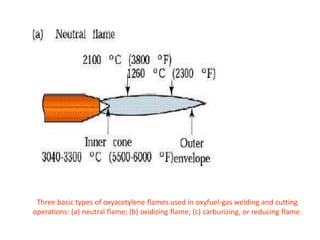
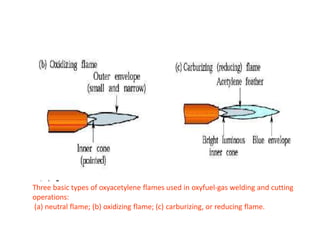
Gas welding involves heating metals with a flame produced by the reaction of fuel gas, typically acetylene, and oxygen. Oxyacetylene welding is the most common type and produces flames over 3,000°C. Flux may be used to clean the weld and form a protective slag layer. There are three main flame types - neutral, reducing, and oxidizing - which are used for different materials like steel, aluminum, or brass. Equipment includes gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and a welding torch. While simple, gas welding has limitations such as low speed and risk of distortion.