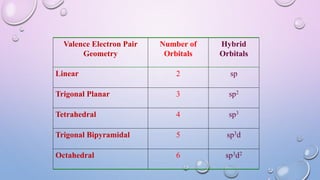
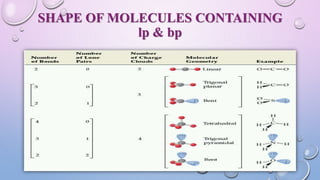
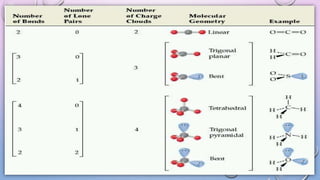
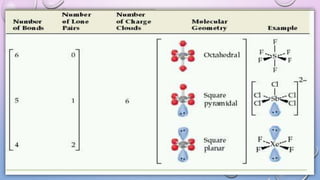
The document outlines Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory, which explains how the spatial arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom affects molecular shape. It highlights key postulates, including the impact of lone pairs and bond pairs on molecular geometry and individual bond repulsion strengths. The document also discusses the influence of electronegativity on bond angles and provides references for further reading.




![INTRODUCTION
• VSEPR theory was suggested by Sidgwick and Powell [1940]
• It was further improved by Gillespie and Nyholm in 1957.
• Based on that in a polyatomic molecule the direction bonds around the
central atom depends on the total number of bonding &non-bonding
electron pairs in its valance shell.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valenceshellelectronpairrepulsiontheory-170524112504/85/Valence-shell-electron-pair-repulsion-theory-VSEPR-THEORY-5-320.jpg)




![EFFCT OF ELECTRONEGATIVITY
Five electrons in the valance shell of
Nitrogen. [1s2 2s2 2p3]
Molecular geometry- Tetrahedral [e-pairs arrangement]
or Trigonal Pyramidal [VSEPR]
Presence of lone pair causes slight distortion from 109⁰28′ to 107⁰48′ to 102⁰30′
Repulsion between bondpair-bondpair is less in NF3 than in NH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/valenceshellelectronpairrepulsiontheory-170524112504/85/Valence-shell-electron-pair-repulsion-theory-VSEPR-THEORY-10-320.jpg)