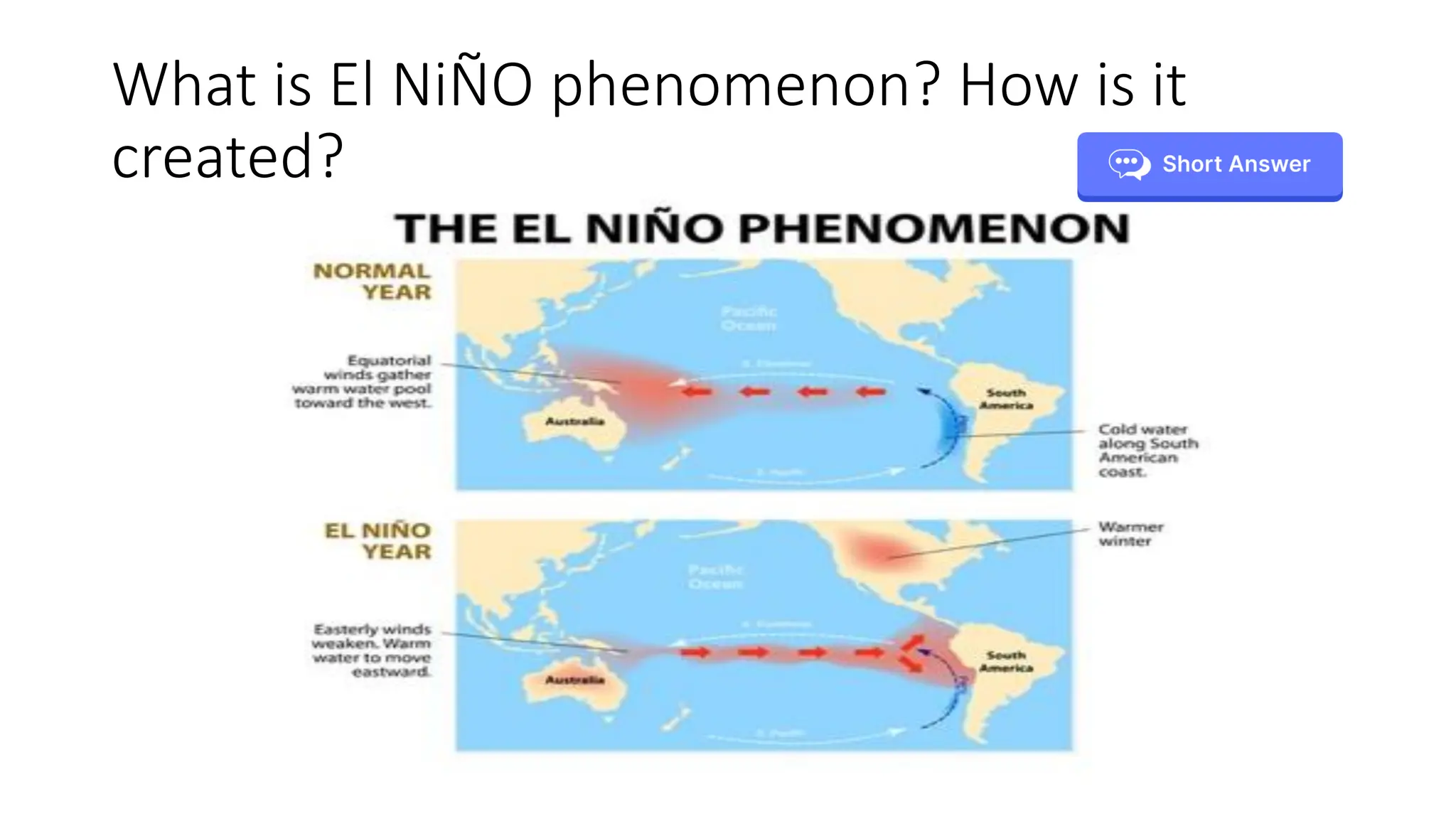
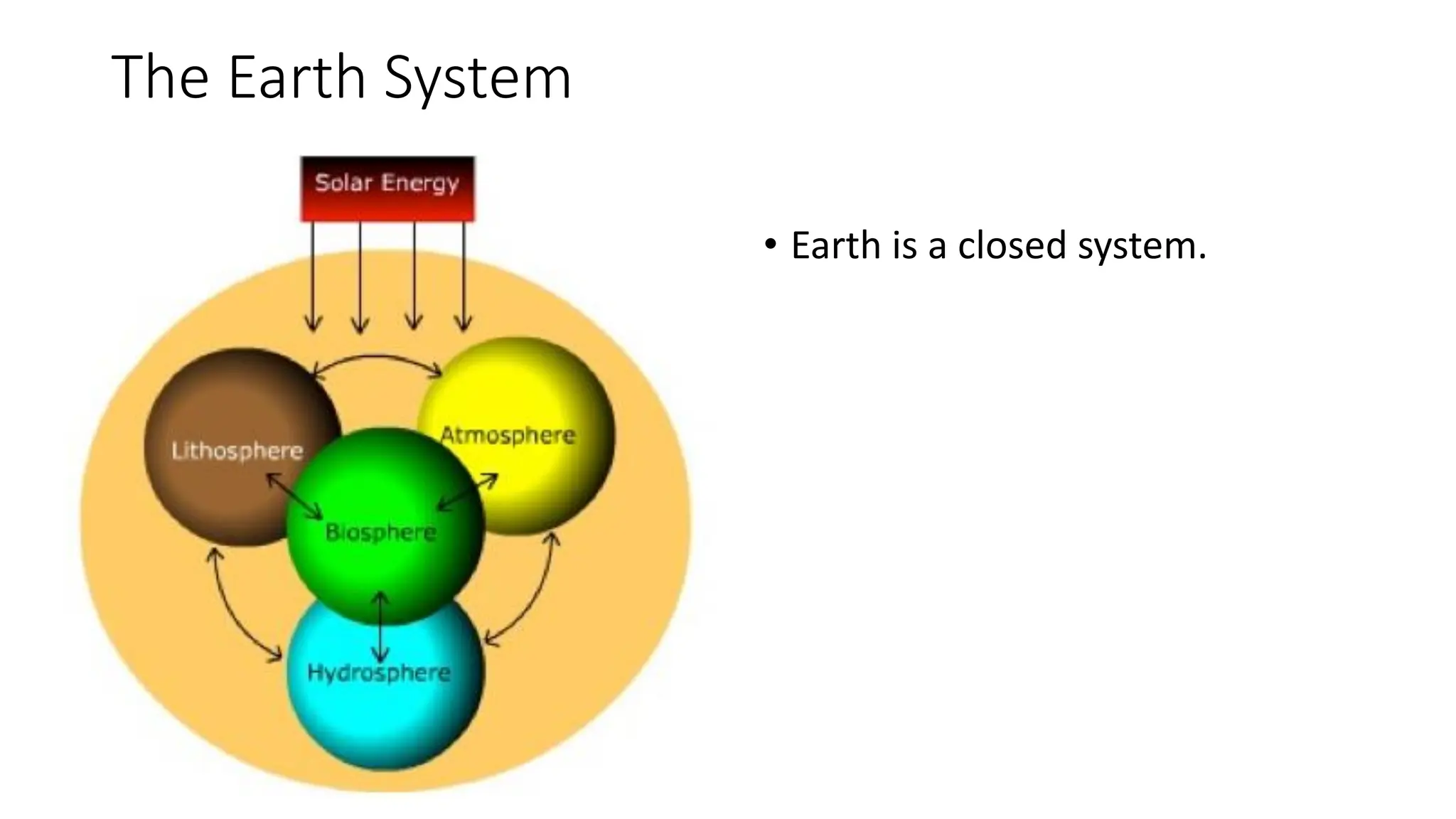
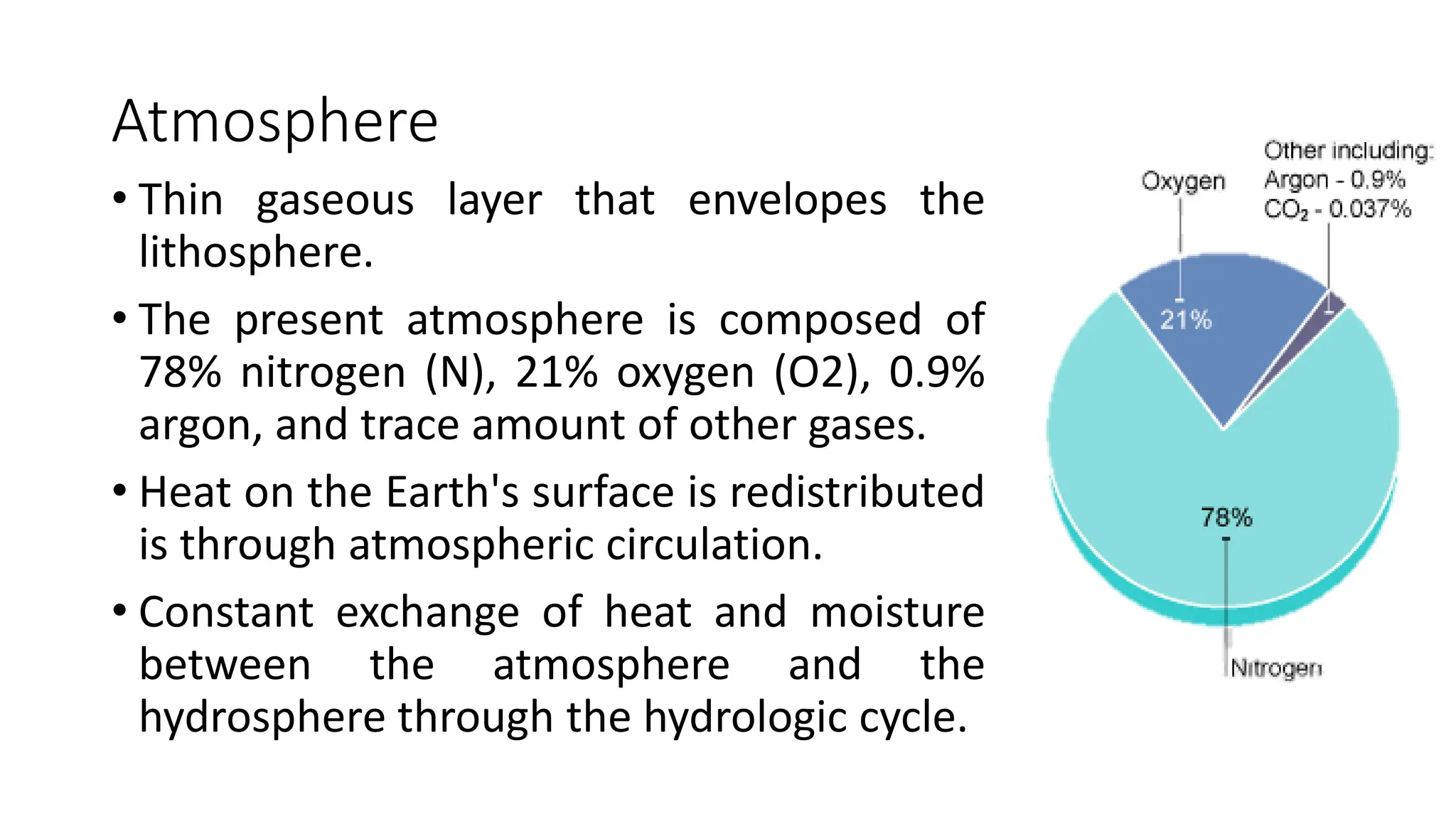
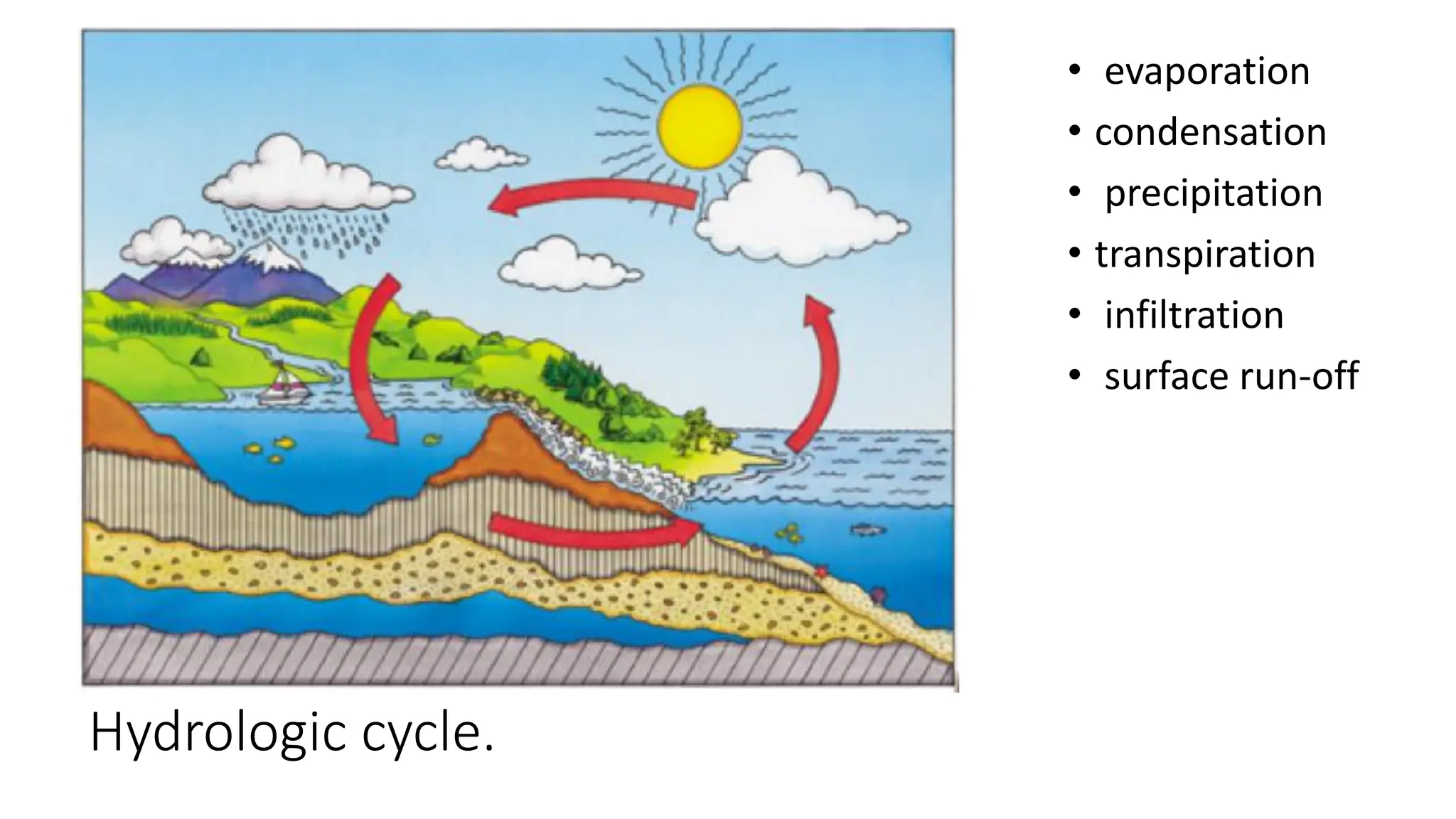
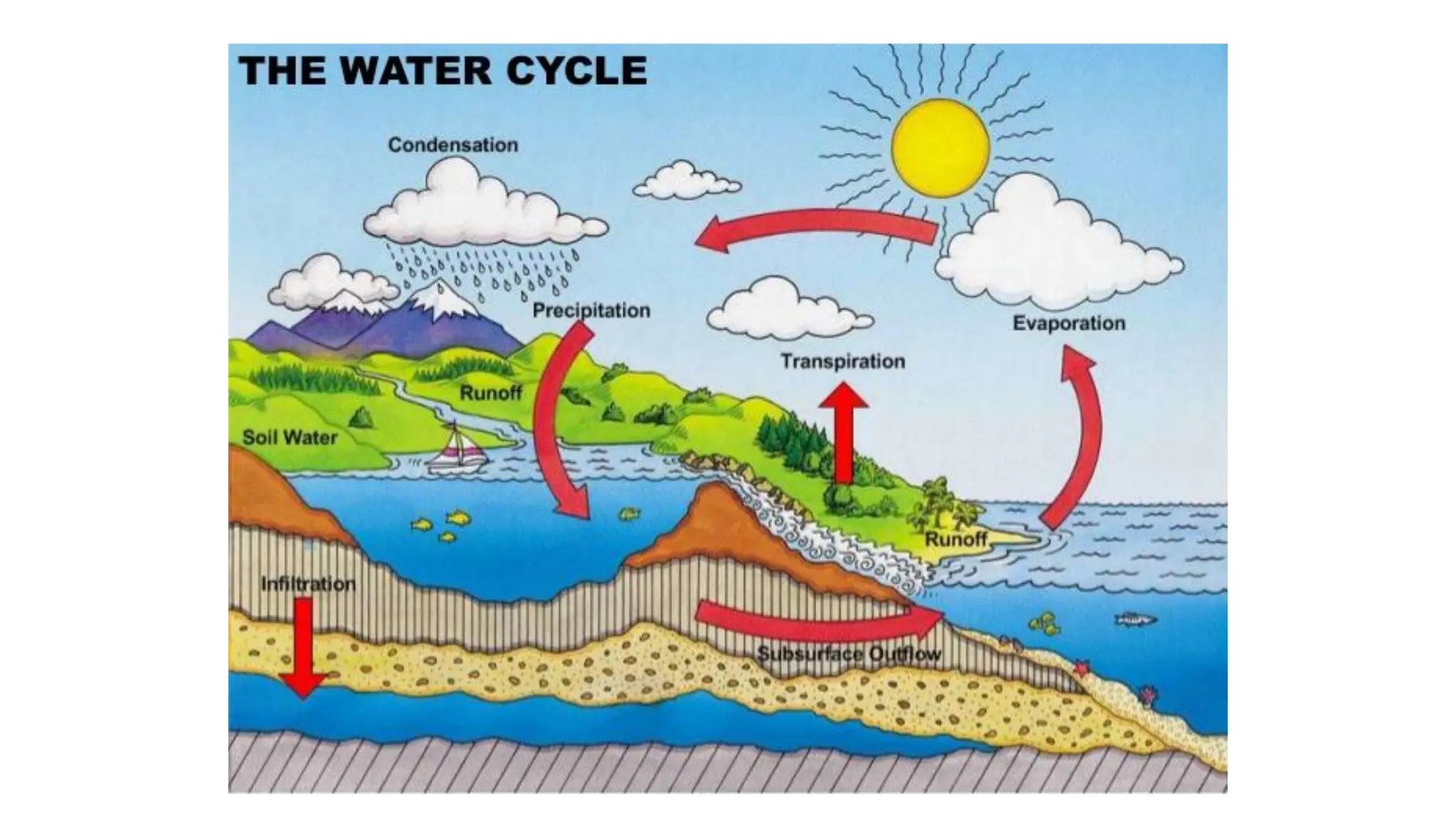
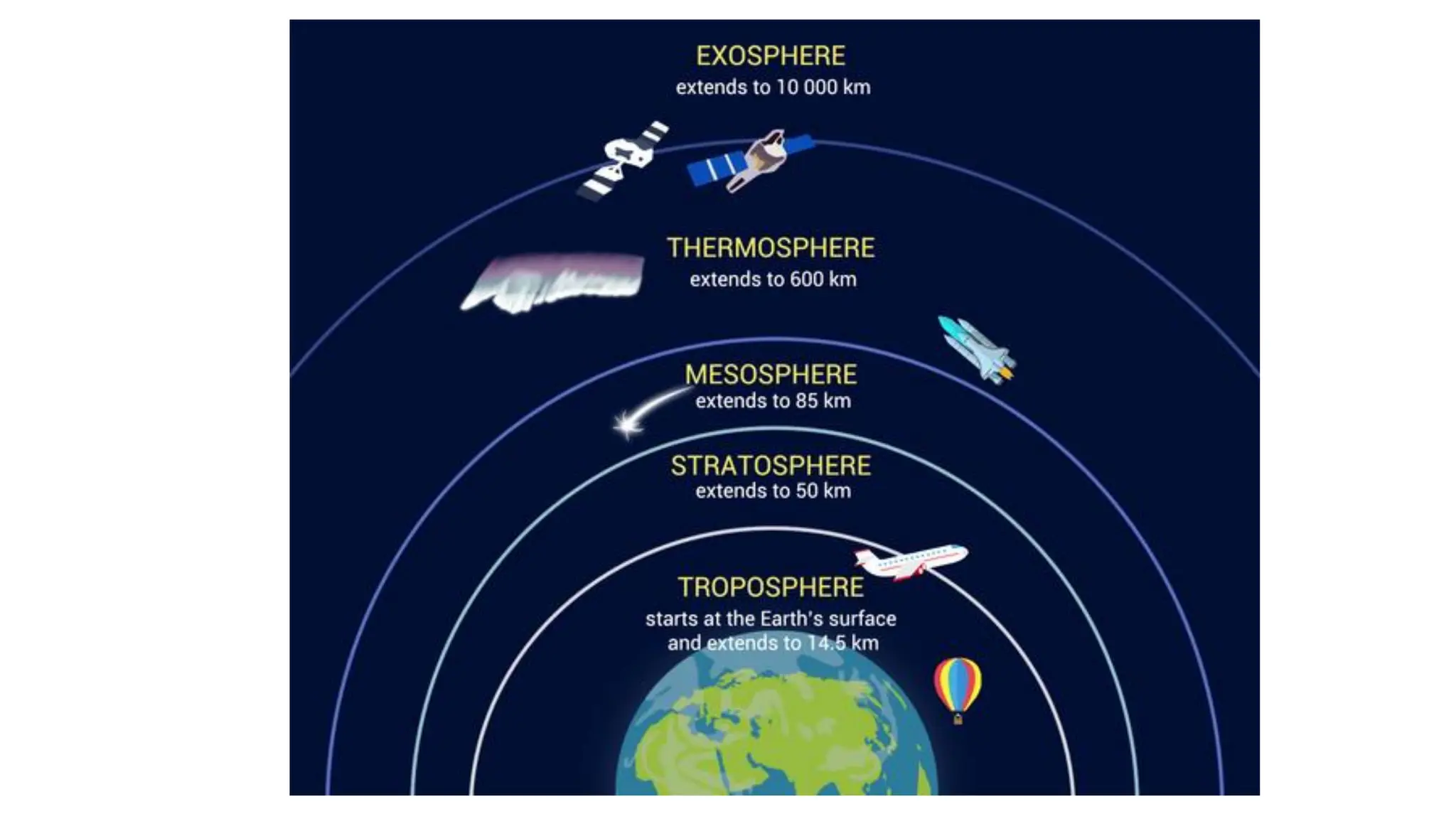
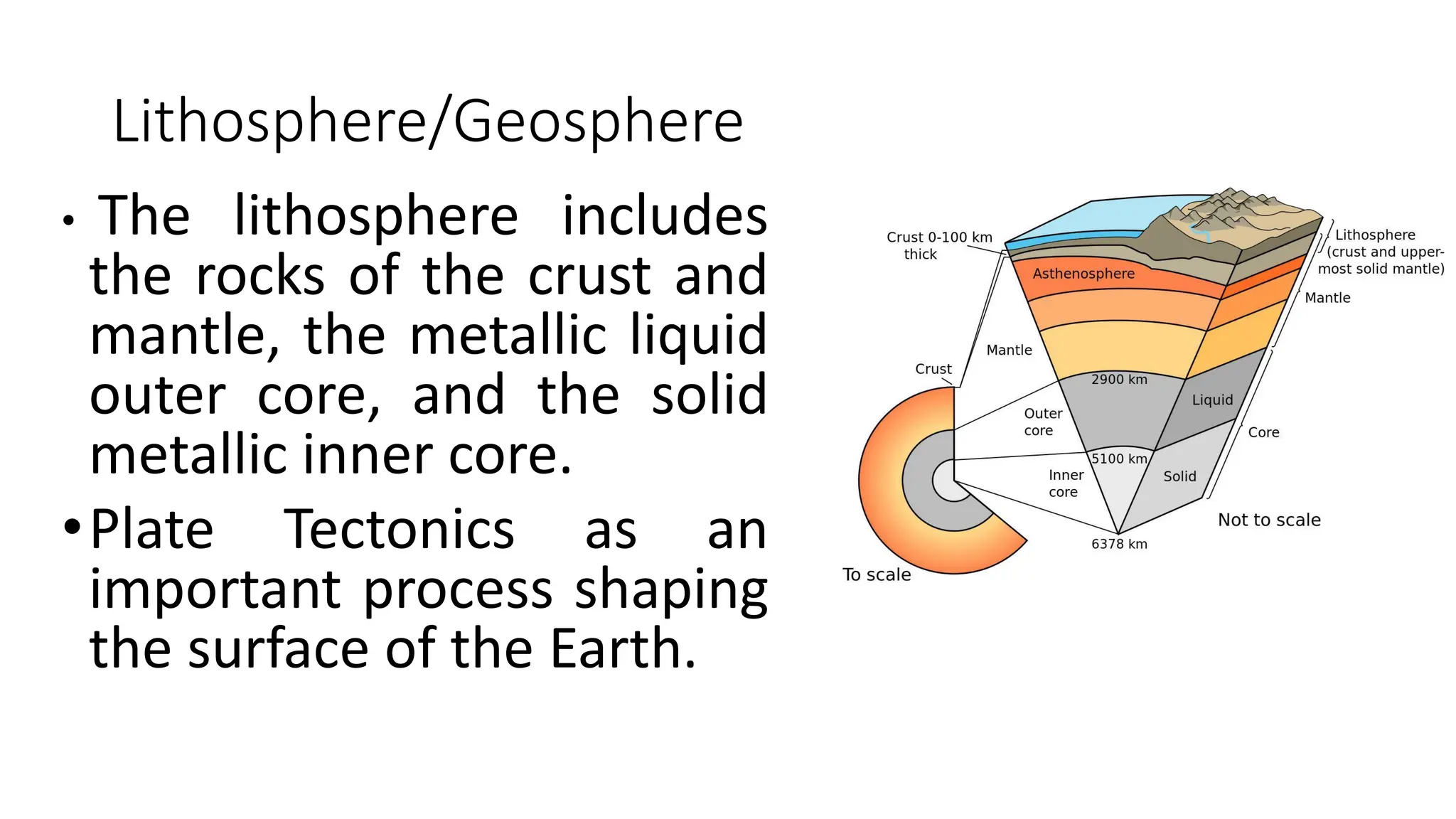
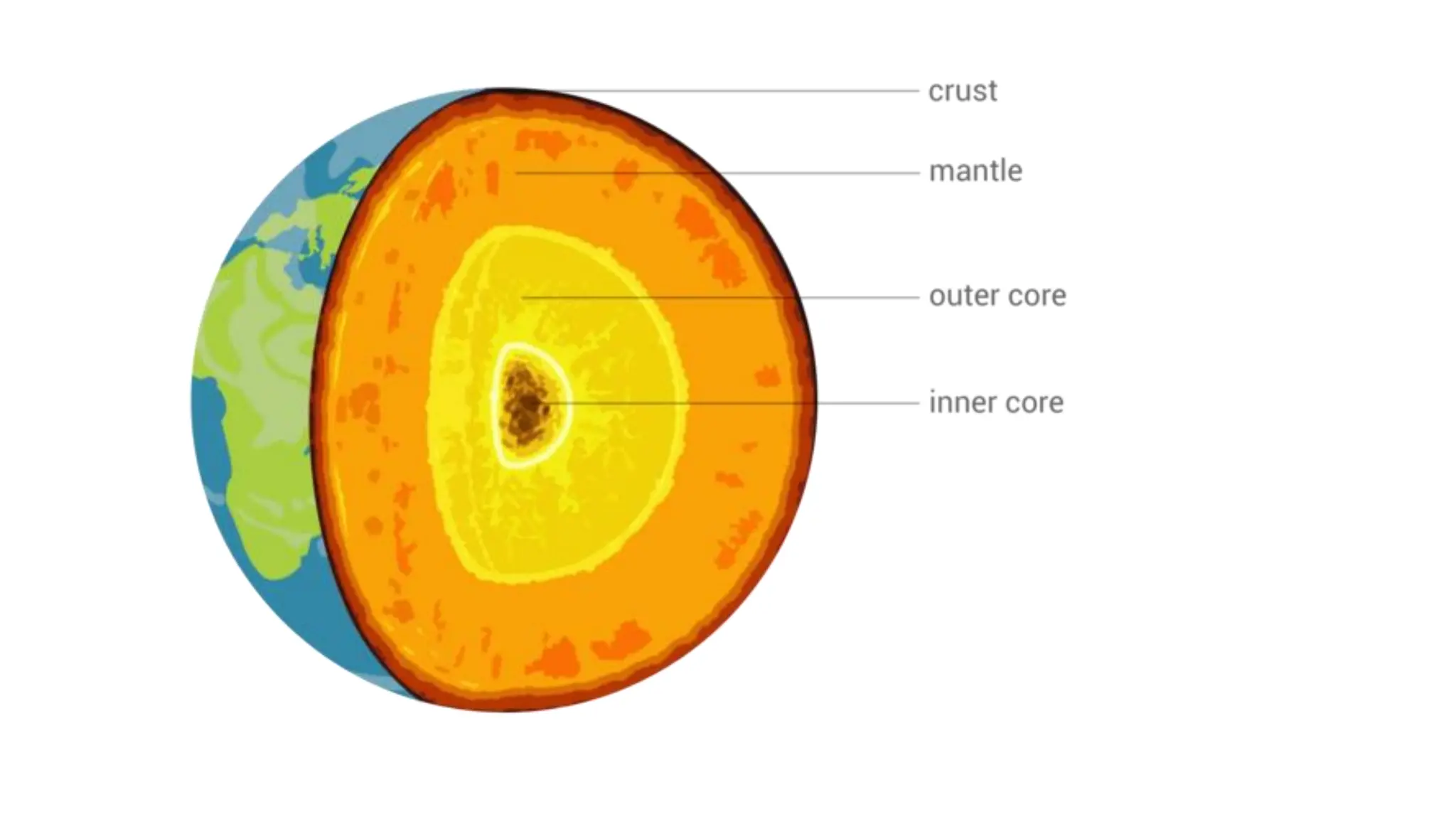
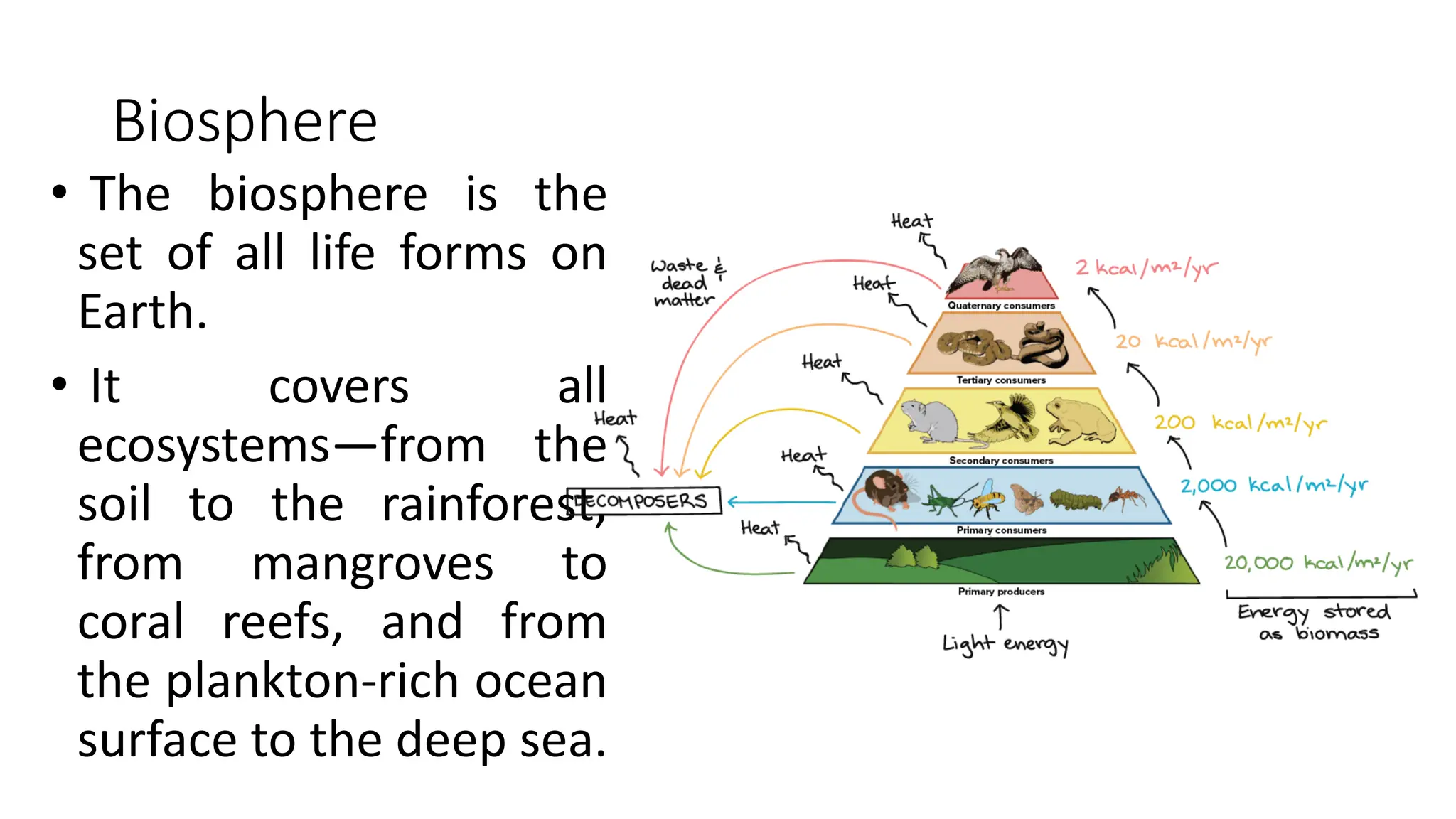
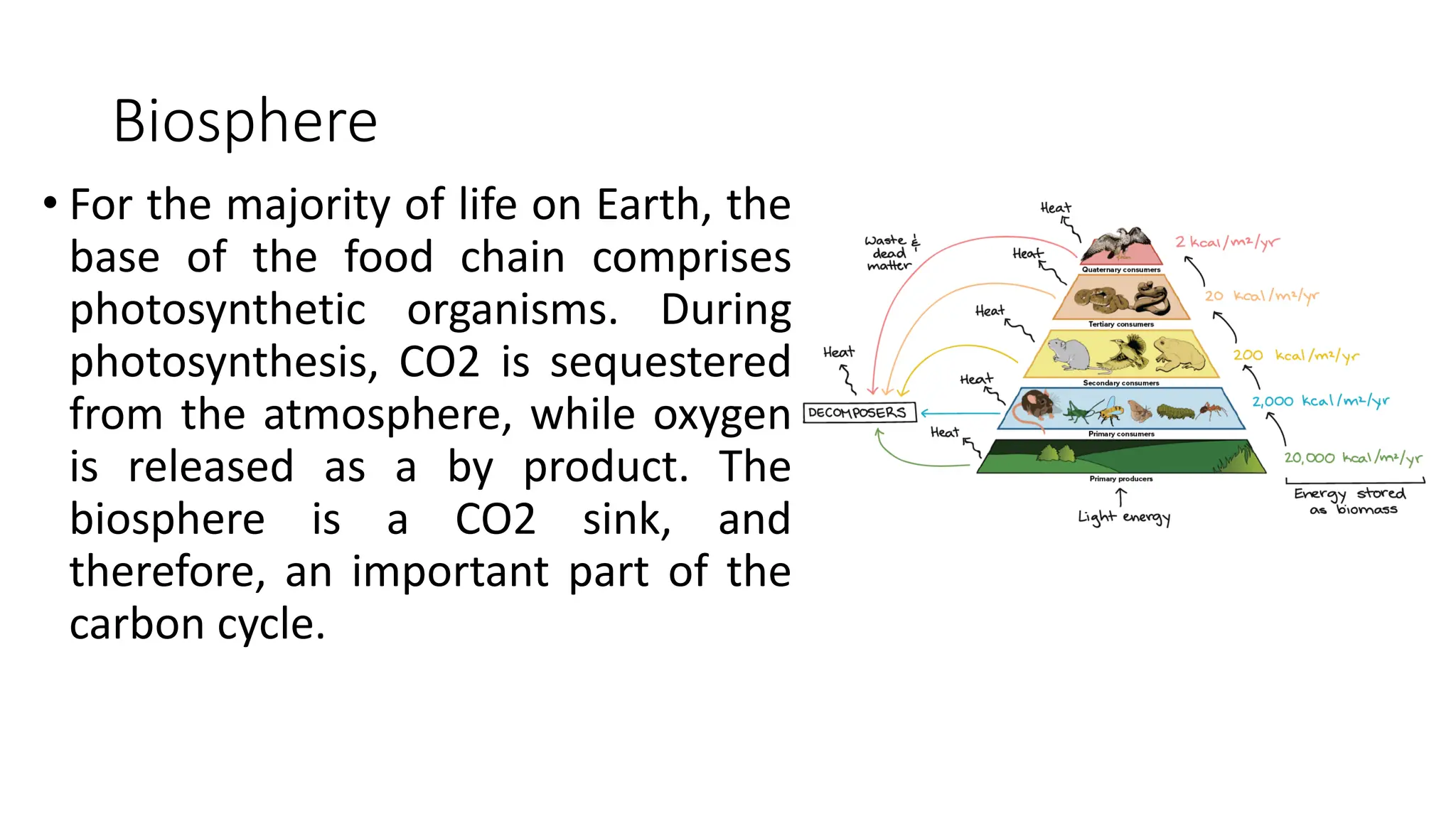
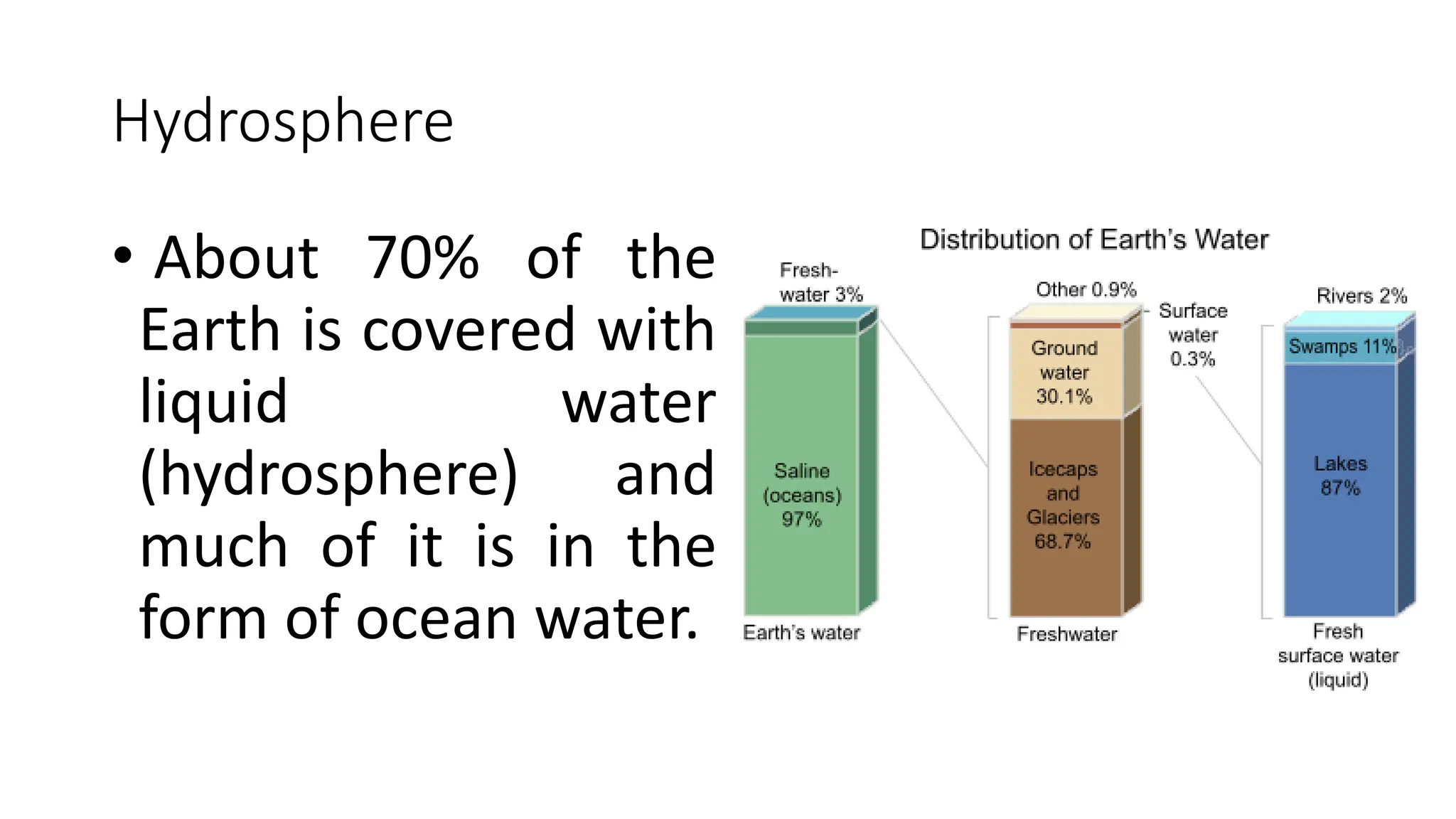
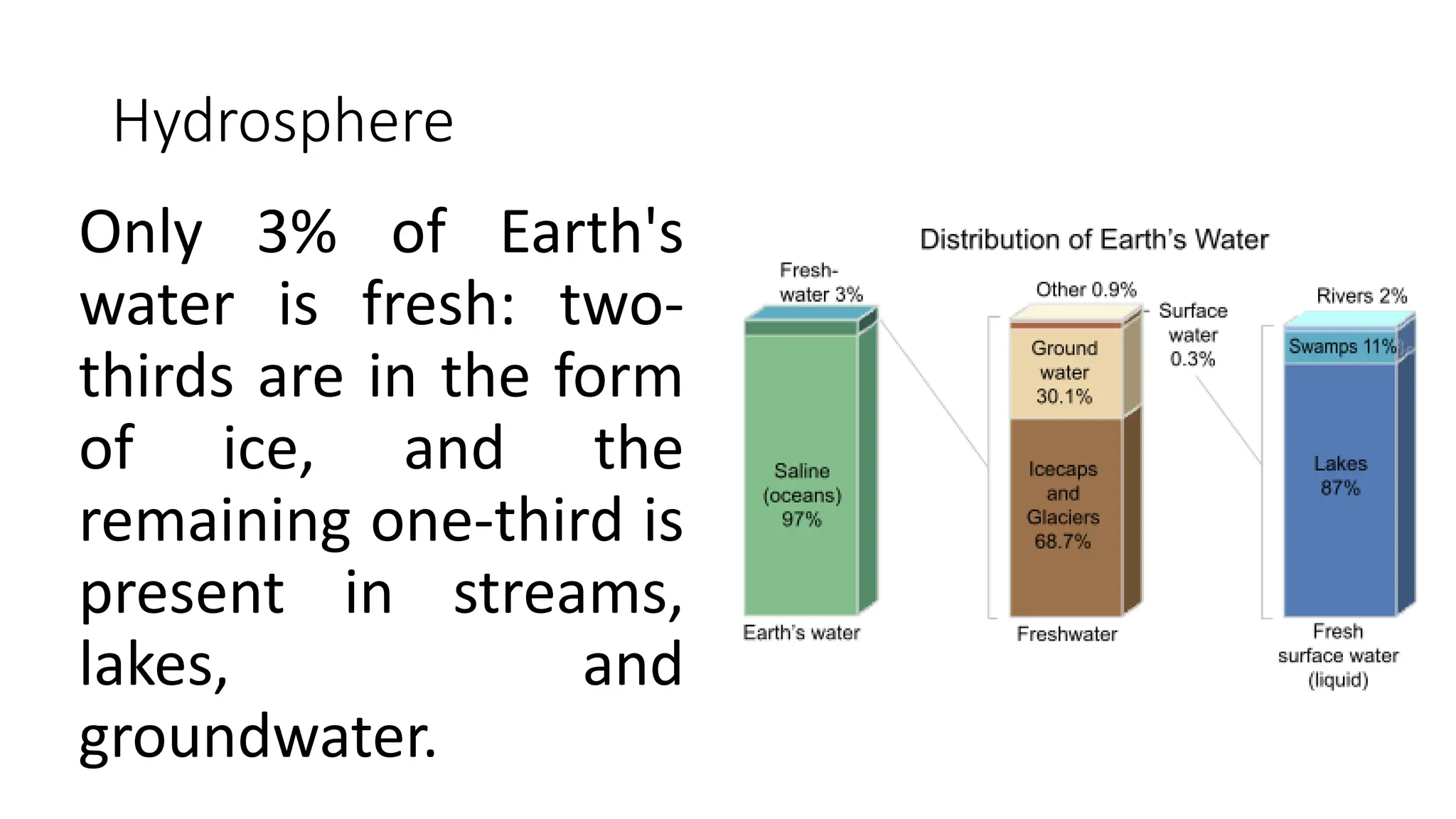
The document discusses the key subsystems that make up the Earth system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, biosphere, and how they interact. It provides details on the composition and important processes of each subsystem. The atmosphere contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and is responsible for heat redistribution and the hydrologic cycle. The hydrosphere covers 70% of the Earth as ocean water and freshwater. The lithosphere includes the crust and mantle, and plate tectonics shape the Earth's surface. The biosphere is the set of all life forms and the carbon cycle. Each subsystem interacts with the others, making life possible on Earth.