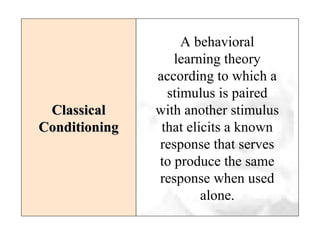
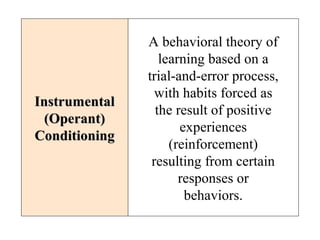
This document discusses consumer learning theories. It explains that consumer learning is the process by which individuals acquire knowledge about purchasing, using, maintaining, and disposing of products. It then outlines several learning theories including behavioral theories based on stimulus-response, cognitive theories involving mental information processing, classical conditioning involving pairing stimuli, and instrumental conditioning involving trial-and-error learning from rewards and punishments. Key concepts discussed include repetition, generalization, discrimination, reinforcement, and observational learning.