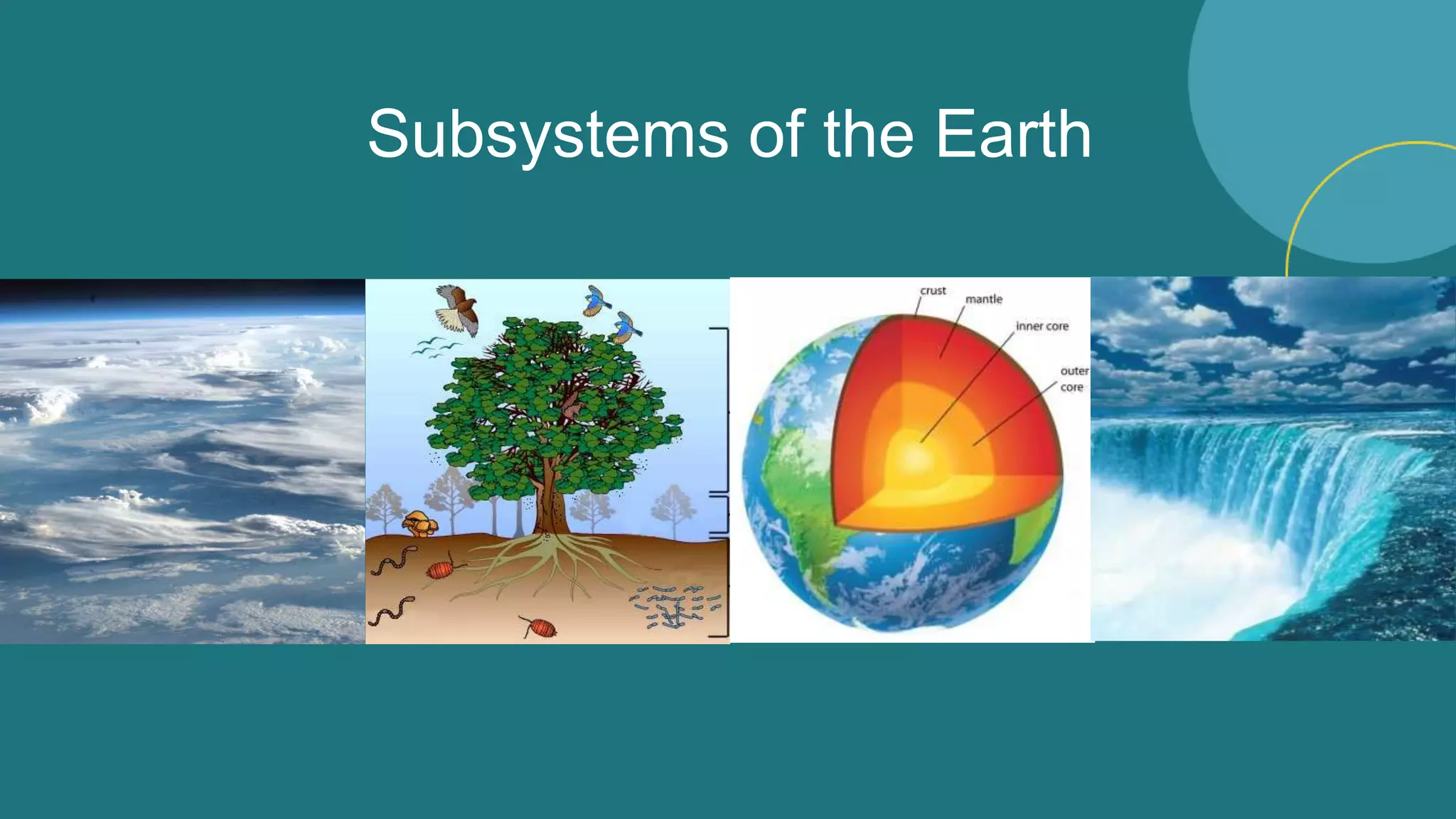
The document discusses the four main subsystems that make up the Earth system: the atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere. The atmosphere provides heat and energy to the geosphere. The biosphere receives gases, heat, and sunlight from the atmosphere, and receives water from the hydrosphere and a living medium from the geosphere. Energy and matter flow continuously across the boundaries of Earth's four subsystems.