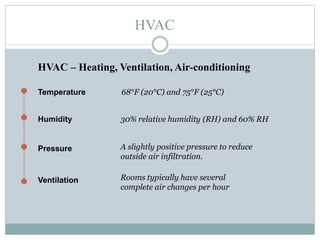
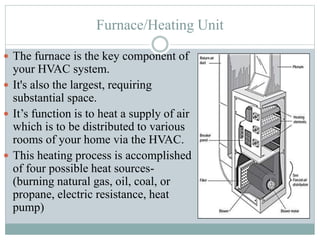
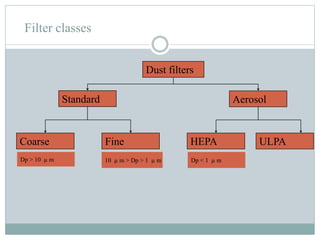
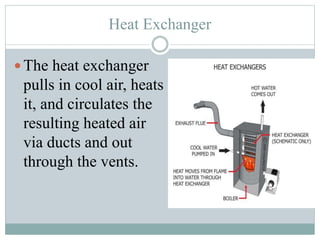
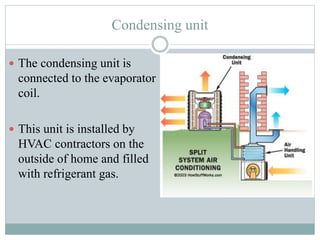
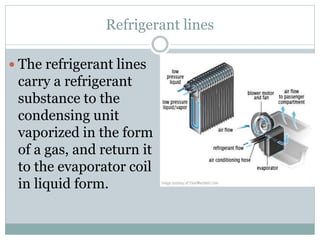
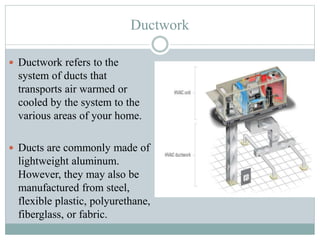
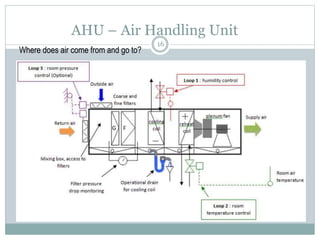
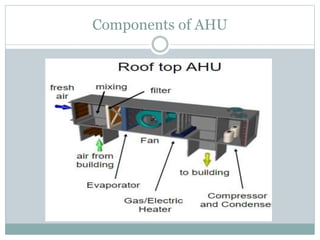
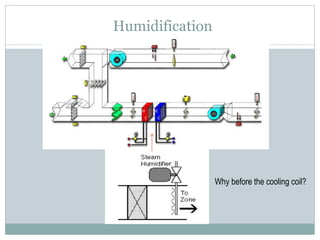
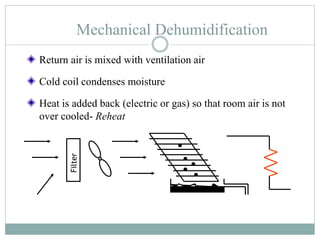
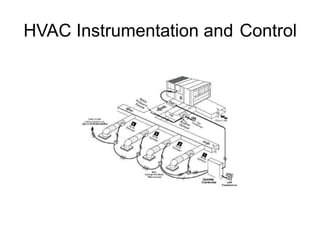
The document discusses HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems. It describes common components of HVAC systems like thermostats, furnaces, air filters, heat exchangers, evaporator coils, condensing units, ductwork, and vents. It explains how these components work together to heat, cool, filter, and circulate air to maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels. The document also discusses air handling units, which condition and circulate air, and their key components like filters, fans, and sensors. Finally, it briefly mentions the importance of HVAC system commissioning to ensure proper installation, documentation, training, and ongoing performance monitoring.