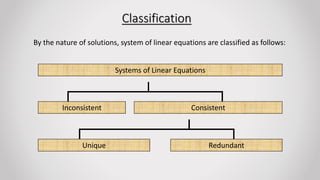
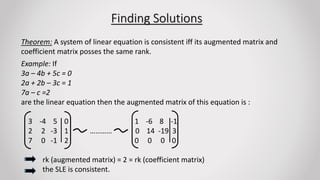
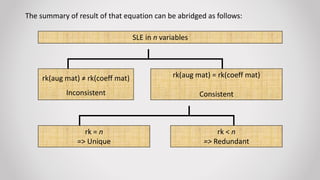
This presentation summarizes key concepts about systems of linear equations. It defines linear equations as those with powers of unknowns equal to 1. Linear equations can have one or multiple unknown variables. Systems of linear equations are classified as consistent or inconsistent based on whether the augmented matrix and coefficient matrix have the same rank. If the ranks are equal, the system is consistent and has either a unique solution or is redundant. If the ranks are unequal, the system is inconsistent. Real-life applications of solving systems of linear equations include event planning, finding unknown quantities, and comparing costs or nutritional information.