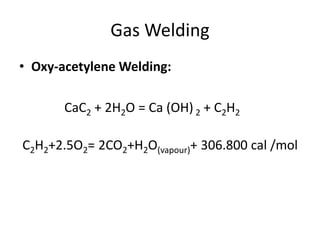
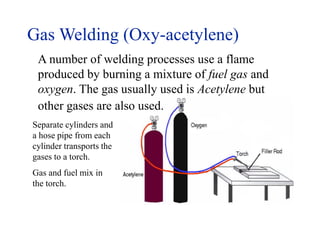
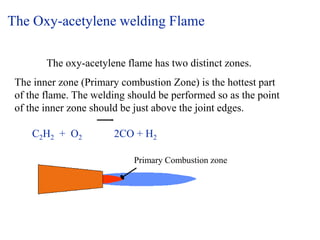
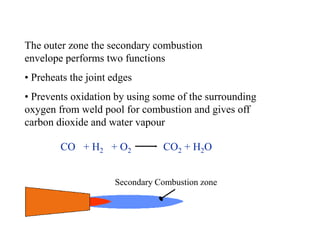
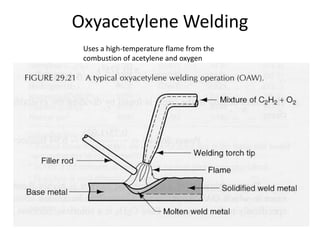
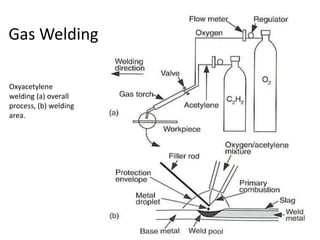
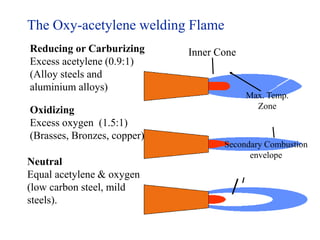
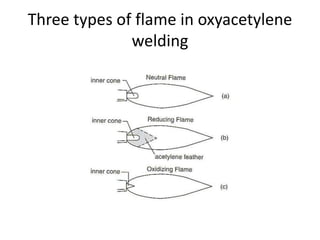
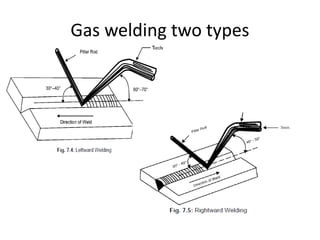
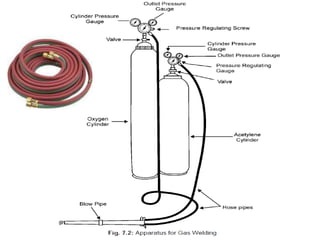
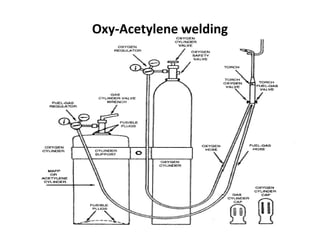
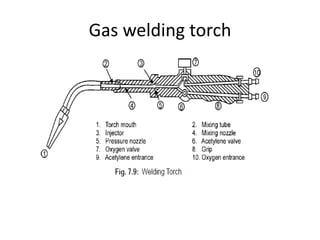
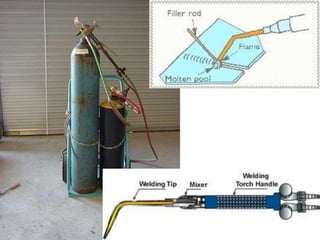
Gas welding is a process that uses a flame from oxygen and a fuel gas, usually acetylene, to heat and join metals. Oxy-acetylene welding is the most common type and uses an inner flame cone reaching temperatures over 3000°C to melt the metals. There are three types of flames - neutral, reducing, and oxidizing - which are used for different materials. The equipment includes gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and a welding torch. While inexpensive and portable, gas welding has limitations such as low welding speed and risk of distortion.