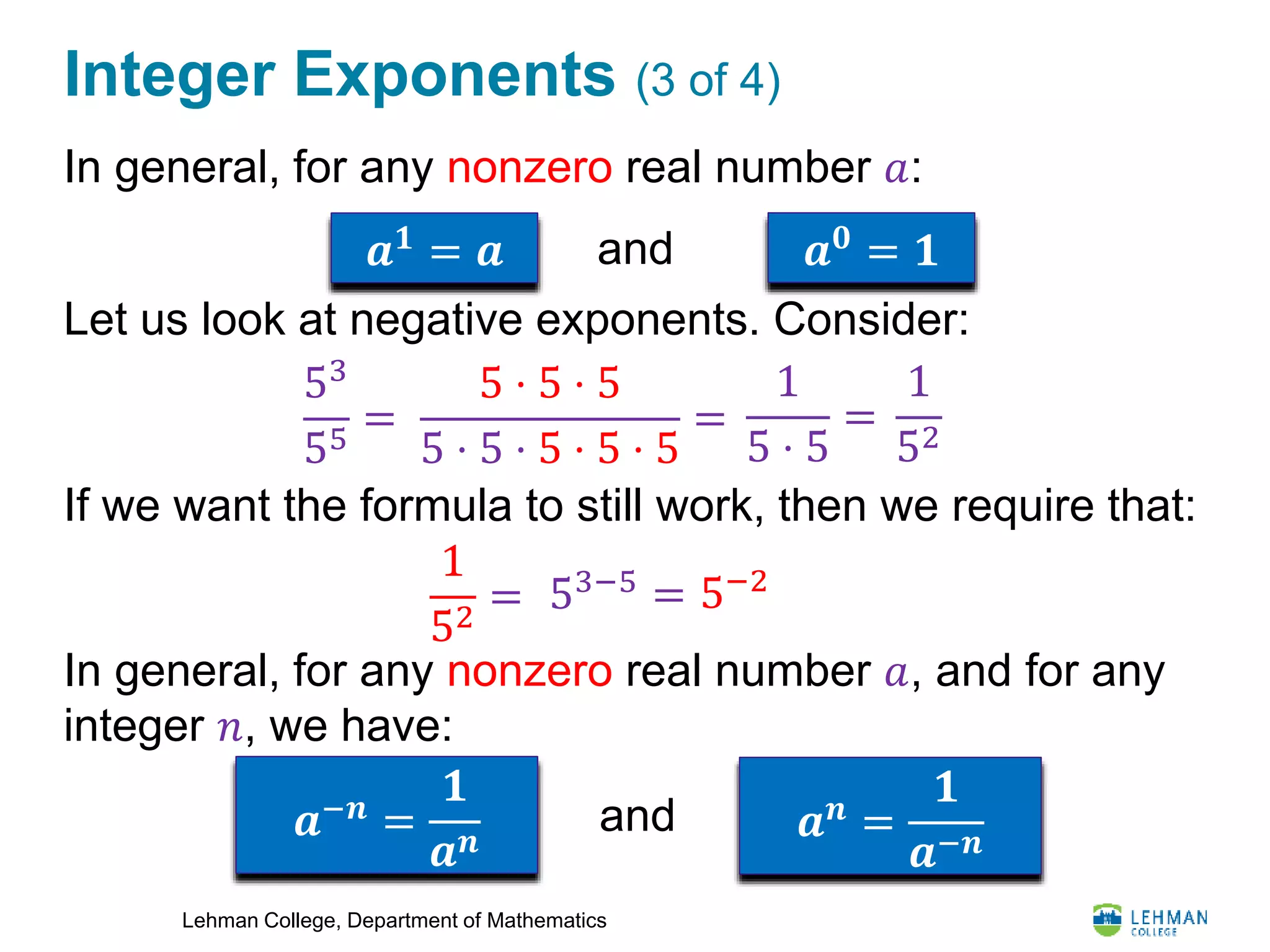
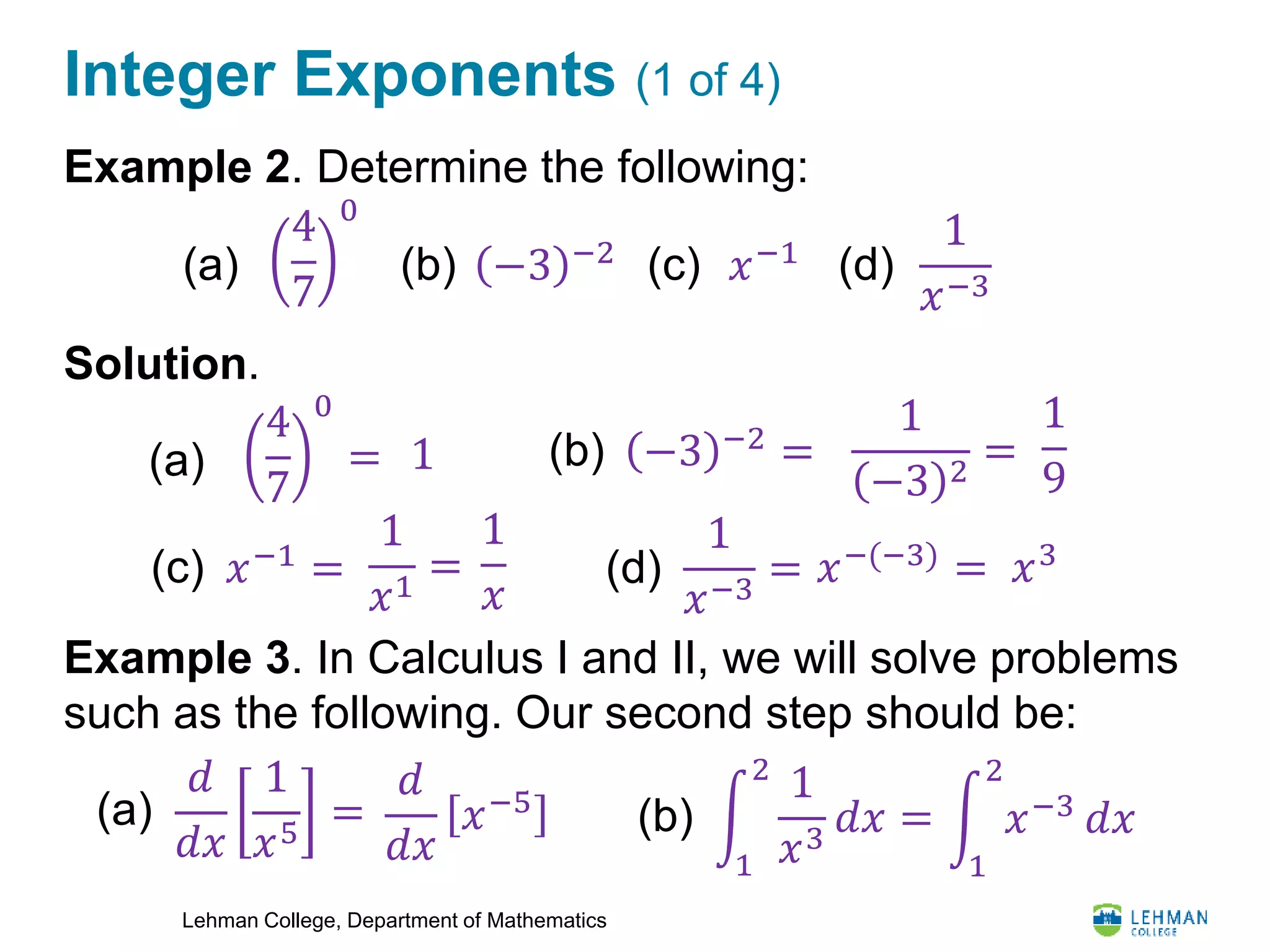
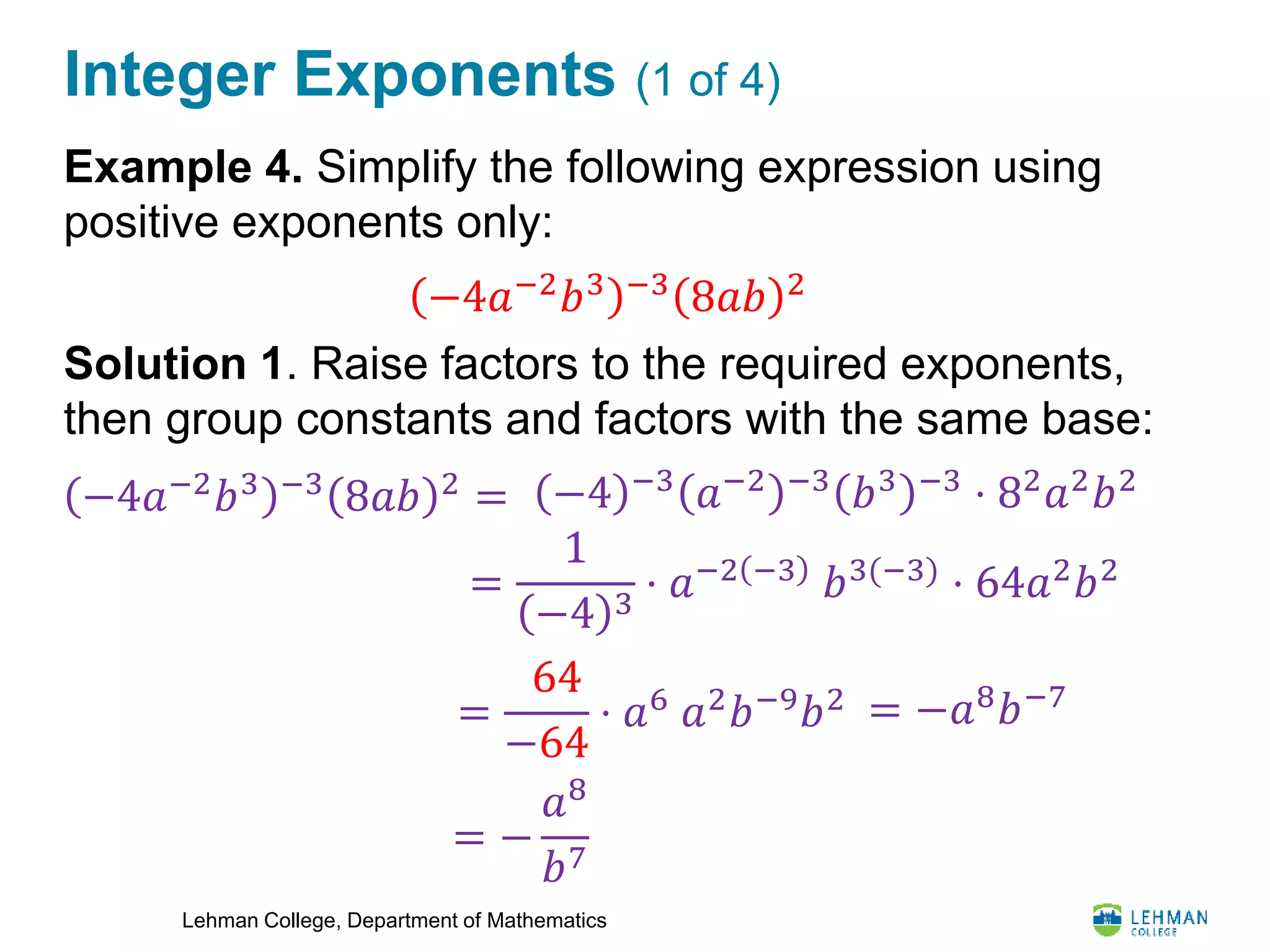
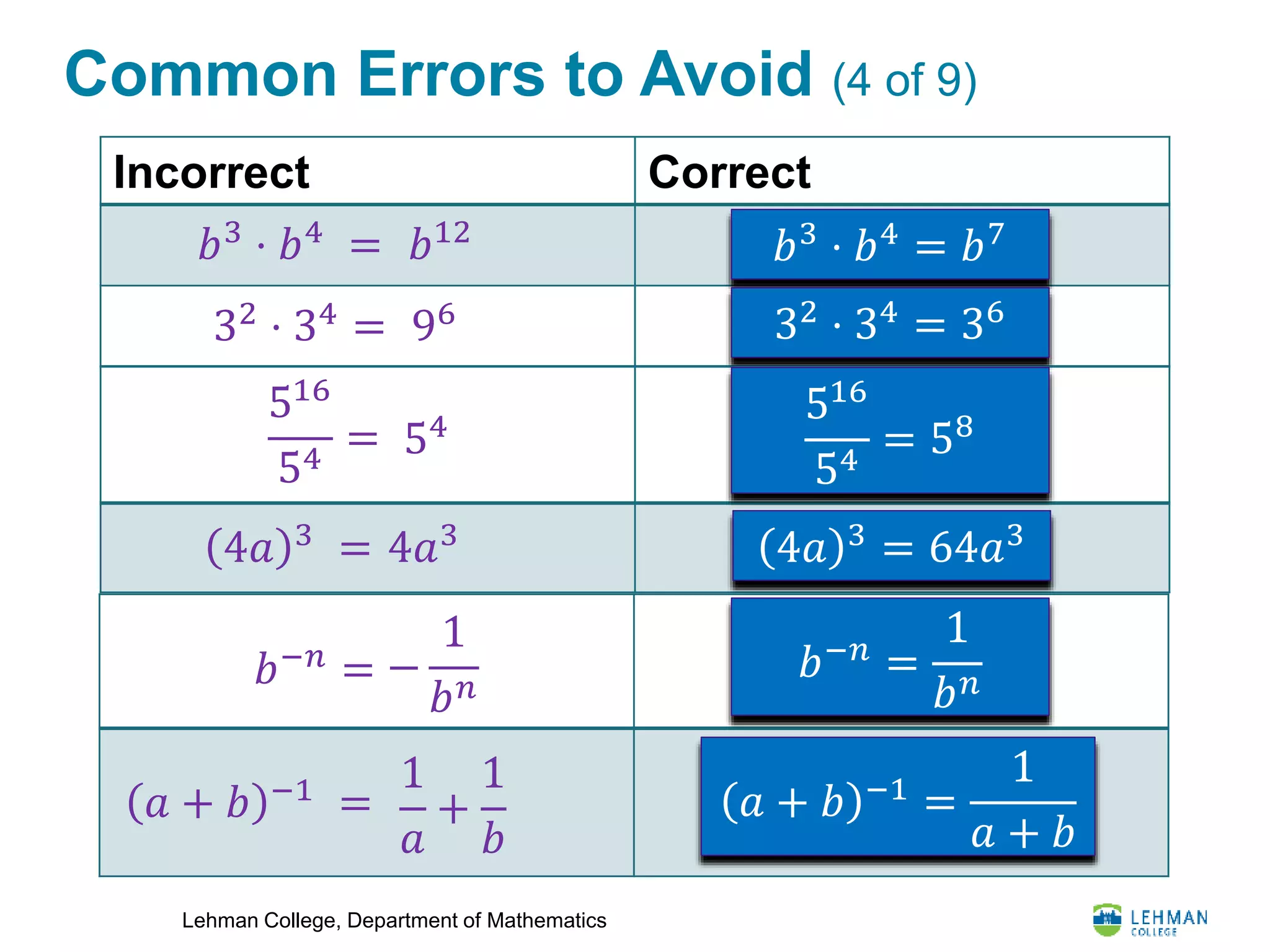
This document provides an overview of integer exponents and exponential notation. It defines exponential notation as a product of identical numbers written as a base with an exponent. Some key rules covered include: when multiplying powers of the same base, add the exponents; when dividing powers of the same base, subtract the exponents; when raising a power to another power, multiply the exponents; and how to simplify expressions using positive exponents. Examples are provided to demonstrate applying these rules to simplify exponential expressions.