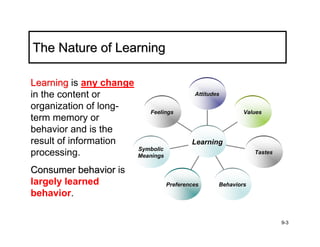
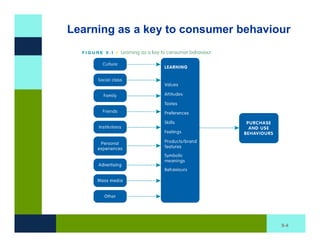
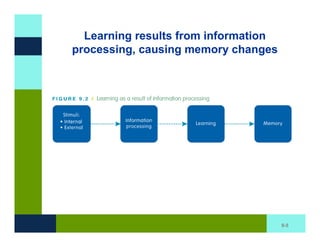
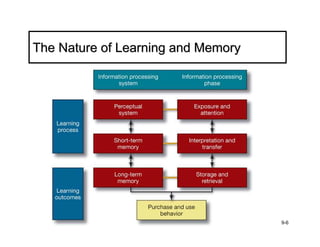
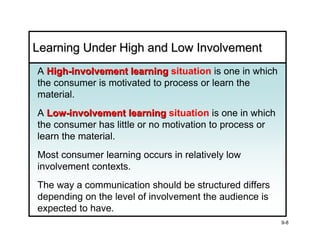
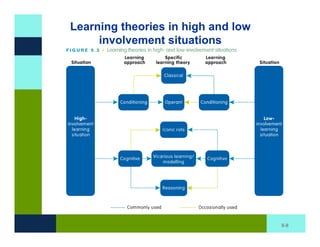
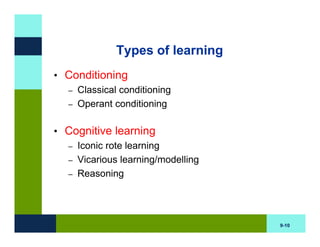
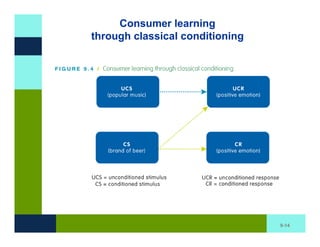
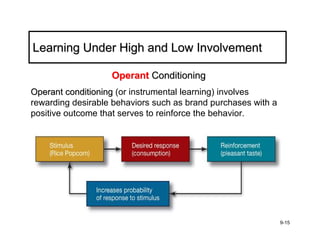
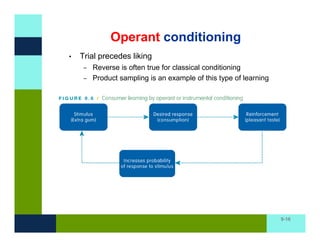
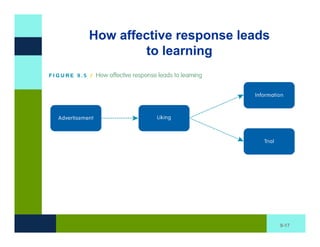
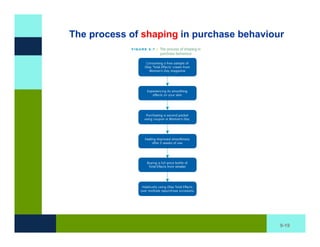
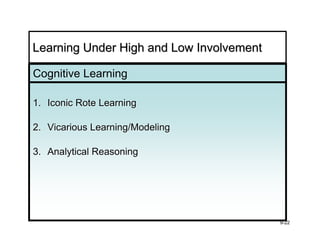
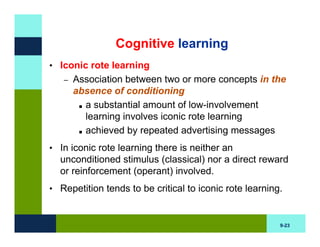
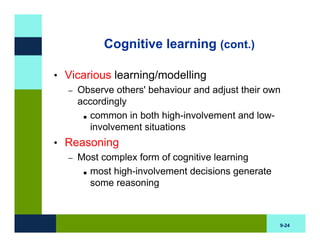
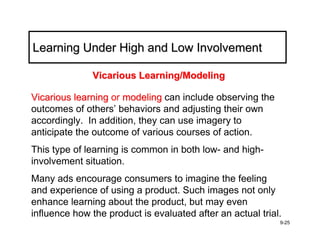
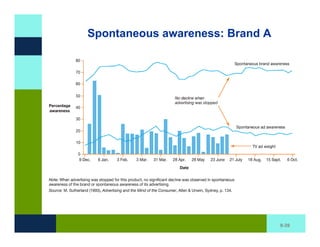
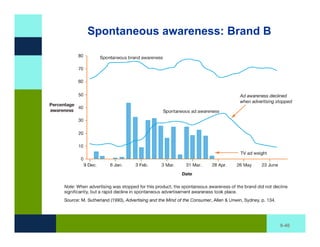
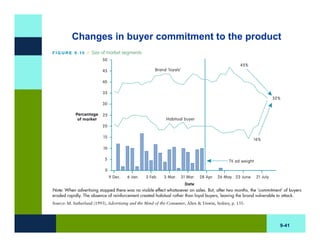
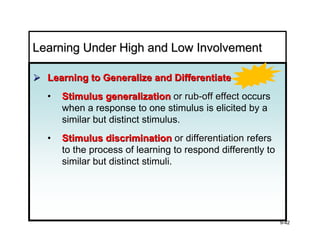
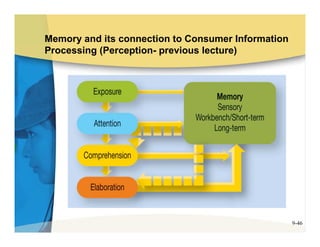
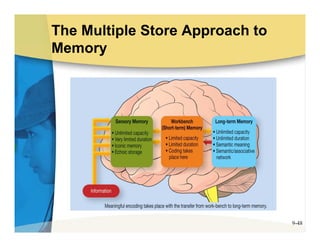
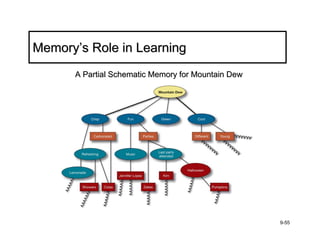
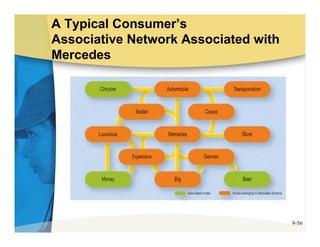
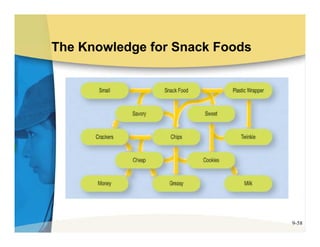
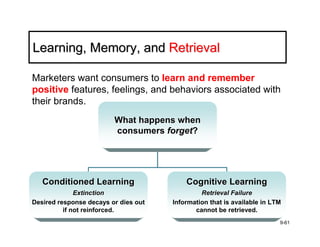
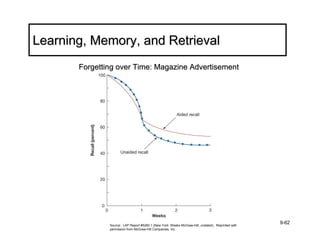
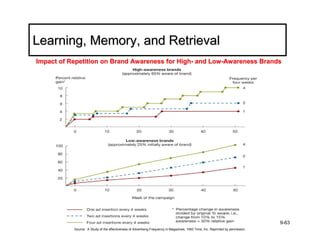
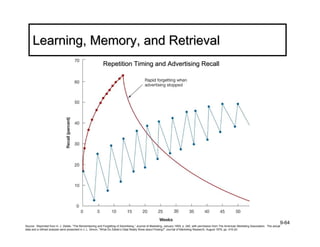
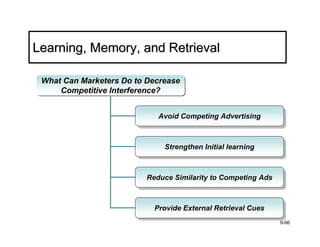
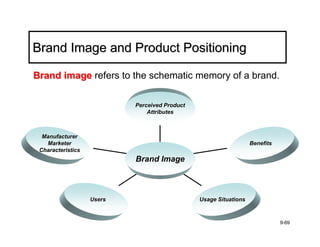
The document discusses learning and memory in consumer behavior. It defines learning as any change in long-term memory or behavior resulting from information processing. Consumer behavior is largely learned behavior. There are different types of learning, including conditioning (classical and operant conditioning) and cognitive learning (rote learning, modeling, and reasoning). Most consumer learning occurs through low involvement contexts using techniques like classical conditioning, iconic rote learning, and vicarious learning. The strength of learning is influenced by factors like importance, involvement, mood, reinforcement, stimulus repetitions, and imagery.