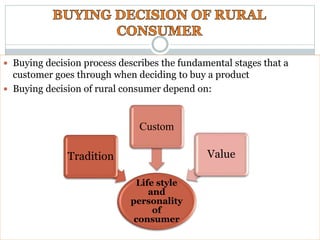
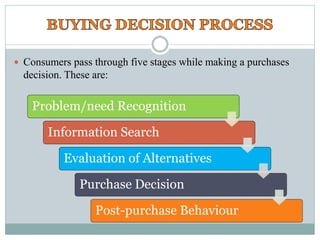
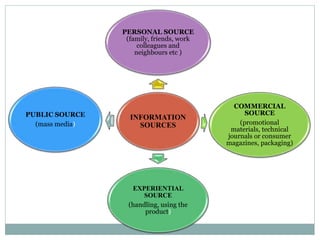
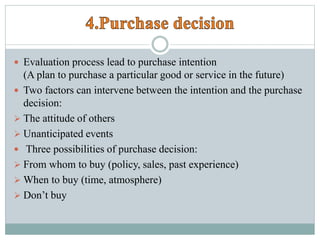
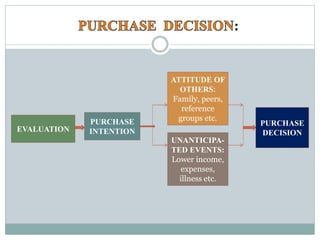
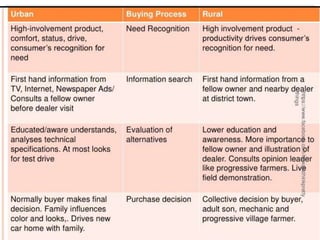
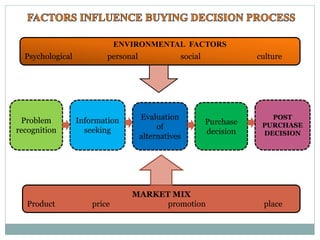
The document summarizes the five stages of a consumer's buying decision process: problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. It then provides more details on each stage, including factors that influence rural consumers' decisions and sources of information. The stages are influenced by personal, environmental, and marketing factors.