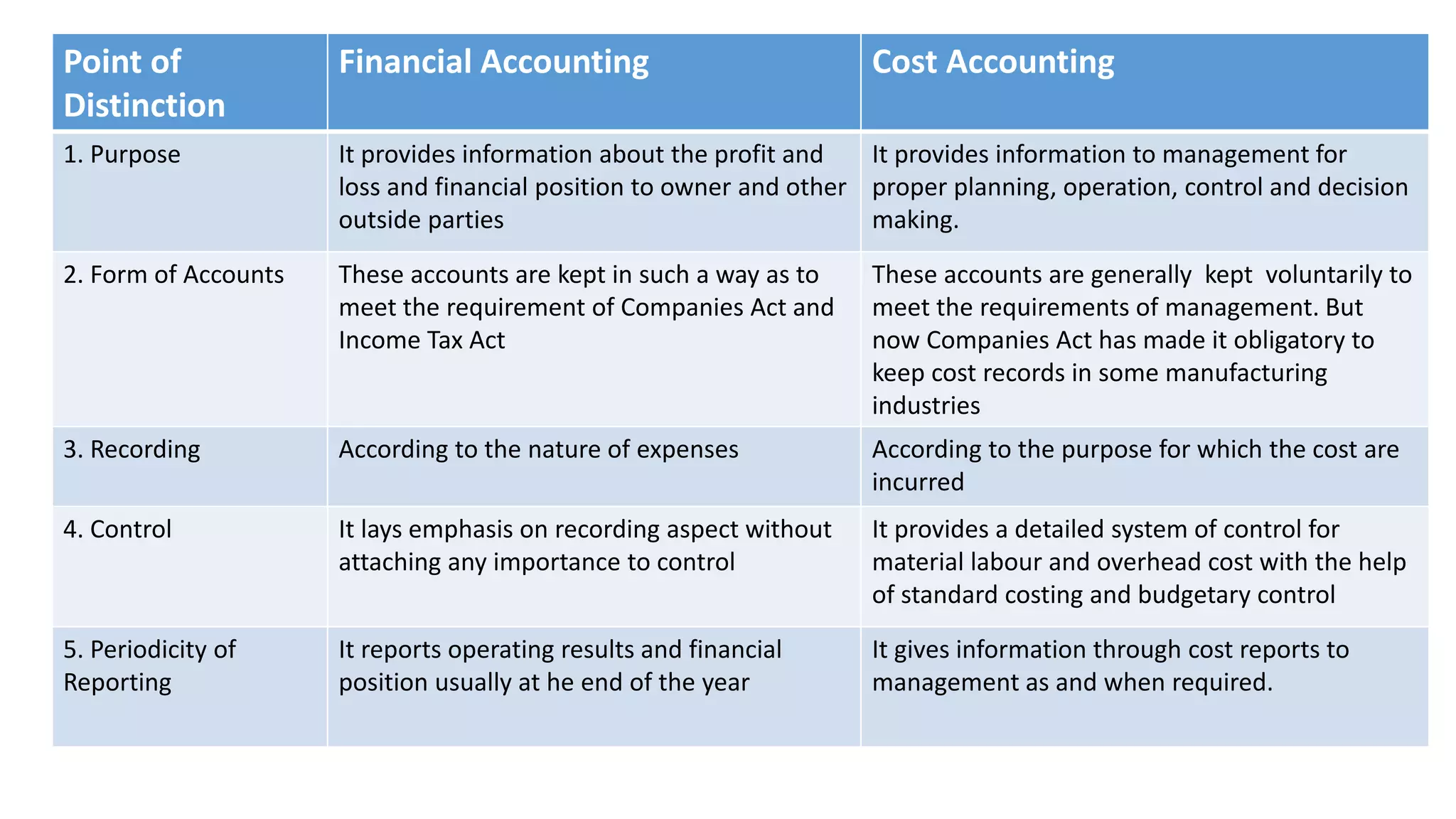
The document compares and contrasts financial accounting, cost accounting, and management accounting. Financial accounting provides information to external parties and focuses on reporting profits and financial position. Cost accounting provides information to management for planning, operations, control, and decision making. It breaks costs down on a unit basis. Management accounting helps managers make effective decisions and uses both historical and predictive information. It has a broader scope than cost accounting.