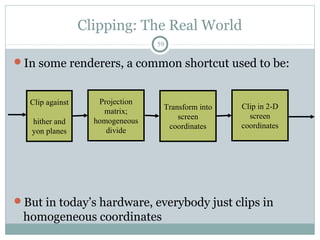
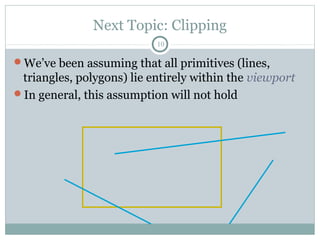
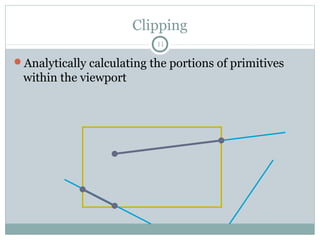
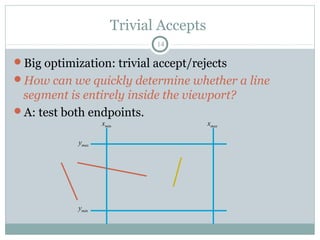
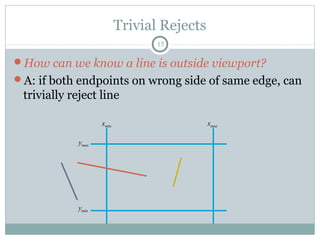
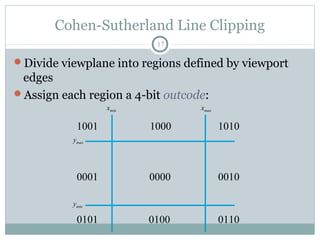
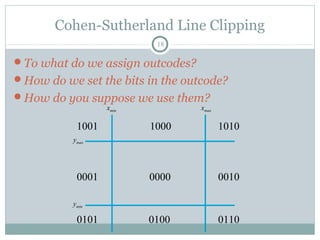
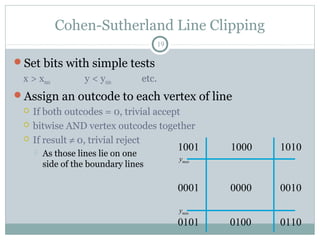
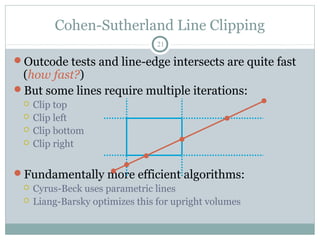
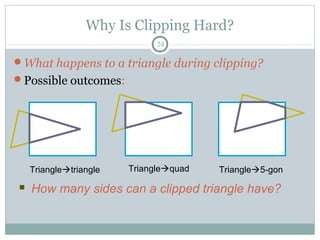
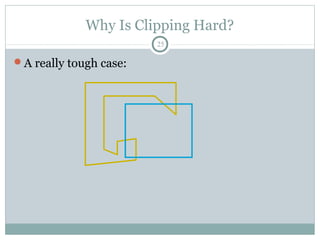
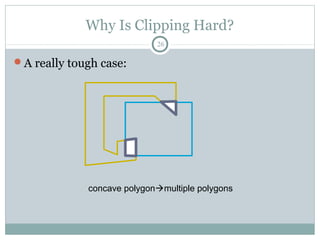
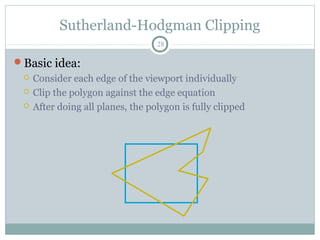
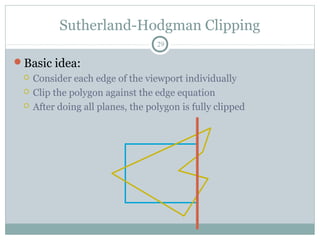
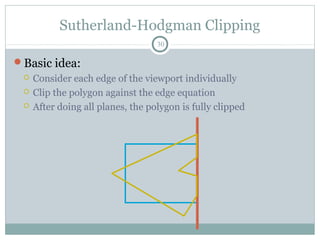
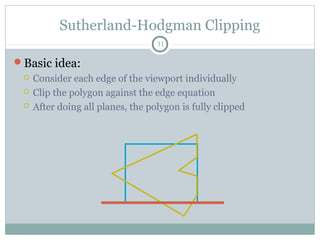
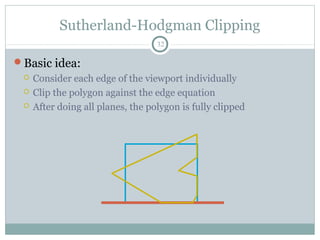
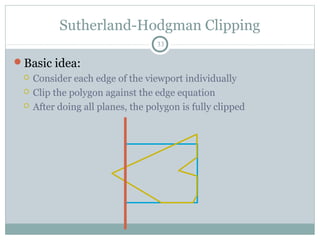
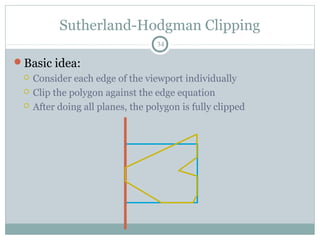
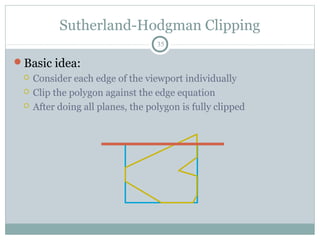
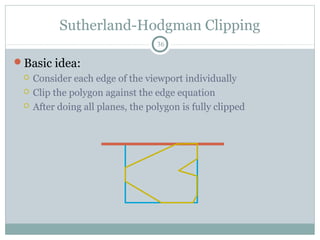
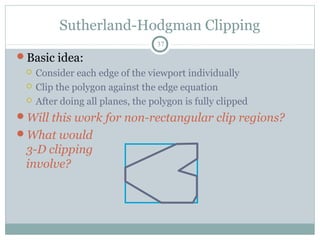
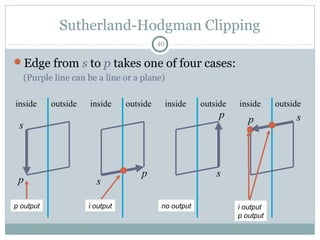
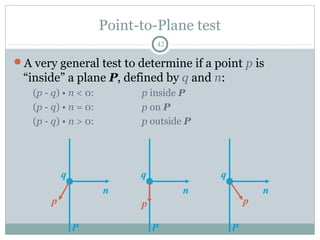
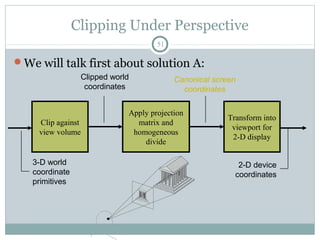
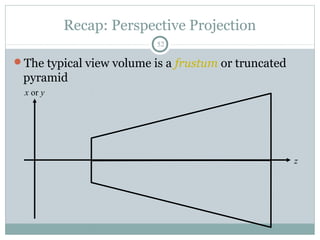
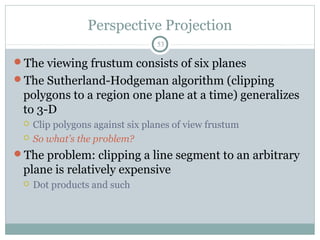
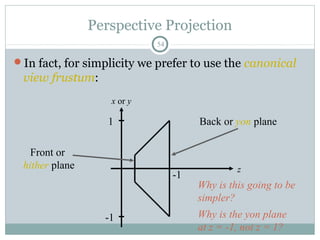
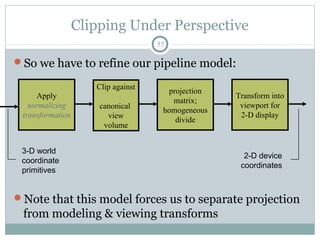
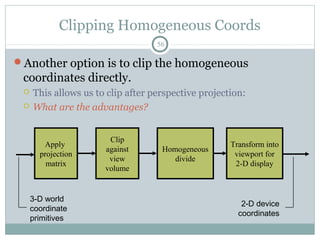
Clipping is a technique used to remove portions of lines, polygons, and other primitives that lie outside the visible viewing area or viewport. There are several common clipping algorithms. Cohen-Sutherland line clipping uses bit codes to quickly determine if a line segment can be fully accepted or rejected for clipping. Sutherland-Hodgman polygon clipping considers each viewport edge individually, clips the polygon against that edge plane, and generates a new clipped polygon. Perspective projection transforms 3D objects to 2D screen coordinates, and clipping must account for objects behind the viewer; this can be done by clipping in camera coordinates before perspective projection or in homogeneous screen coordinates after projection.
















![Finding Line-Plane Intersections
45
Edge intersects plane P where E(t) is on P
q is a point on P
n is normal to P
(E(t) - q) • n = 0
(s + t(p - s) - q) • n = 0
t = [(q - s) • n] / [(p - s) • n]
The intersection point i = E(t) for this value of t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clipping-161115180444/85/Clipping-in-Computer-Graphics-45-320.jpg)
![Line-Plane Intersections
46
Note that the length of n doesn’t affect result:
t = [(q - s) • n] / [(p - s) • n]
Again, lots of opportunity for optimization](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clipping-161115180444/85/Clipping-in-Computer-Graphics-46-320.jpg)
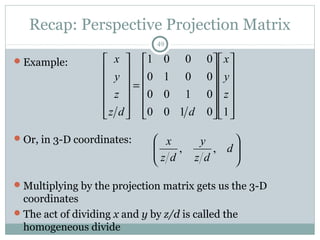


![Clipping Homogeneous Coords
58
So how do we clip homogeneous coordinates?
Briefly, thus:
Remember that we have applied a transform to normalized
device coordinates
x, y [-1, 1]
z [0, 1]
When clipping to (say) right side of the screen (x = 1), instead
clip to (x = w)
Can find details in book or on web](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clipping-161115180444/85/Clipping-in-Computer-Graphics-58-320.jpg)