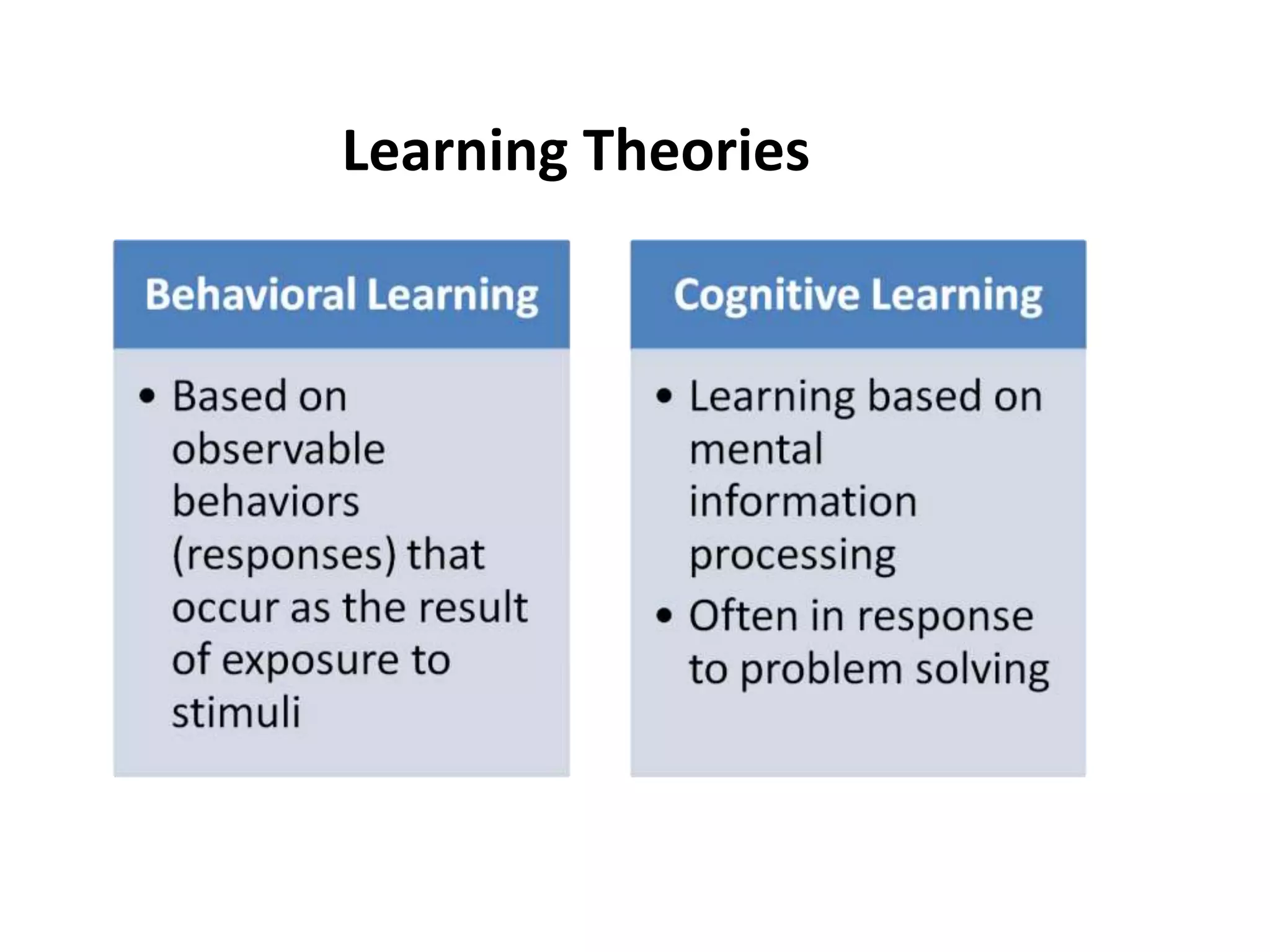
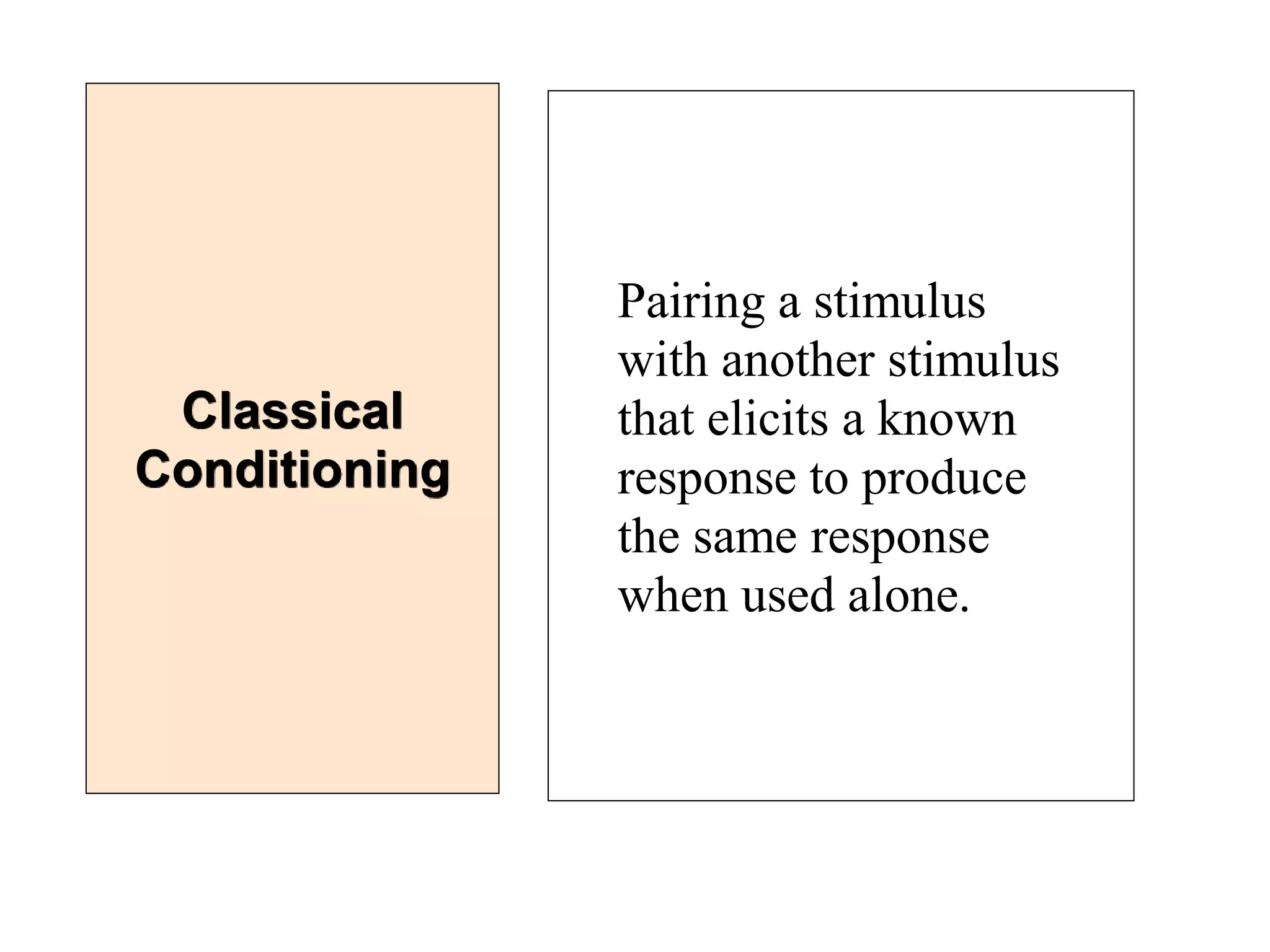
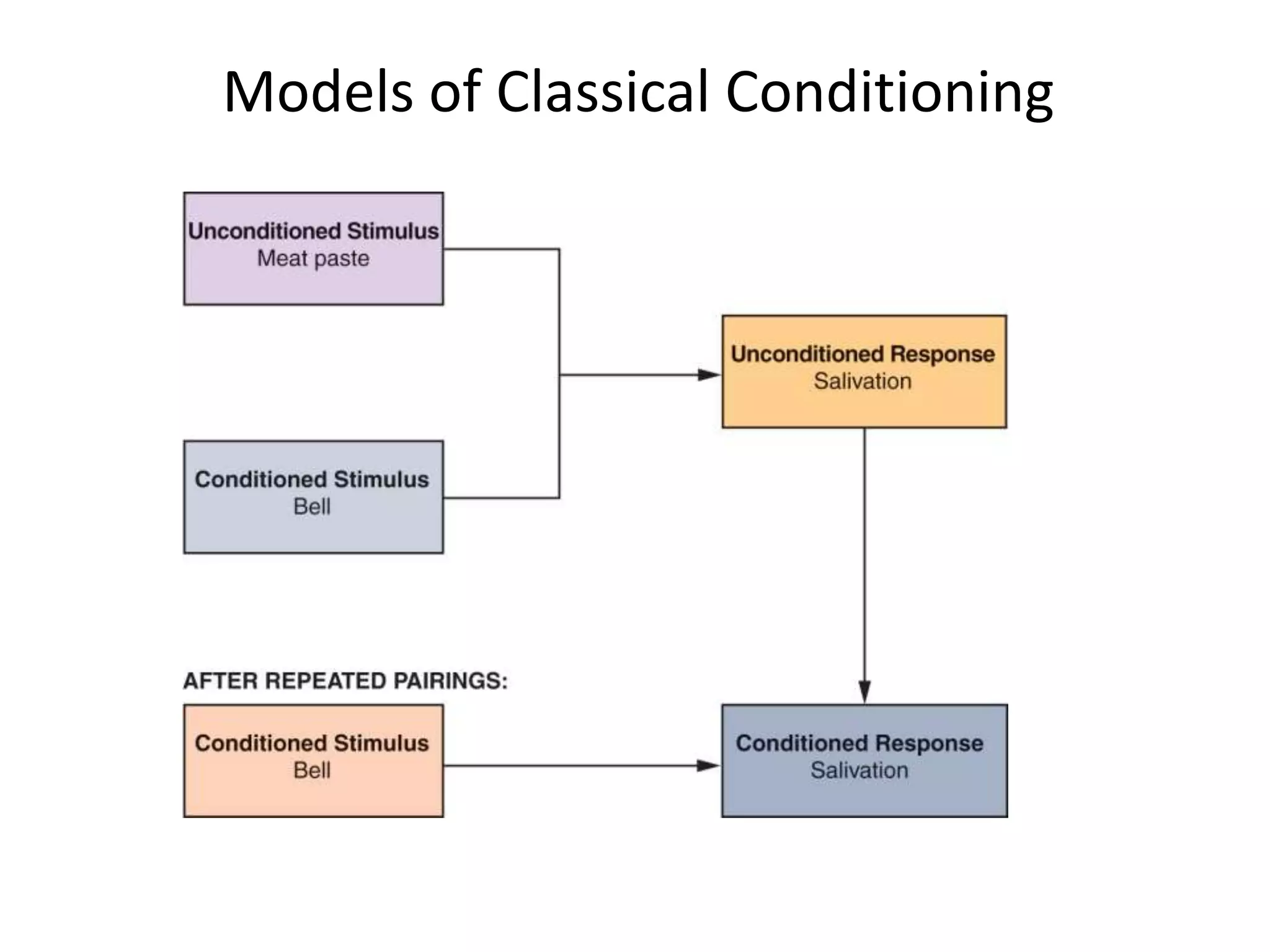
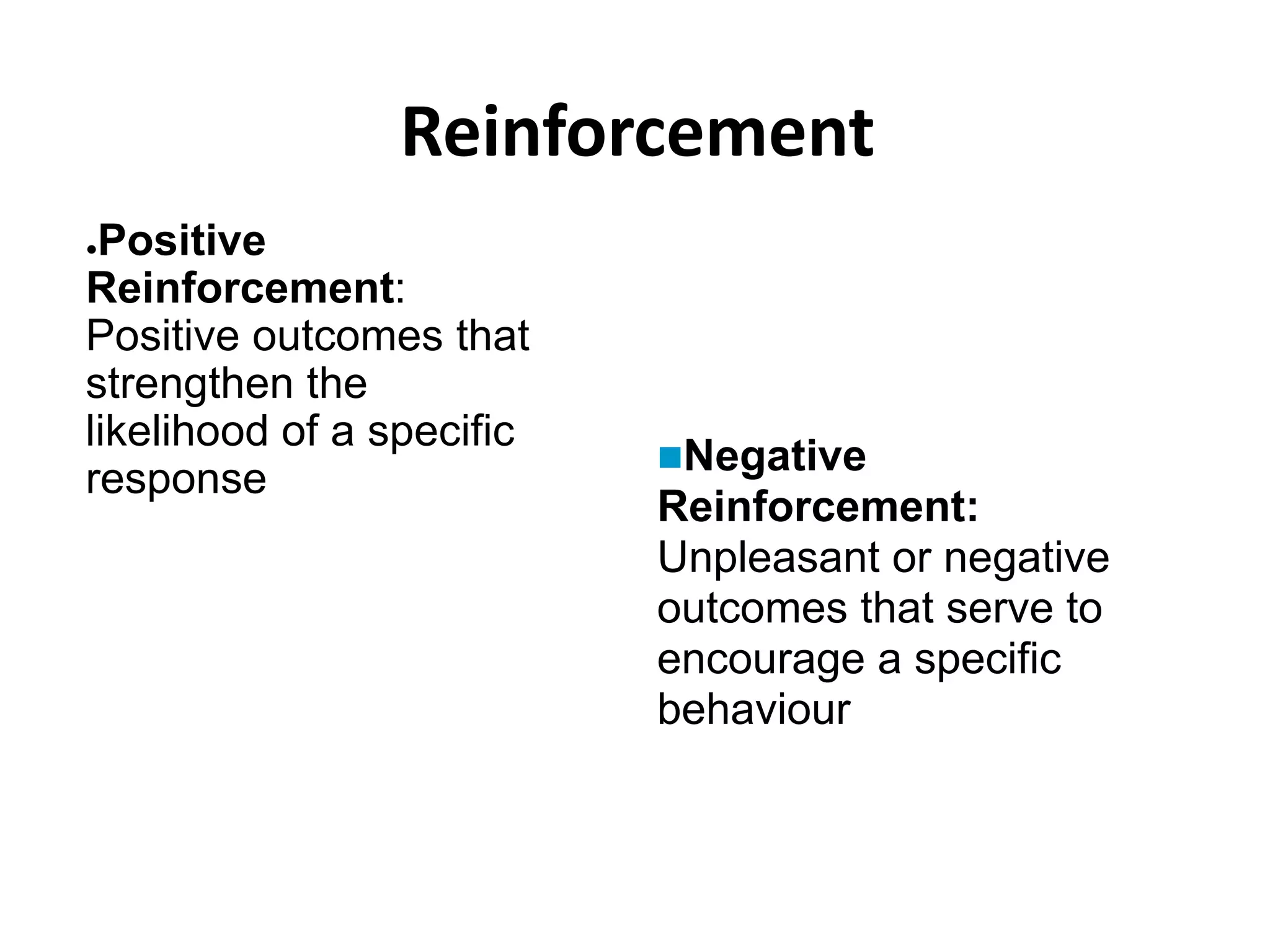
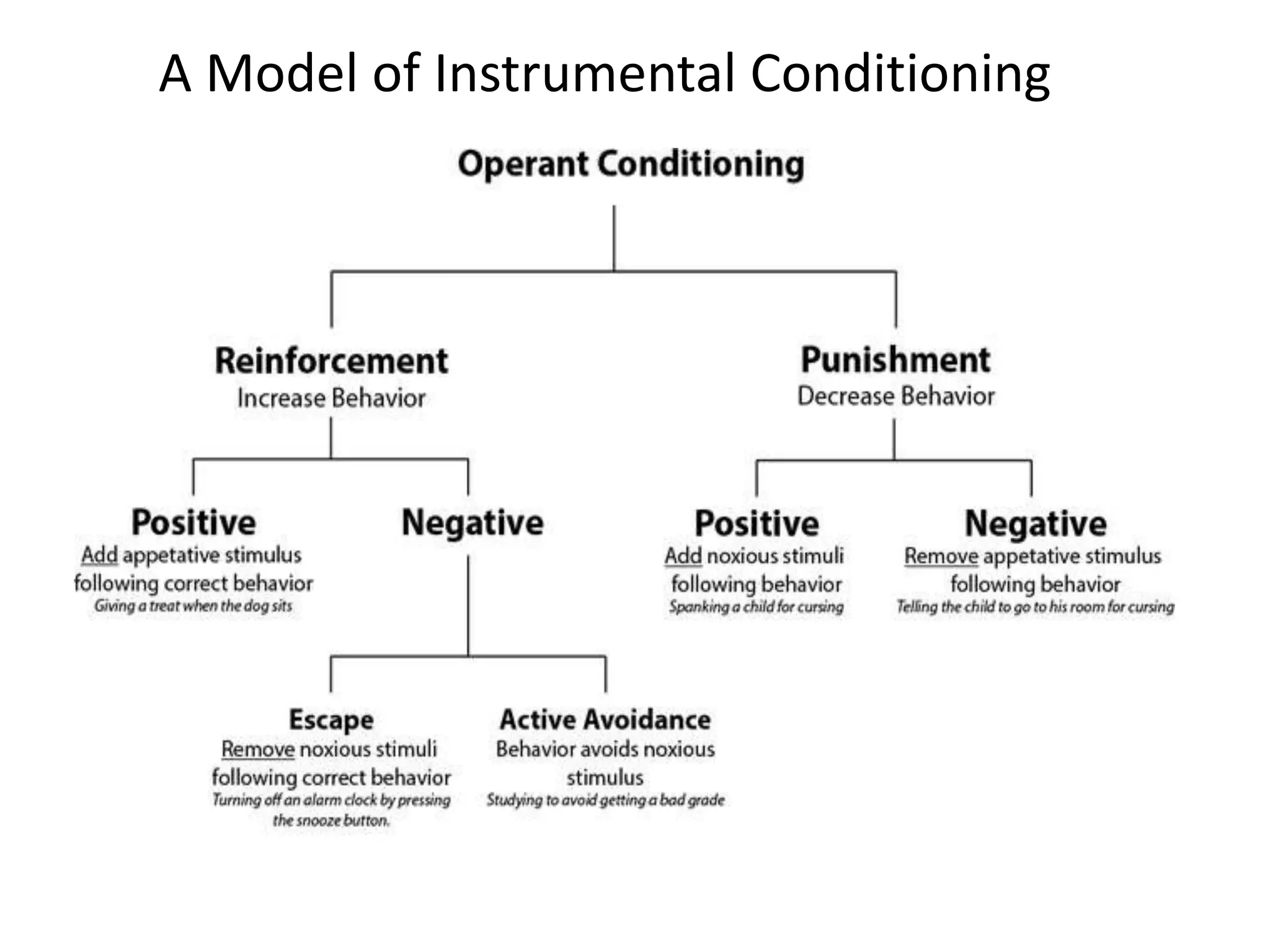
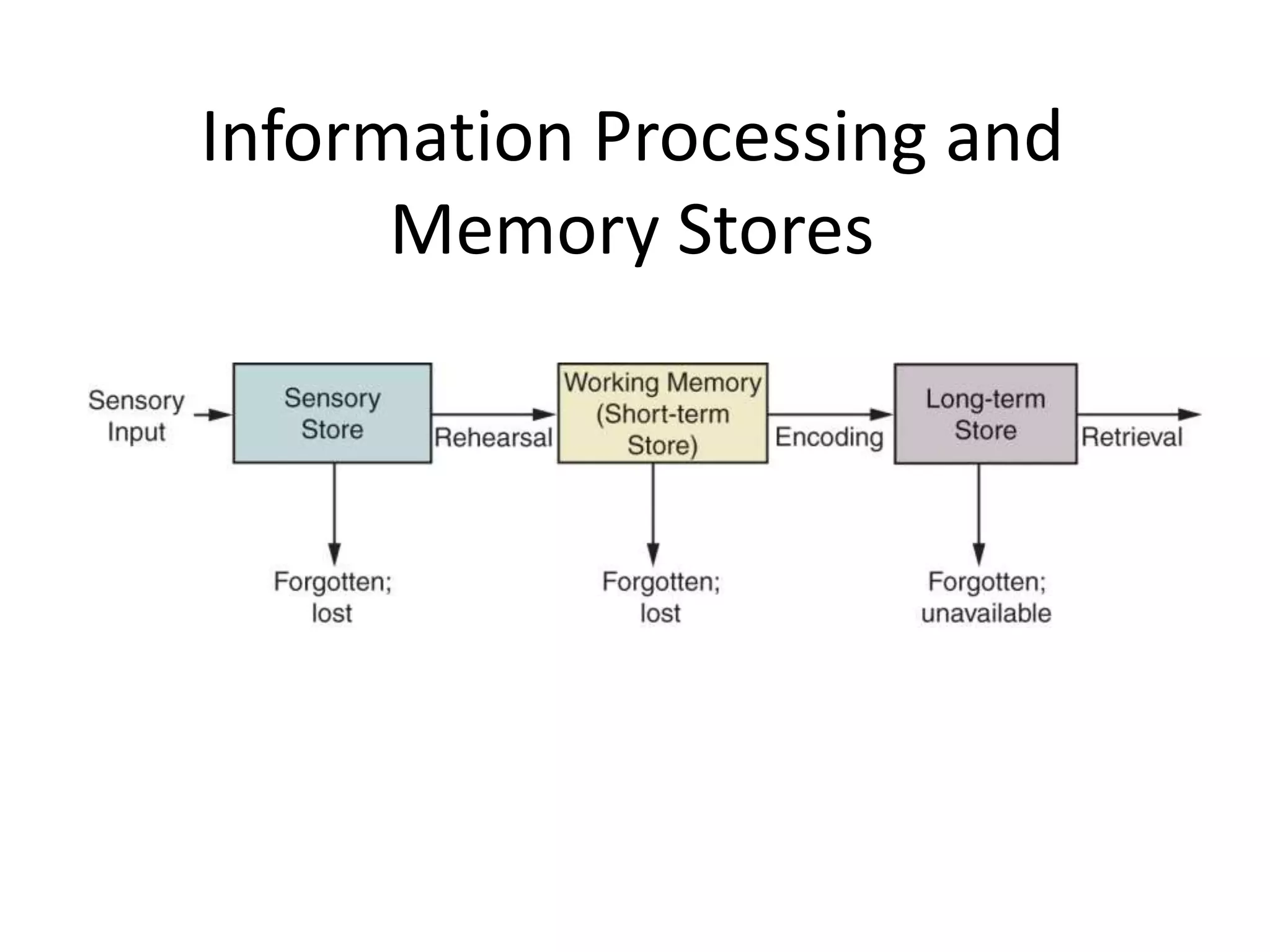
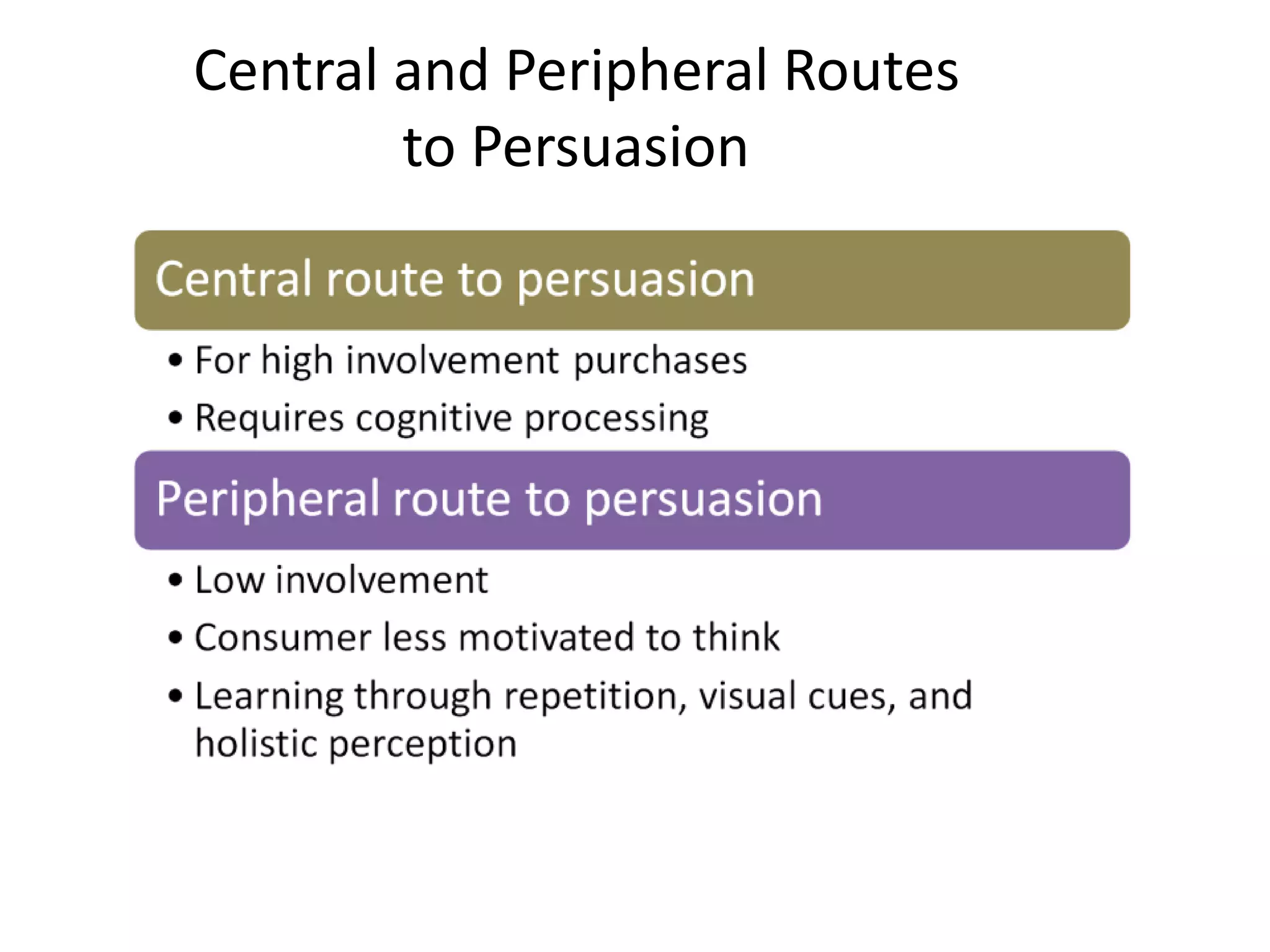
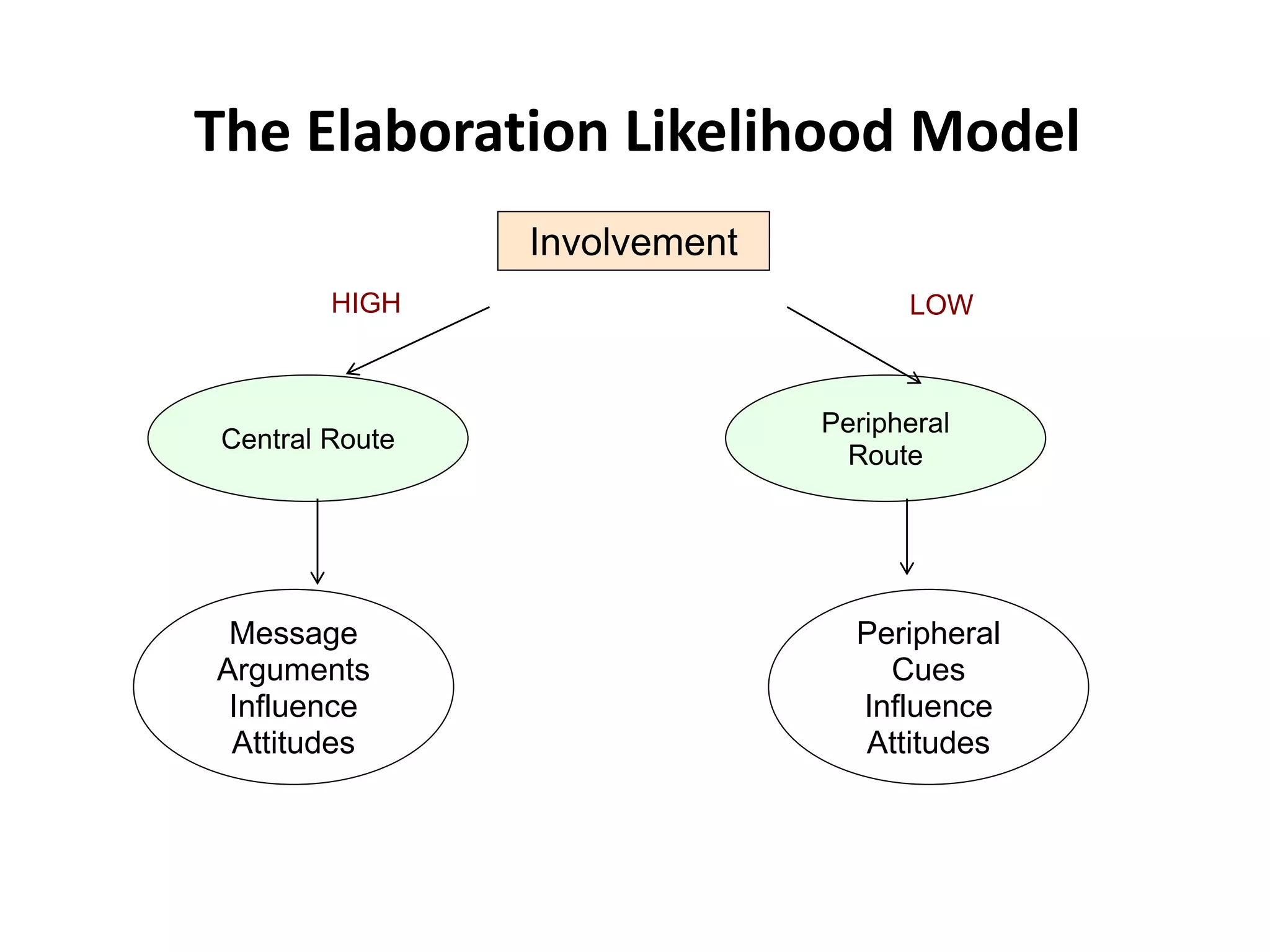
This document outlines the key topics and learning objectives covered in Chapter 6 on Consumer Learning. It discusses the four elements of learning theories: motivation, cues, response, and reinforcement. It also covers behavioral learning theories like classical and instrumental conditioning. Cognitive learning theories like observational, rote, and reasoning learning are examined. The effects of consumer involvement on central and peripheral routes of persuasion are discussed. Finally, ways to measure outcomes of consumer learning like recognition, recall, attitudes and behaviors are presented.