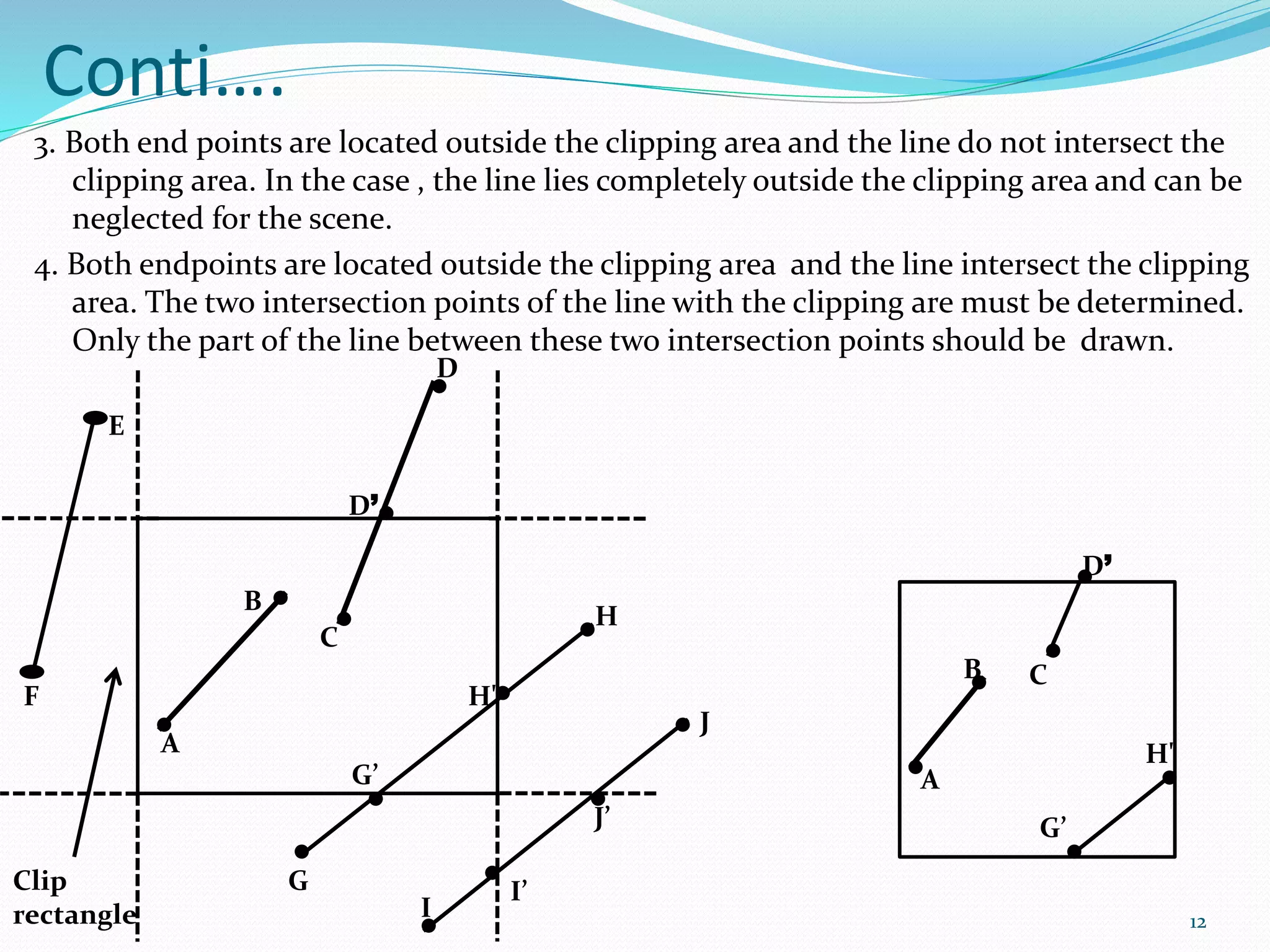
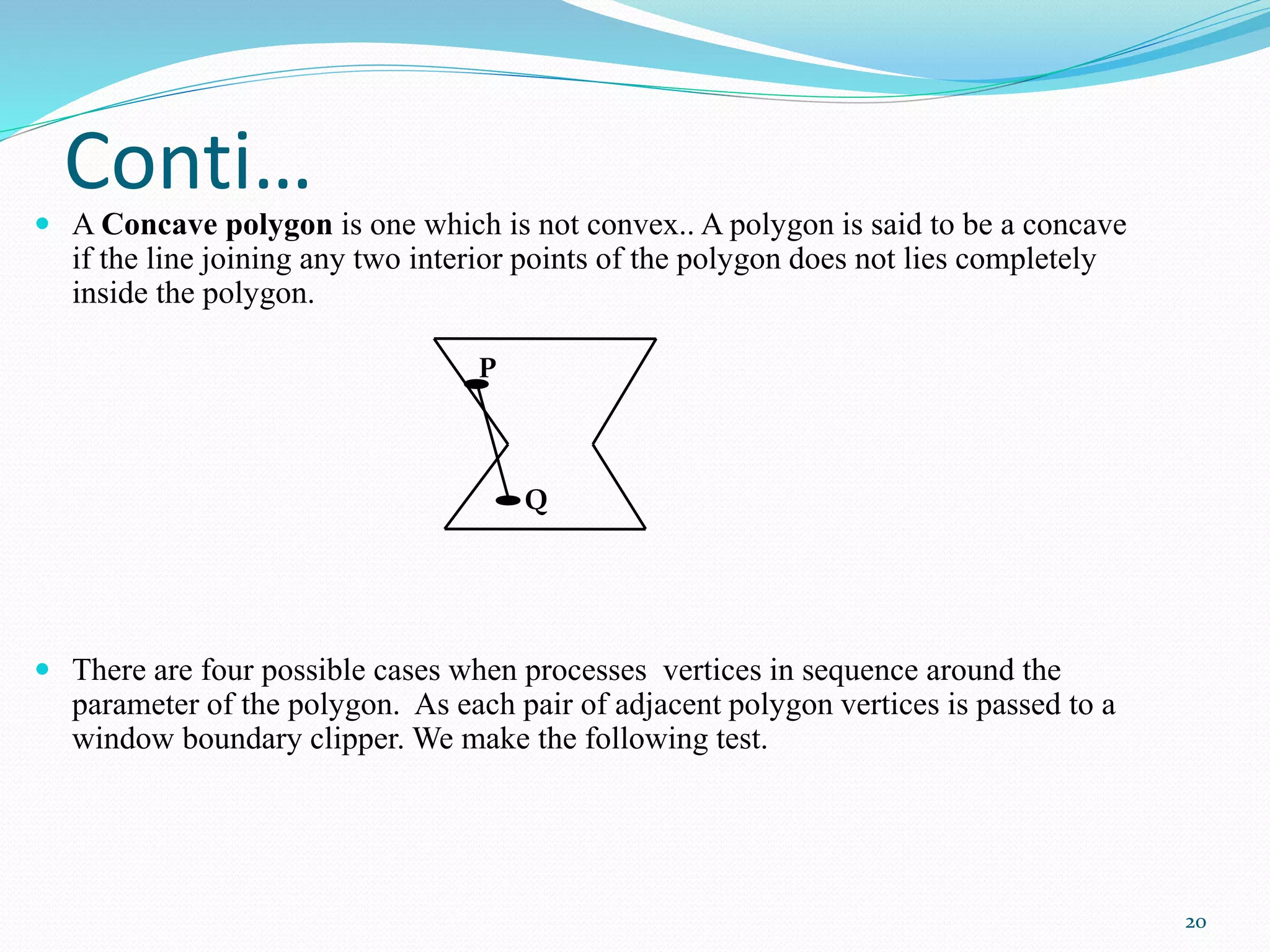
1. There are four cases for line clipping: both endpoints inside the clipping area, both outside and don't intersect, both outside but intersect, and one inside and one outside.
2. The midpoint subdivision algorithm divides lines into three categories - visible, not visible, and candidates for clipping - and recursively subdivides candidate lines until they are categorized.
3. The Cohen-Sutherland and midpoint subdivision algorithms both clip lines but the latter uses midpoint approximation instead of equation solving, making it faster.