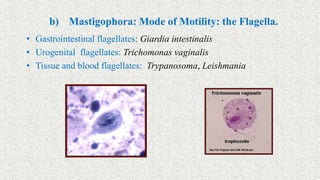
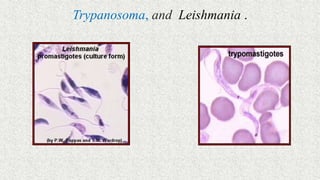
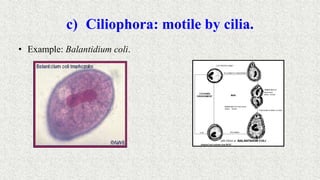
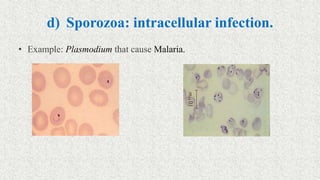
1. Microorganisms are classified through taxonomy, which involves identification, classification, and nomenclature of organisms.
2. Taxonomic classification categories arrange species in a hierarchical order from domain to genus. Identification techniques include microscopy, culture characteristics, biochemical tests, and nucleic acid analysis.
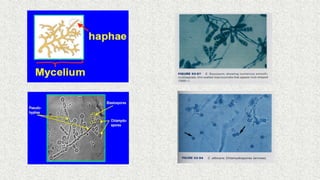
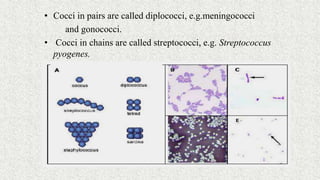
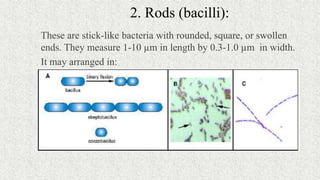
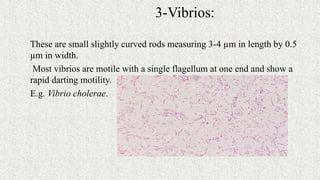
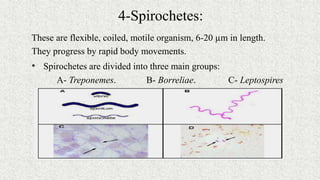
3. Bacteria can be classified by morphology, staining, culture characteristics, oxygen requirements, metabolism, and environmental tolerances. Cocci, bacilli, vibrios, spirochetes, and spirilla are morphological groups.