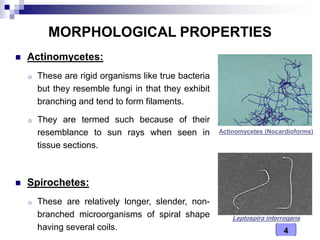
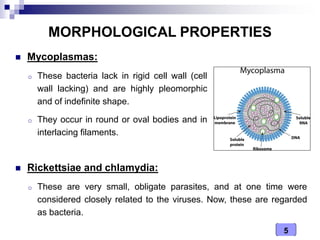
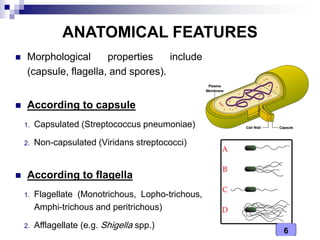
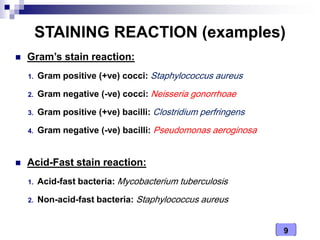
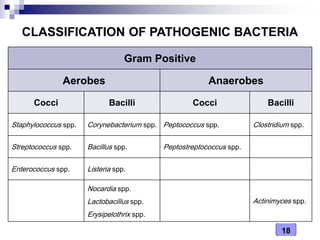
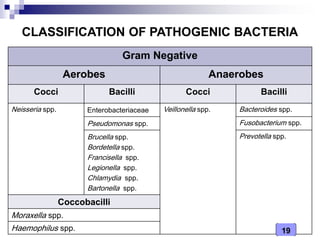
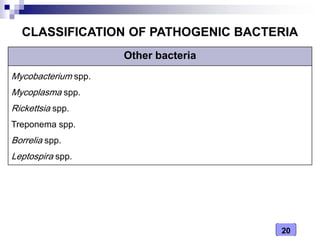
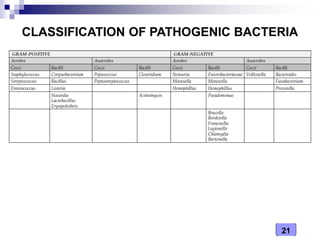
This document discusses the classification of pathogenic bacteria according to their morphological, anatomical, staining, environmental, and pathogenic properties. Bacteria can be classified into six main groups based on their cell shape and structure: cocci, bacilli, actinomycetes, spirochetes, mycoplasmas, and rickettsiae. Other classification schemes include whether bacteria are gram-positive or gram-negative, form spores or flagella, are acid-fast or not, and whether they are aerobic or anaerobic. Pathogenic bacteria are further classified based on if they cause disease, their relationship with the host, and their nutritional requirements.