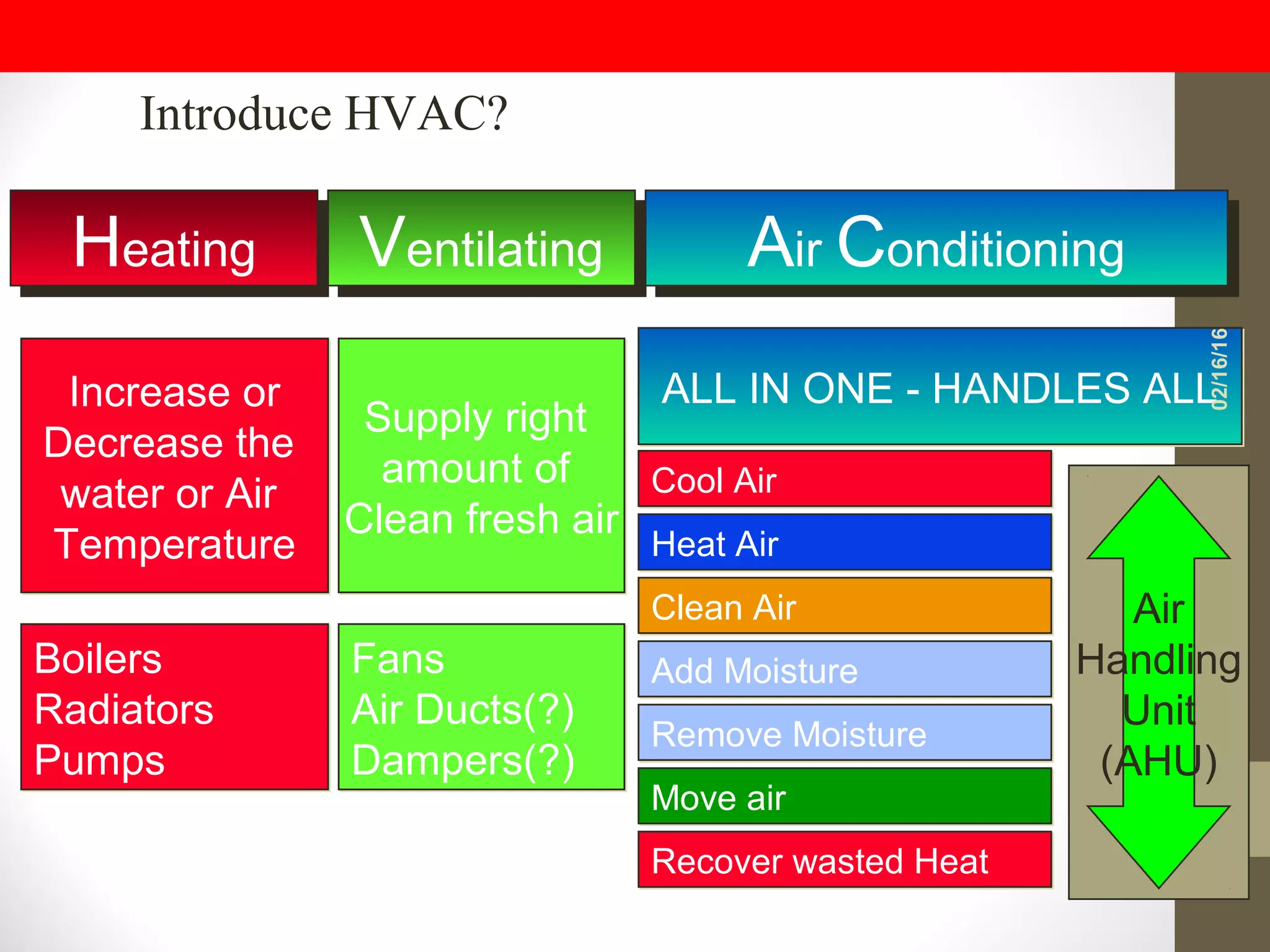
The document covers the fundamentals of HVAC systems, emphasizing the importance of building management systems (BMS) for safety, comfort, and energy efficiency. It explains key concepts, components, and terminology related to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, including air handling units, refrigeration systems, and controls. The content is structured to provide a comprehensive understanding of HVAC operations and the necessity for effective control measures in various types of buildings.