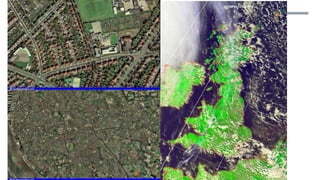
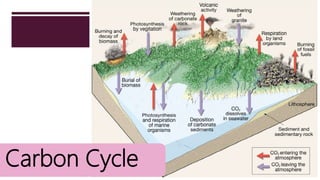
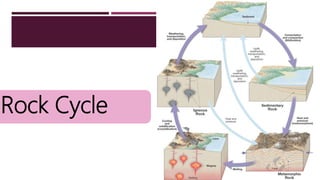
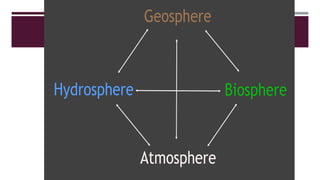
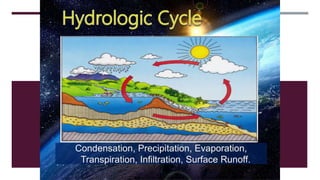
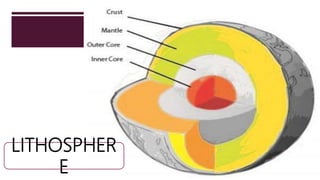
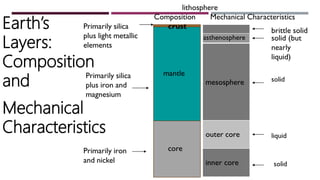
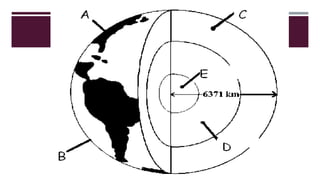
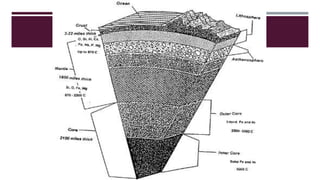
The document discusses Earth as a closed system composed of interconnected components, emphasizing its uniqueness in supporting life within the solar system. It outlines the Earth's layers, including the biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere, detailing their characteristics and the processes that govern them. Major themes include energy sources, cycles, and the various scales of processes impacting Earth.