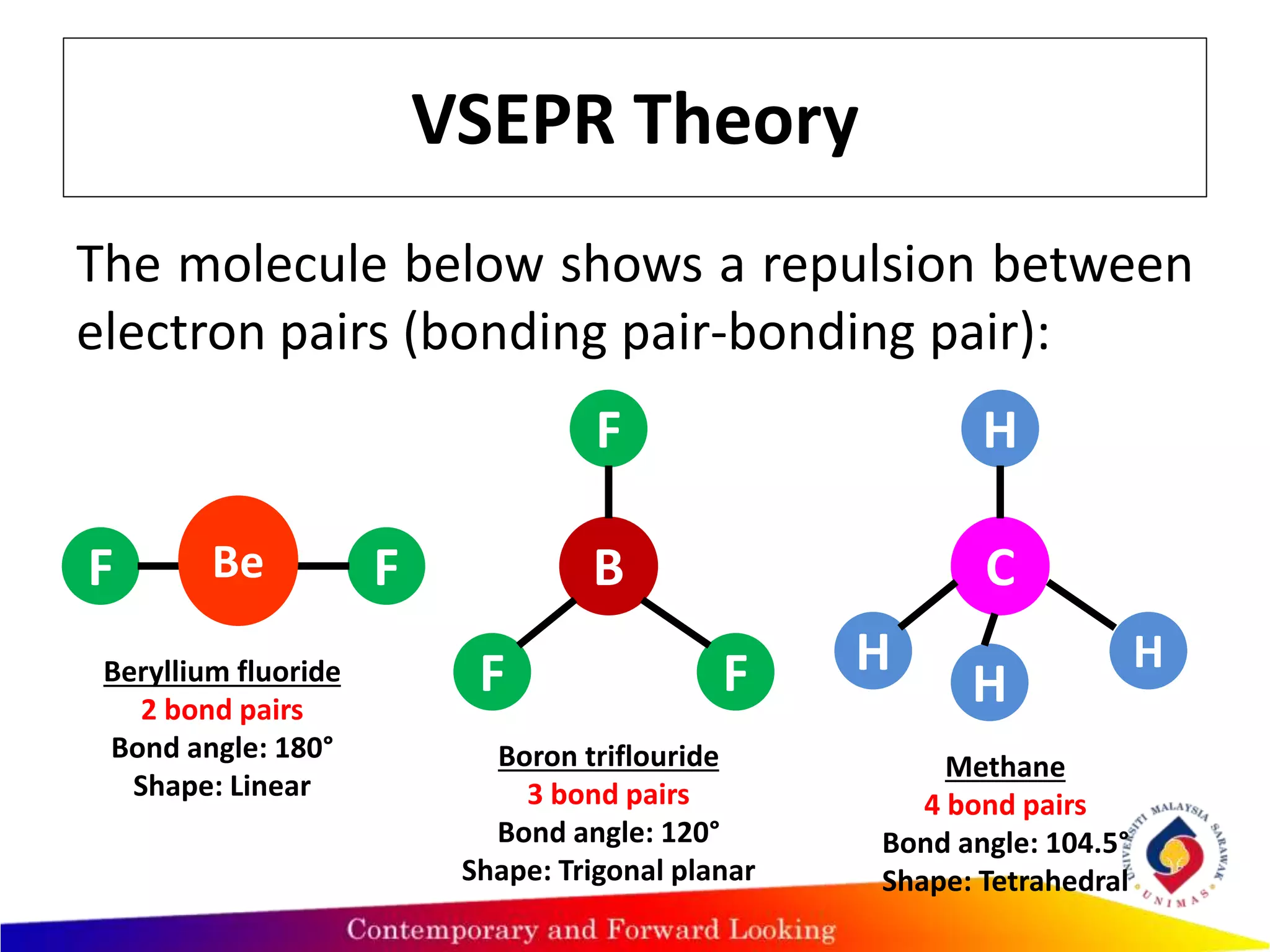
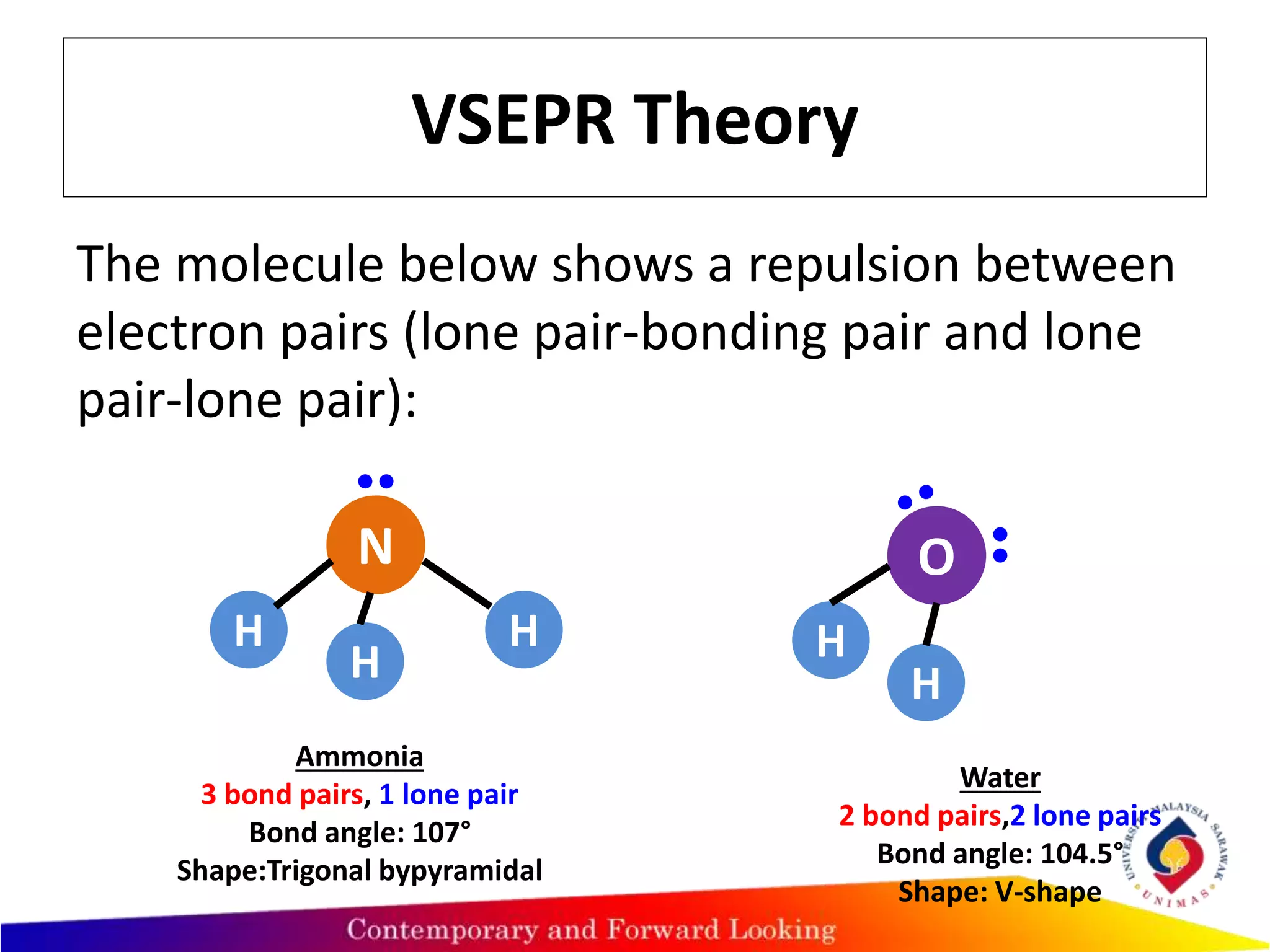
This document discusses valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory, which is used to predict the shape of covalent molecules and polyatomic ions based on the arrangement of electron pairs around the central atom. According to VSEPR theory, electron pairs around the central atom repel each other and arrange themselves as far apart as possible to minimize repulsion. The type of electron pair repulsion determines the molecular shape, with lone pairs repelling each other more than lone pairs and bonding pairs or just bonding pairs alone. Examples are provided to illustrate VSEPR theory predictions of molecular geometry.