This document discusses exponents and powers. It begins with an introduction that explains how exponents are used to write very large numbers in a shorter form. It then defines exponents and bases. Several laws of exponents are covered, including multiplying and dividing powers with the same base, taking powers of powers, and multiplying powers with the same exponent. Examples are provided to illustrate each law and concept. The document appears to be from a textbook on exponents and powers for students.







![1.3 LAWS OF EXPONENTS
1.3.1 Multiplying Powers with the Same Base
(i) Let us calculate 22 x 23
22 x 23 = (2x2) x (2x2x2)
= 2x2x2x2x2 =25=22+3
Note that the base in 22 and 23 is same and the sum of the
exponents, i.e., 2 and 3 is 5
(ii) (-3)4 x (-3)3= [(-3) x (-3) x (-3) x (-3)] x [(-3) x (-3) x (-3)]
= (-3) x (-3) x (-3) x (-3) x (-3) x (-3) x (-3)
= (-3)7
= (-3)4+3
Again, note that the base is same and the sum of exponents,
4 and 3, is 7
(iii) a2 x a4= (a x a ) x (a x a x ax a)
= a x a x a x a x a x a = a6
(Note: the base is the same and the sum of exponents is 2+4
= 6)
From this we can generalize that for any non-zero integer a,
where m and n are whole numbers,
TRY THESE
Simplify and write in exponential form
i) 25x23 ii) p3x p2 iii)43x 42 iv) a3xa2xa7
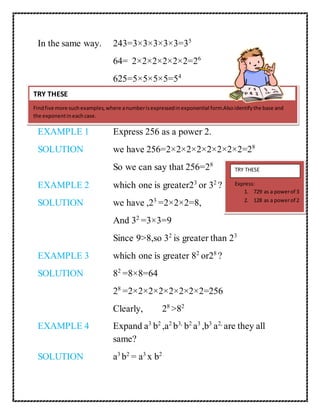
am x an = am+n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitaltextbookganesh-140916030603-phpapp01/85/Digital-textbook-EXPONENTS-AND-POWERS-9-320.jpg)





![1. 4 MISCELLANEOUS EXAMPLES USING THE
LAWS OF EXPONENTS
Let us solve some examples using rules of exponents
developed.
EXAMPLE 10 Write exponential form for 8 x 8 x 8 x 8
taking base as 2.
SOLUTION:
We have 8x8x8x8 =84
But we know that 8= 2 x 2 x 2 =23
Therefore 84=(23)4 =23 x 23 x 23 x 23
= 23x4 (You may also use (am)n= amn )
= 212
EXAMPLE 11 Simplify and write the answer in the
exponential form.
(i) 23 x 22 x 55 (ii) (62x64) ÷ 63
(iii) [(22)3 x 36]x 56 (iv) 82 ÷ 23
SOLUTION
(i) 23 x 22 x 55=23+2 x 55
= 25 x 55=(2 x 5)5=105
(ii) (62x64) ÷ 63 = 62+4 ÷ 63
= 66/63= 66-3= 63
(iii) [(22)3 x 36]x 56 =[26 x 36] x 56
= (2x3)6 x 56
= (2x3x5)6 = 306](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitaltextbookganesh-140916030603-phpapp01/85/Digital-textbook-EXPONENTS-AND-POWERS-15-320.jpg)


