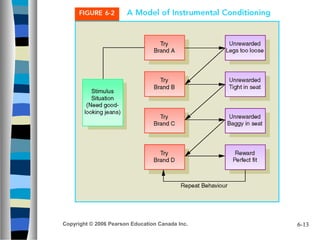
Consumer learning is the process by which consumers acquire knowledge about products through purchase and consumption experiences. There are two main types of learning: intentional learning that comes from a deliberate search for information, and incidental learning that occurs accidentally without effort. Marketers must teach consumers about products through various learning theories, including behavioral theories based on stimulus-response and cognitive theories based on mental information processing. Common cognitive learning methods used in marketing include observational learning from others, rote learning through repetition, and reasoning or problem-solving.