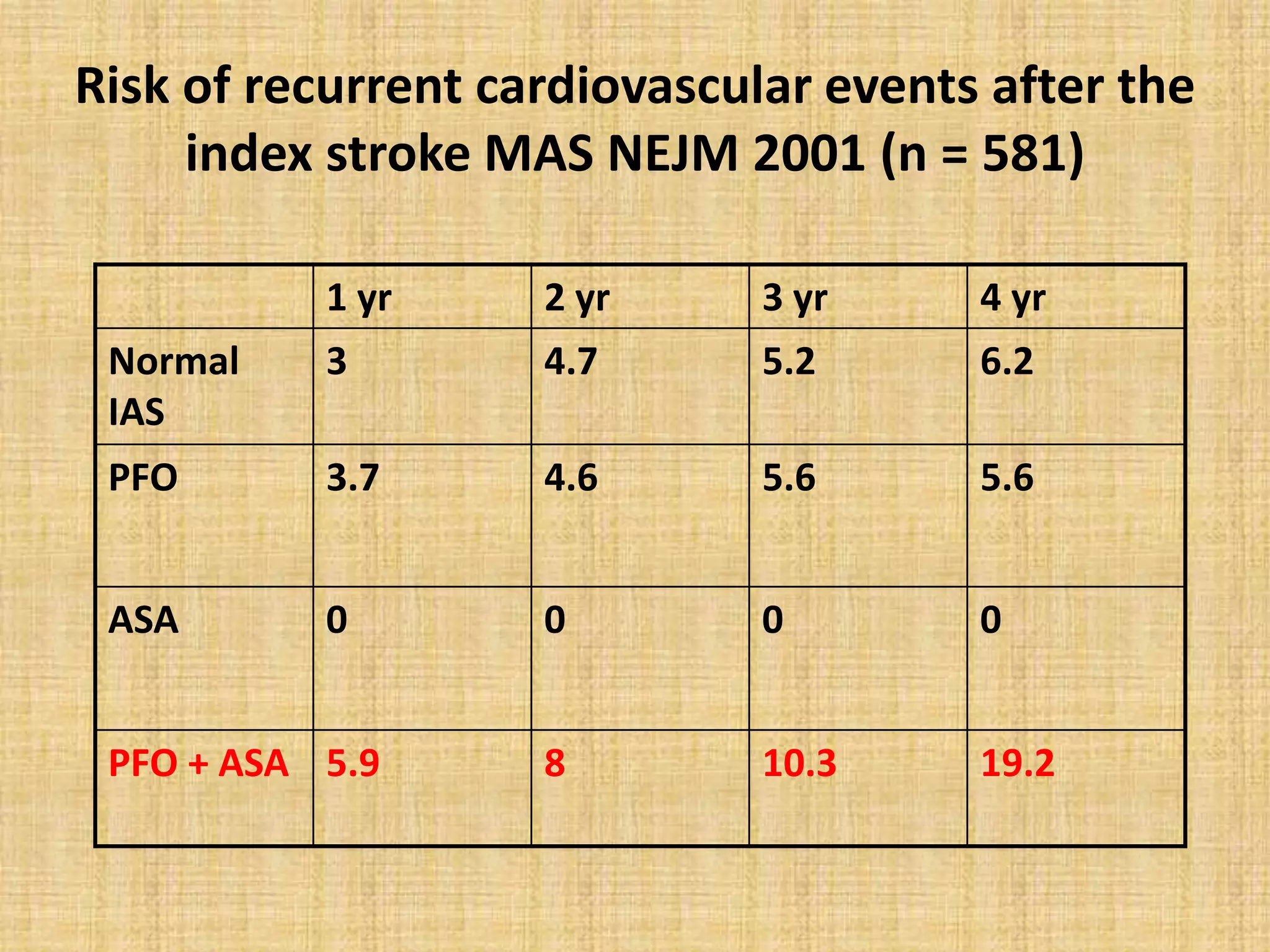
This document discusses the anatomy and physiology of patent foramen ovale (PFO) and its clinical significance. Some key points:
- PFO is a remnant of the fetal circulation that allows blood to bypass the lungs. It normally closes after birth but remains patent in about 25% of adults.
- PFO has been associated with cryptogenic stroke, migraines, decompression illness in divers, and other conditions. Larger PFO size and the presence of an atrial septal aneurysm increase the risk of paradoxical embolism.
- Treatment options include antiplatelet/anticoagulant therapy or transcatheter PFO closure. Randomized trials found PFO closure plus






































![Kaplan–Meier event free survival curves (stroke and transient ischemic attack [TIA])
of patients with cryptogenic cerebrovascular events and a patent foramen ovale
according to different treatment strategies. *The log-rank test was used to calculate
the P value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pfoclosure-170517143738/75/PFO-CLOSURE-43-2048.jpg)
![Kaplan–Meier event free survival curves (stroke and transient ischemic attack [TIA] and
treatment related complications) of patients with cryptogenic cerebrovascular events and a
patent foramen ovale according to different treatment strategies. Complications include
procedure and device problems such as puncture site bleeding, thrombus on the device,
hemopericardium or failed implantation requiring another device and major bleeding
associated with oral anticoagulation. *The log-rank test was used to calculate the P value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pfoclosure-170517143738/75/PFO-CLOSURE-44-2048.jpg)