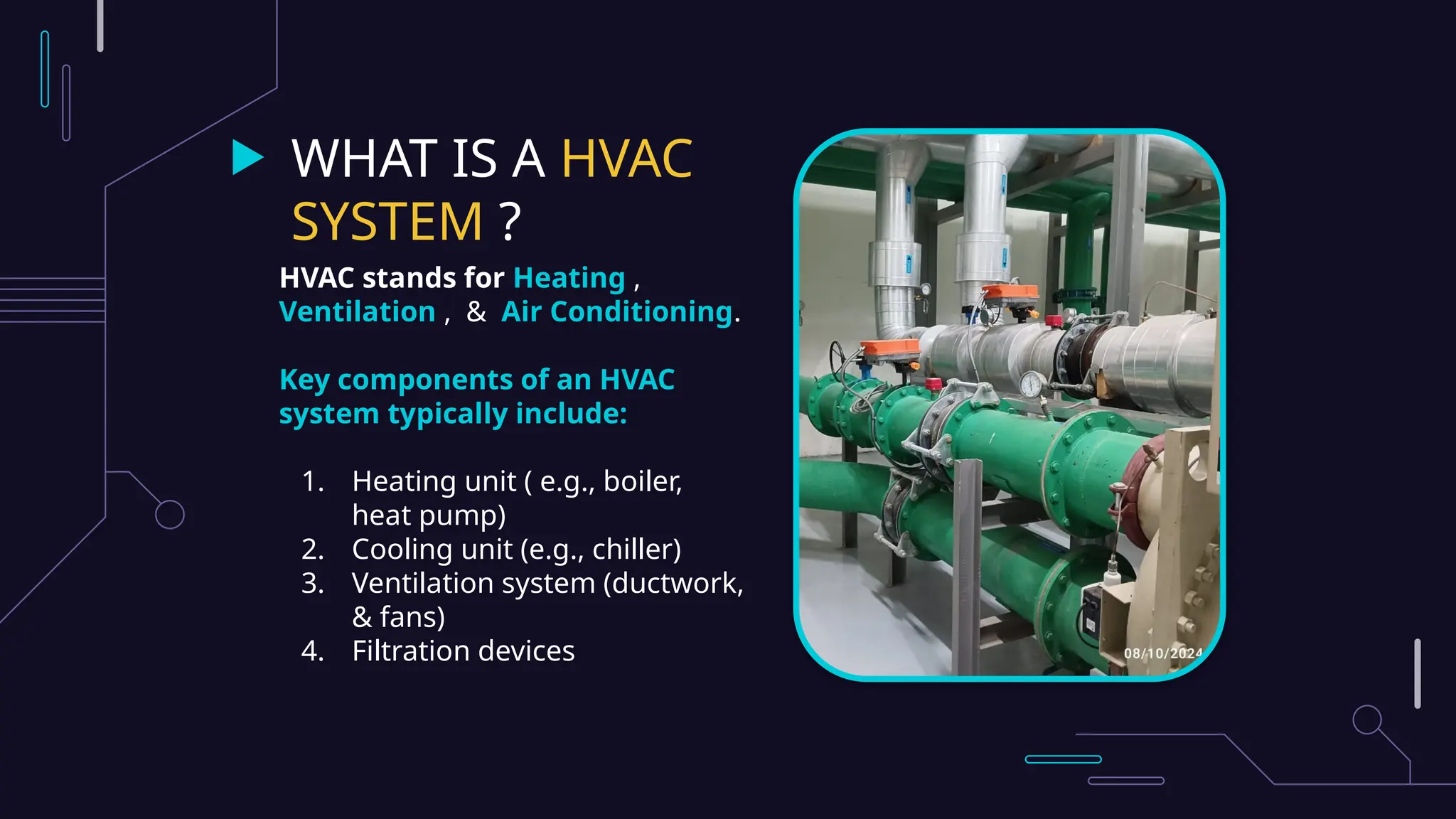
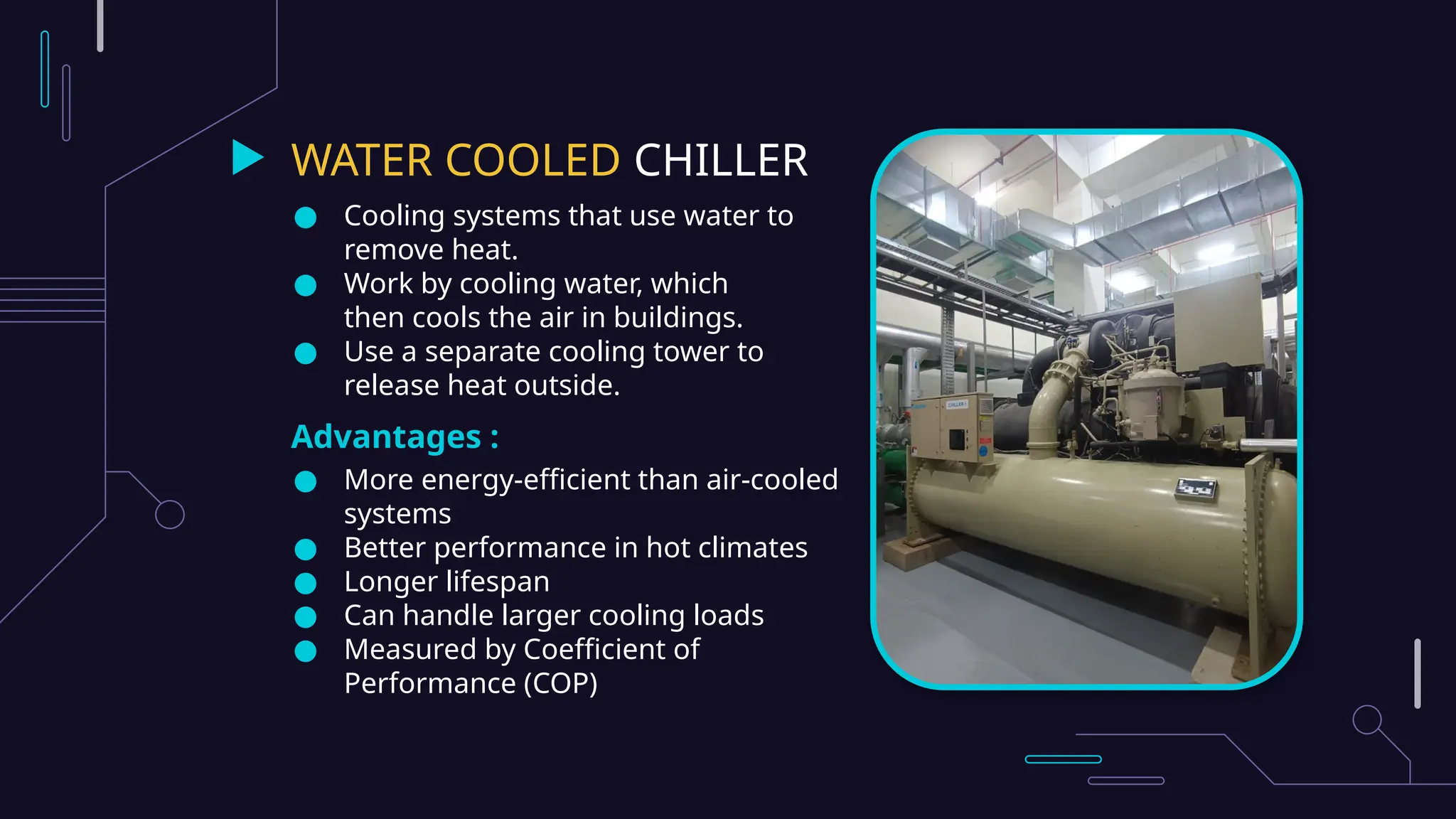
HVAC systems, which include heating, ventilation, and air conditioning components, are essential for maintaining indoor comfort and air quality in modern buildings. They comprise various systems like chillers, ducts, and air handling units to efficiently manage temperature and airflow, while advanced technologies enhance energy efficiency and compliance with standards. These innovations promote sustainable practices, improve operational performance, and contribute to healthier indoor environments.