This document discusses various theories of consumer learning. It begins by defining consumer learning as how individuals acquire knowledge and experience about purchase and consumption that they apply to future behaviors.
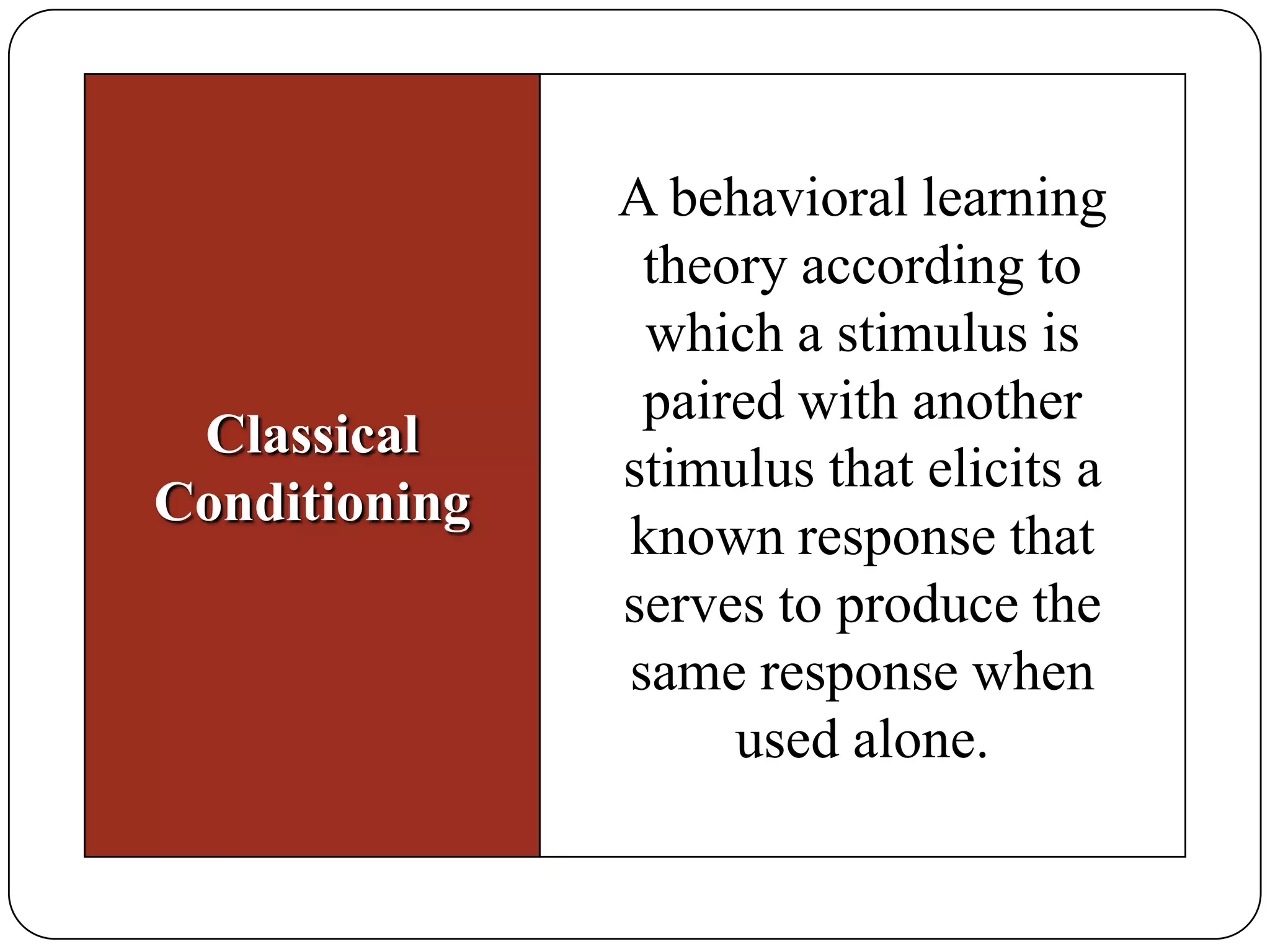
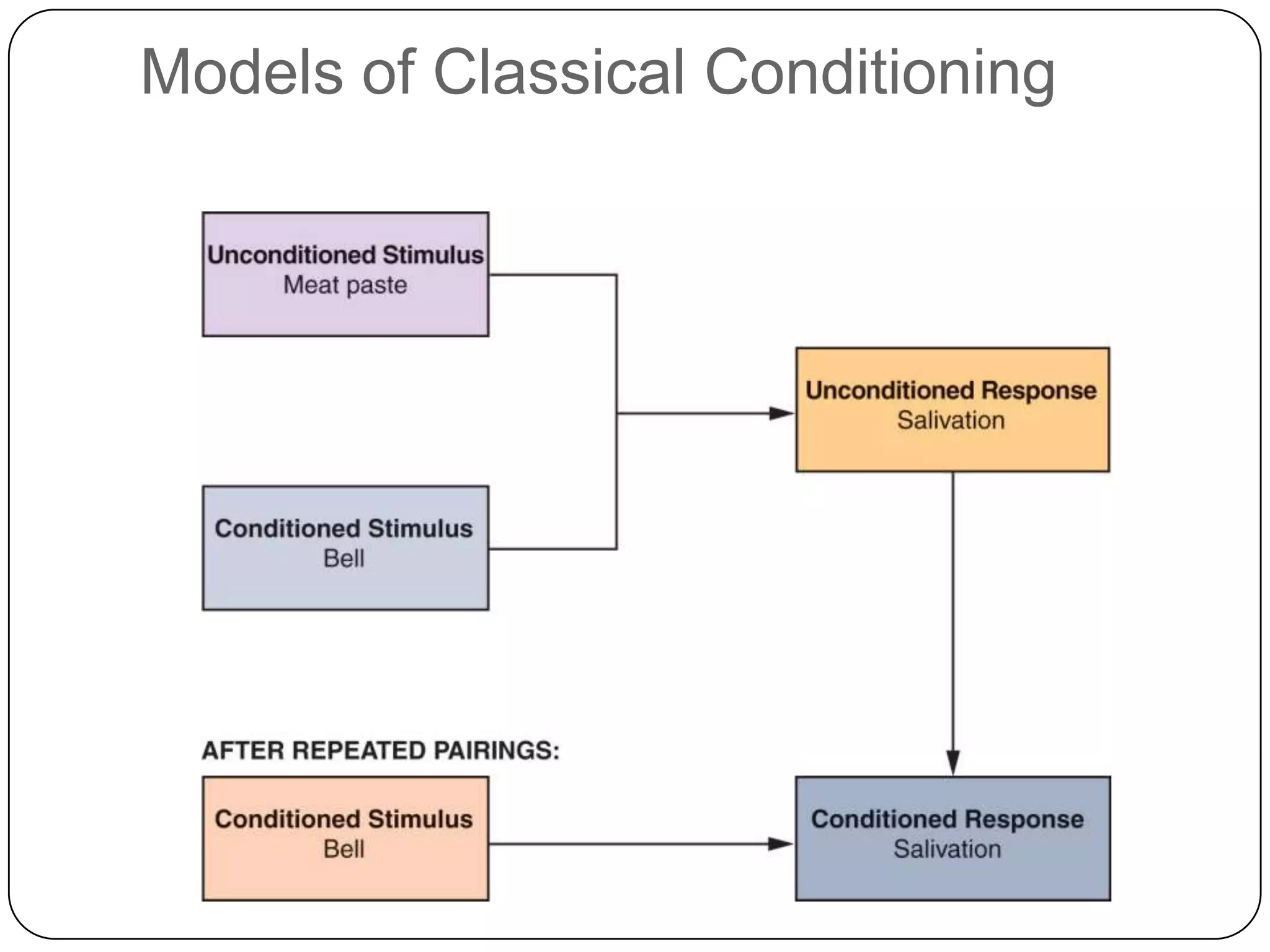
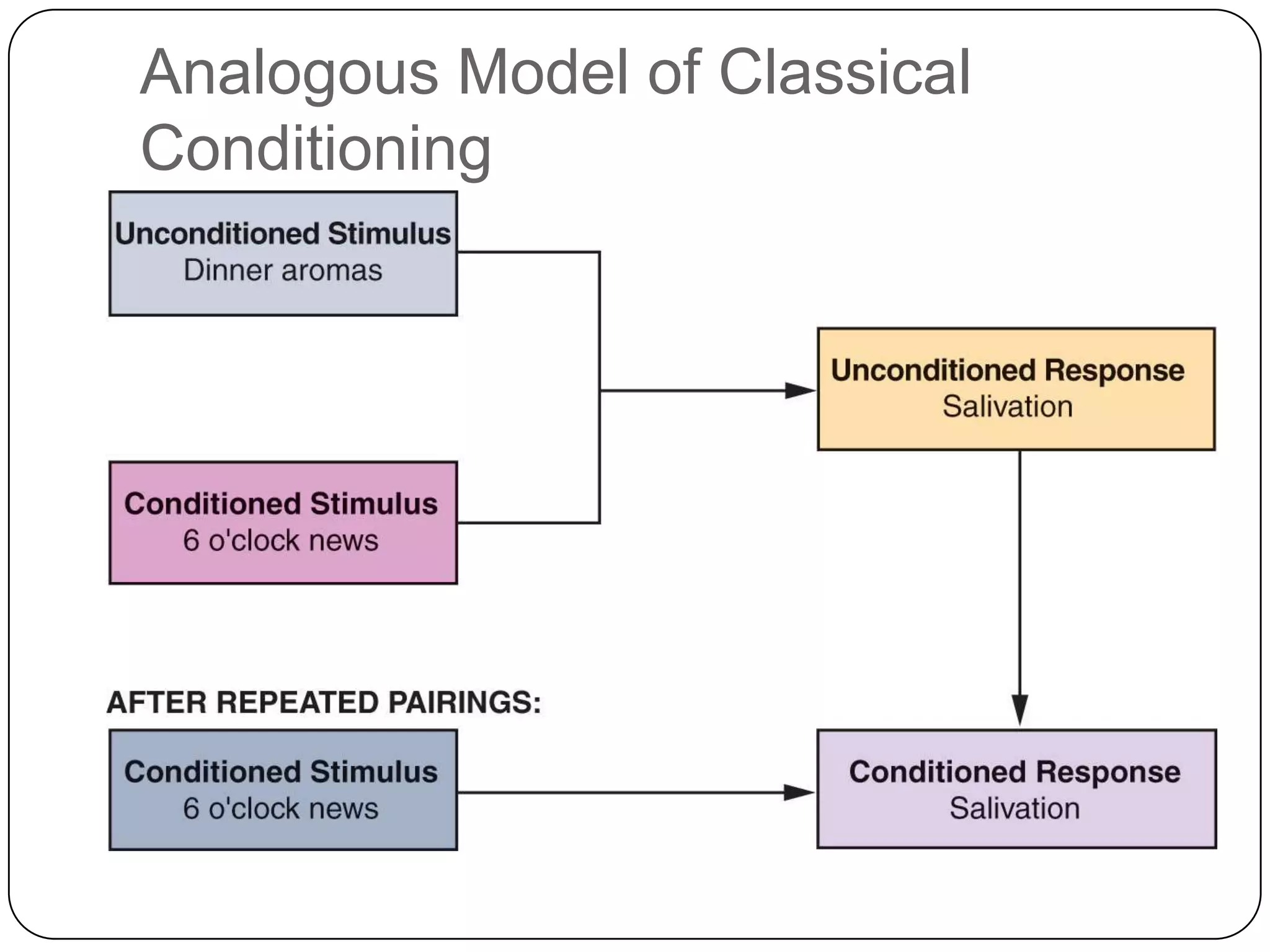
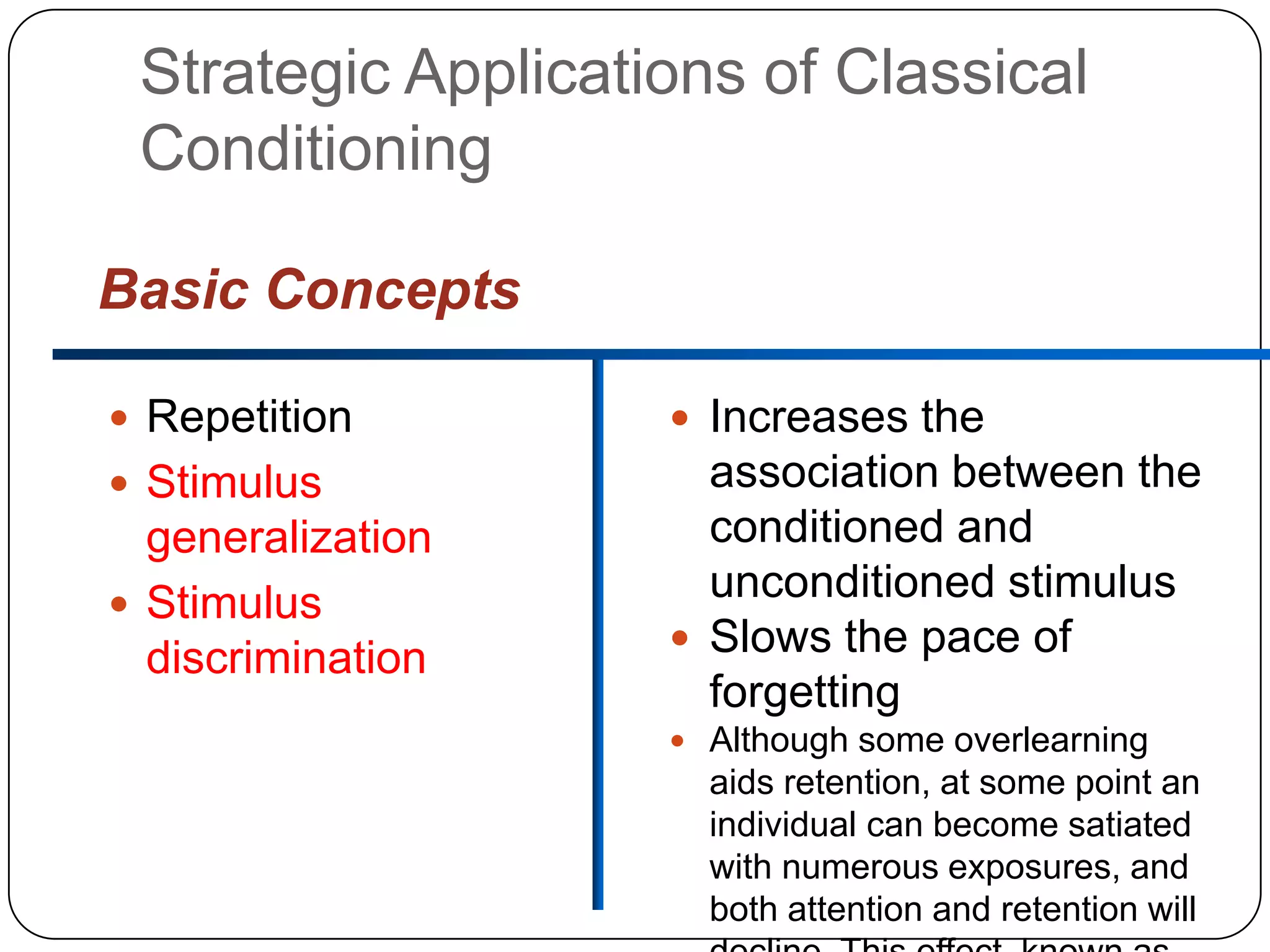
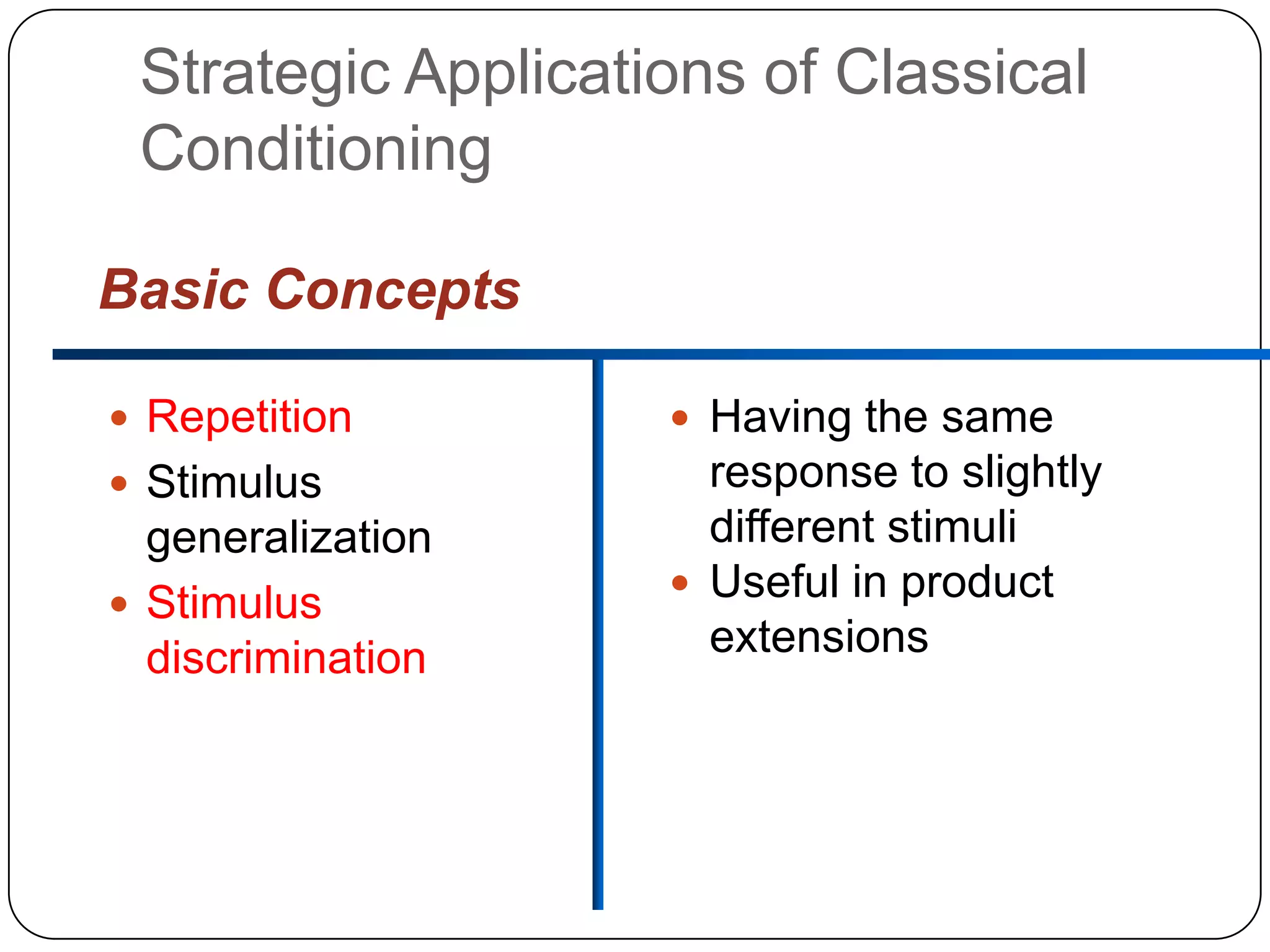
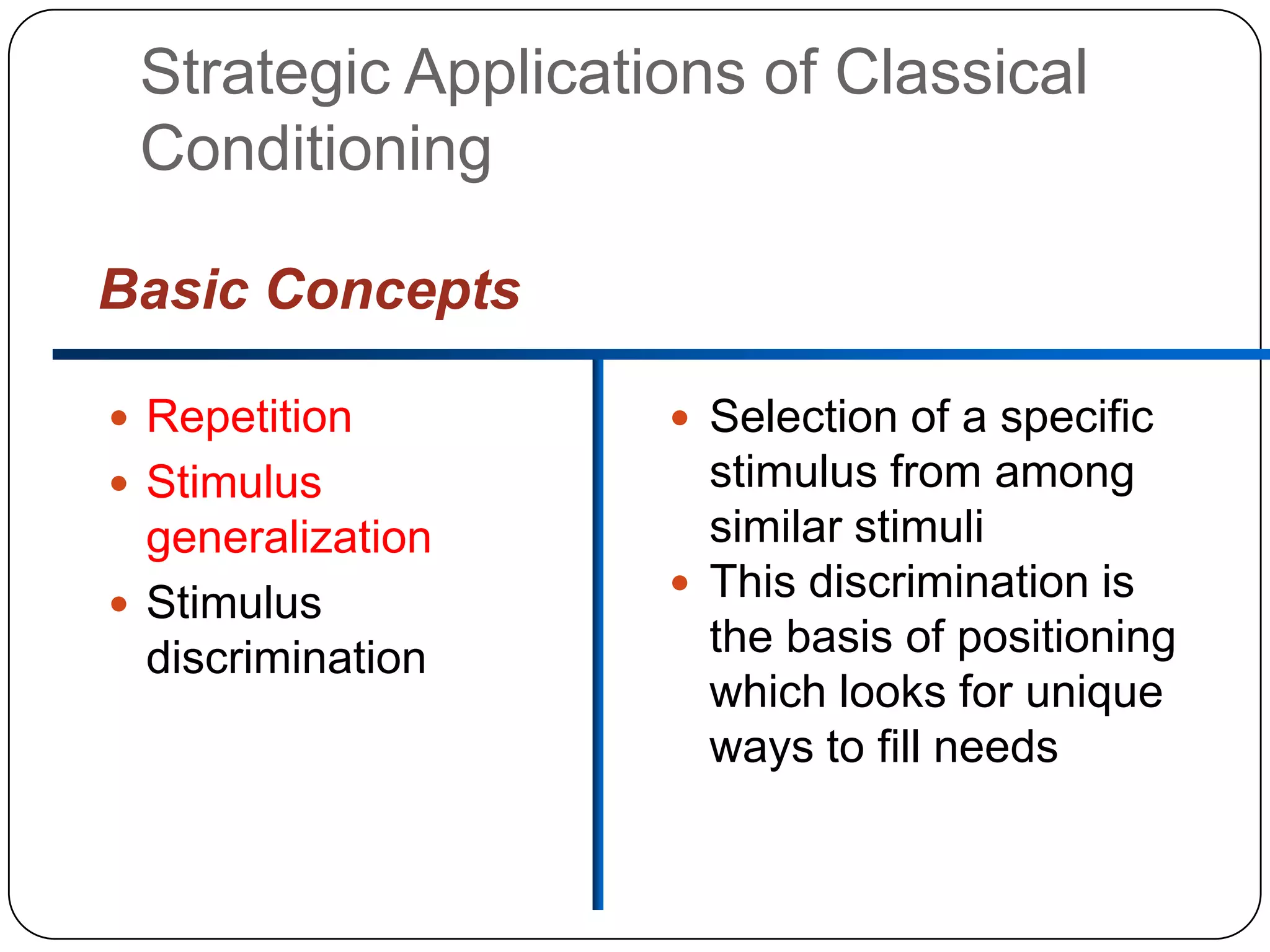
It then outlines the key elements of consumer learning: motivation, cues, response, and reinforcement. It also discusses different behavioral learning theories, including classical and instrumental conditioning. Classical conditioning involves pairing a stimulus with a response, while instrumental conditioning involves learning through rewards and punishments.
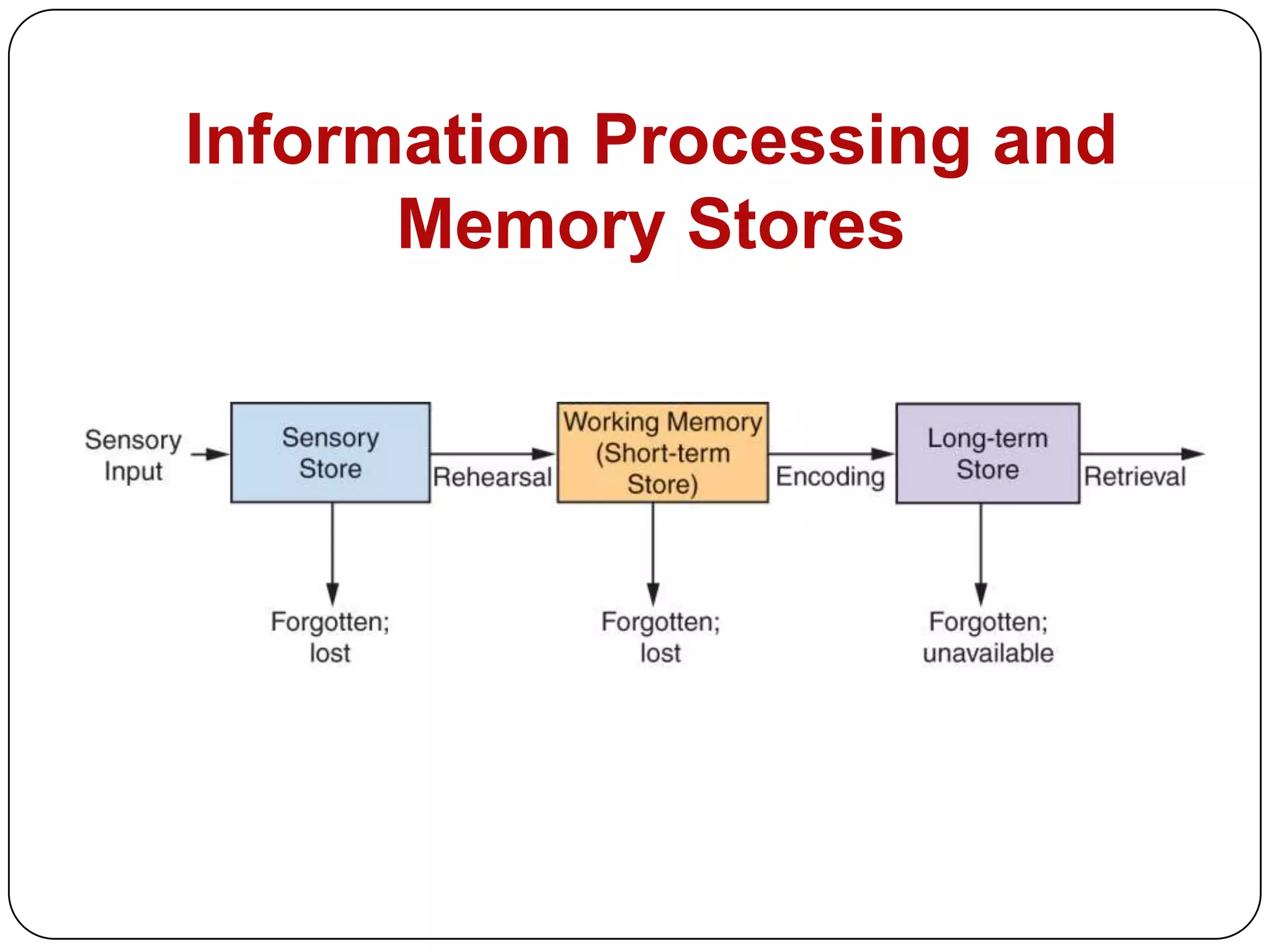
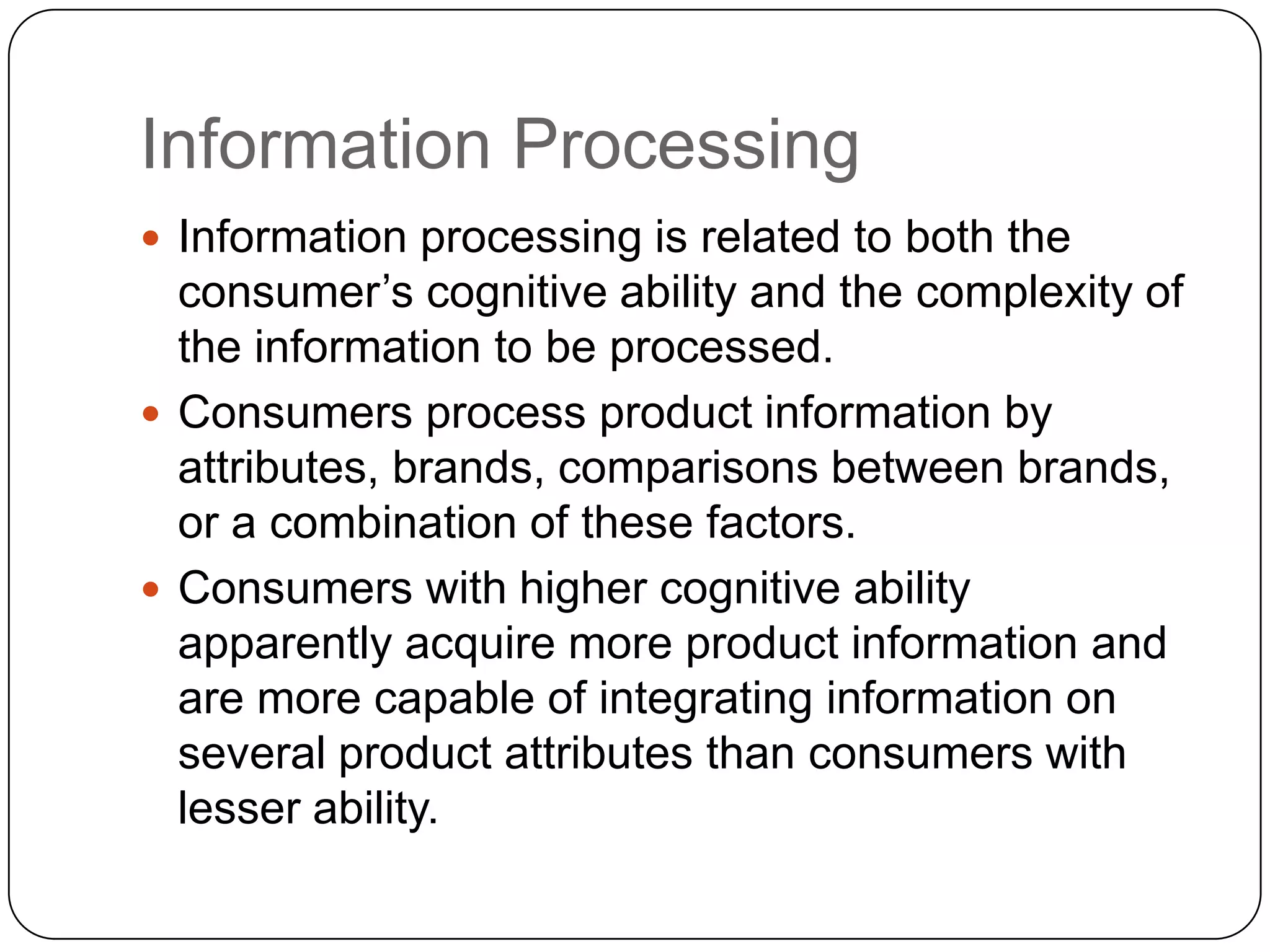
The document also covers observational learning, cognitive learning theory involving problem solving, and involvement theory related to the relevance of purchases and central vs. peripheral routes to persuasion for high vs low involvement decisions.