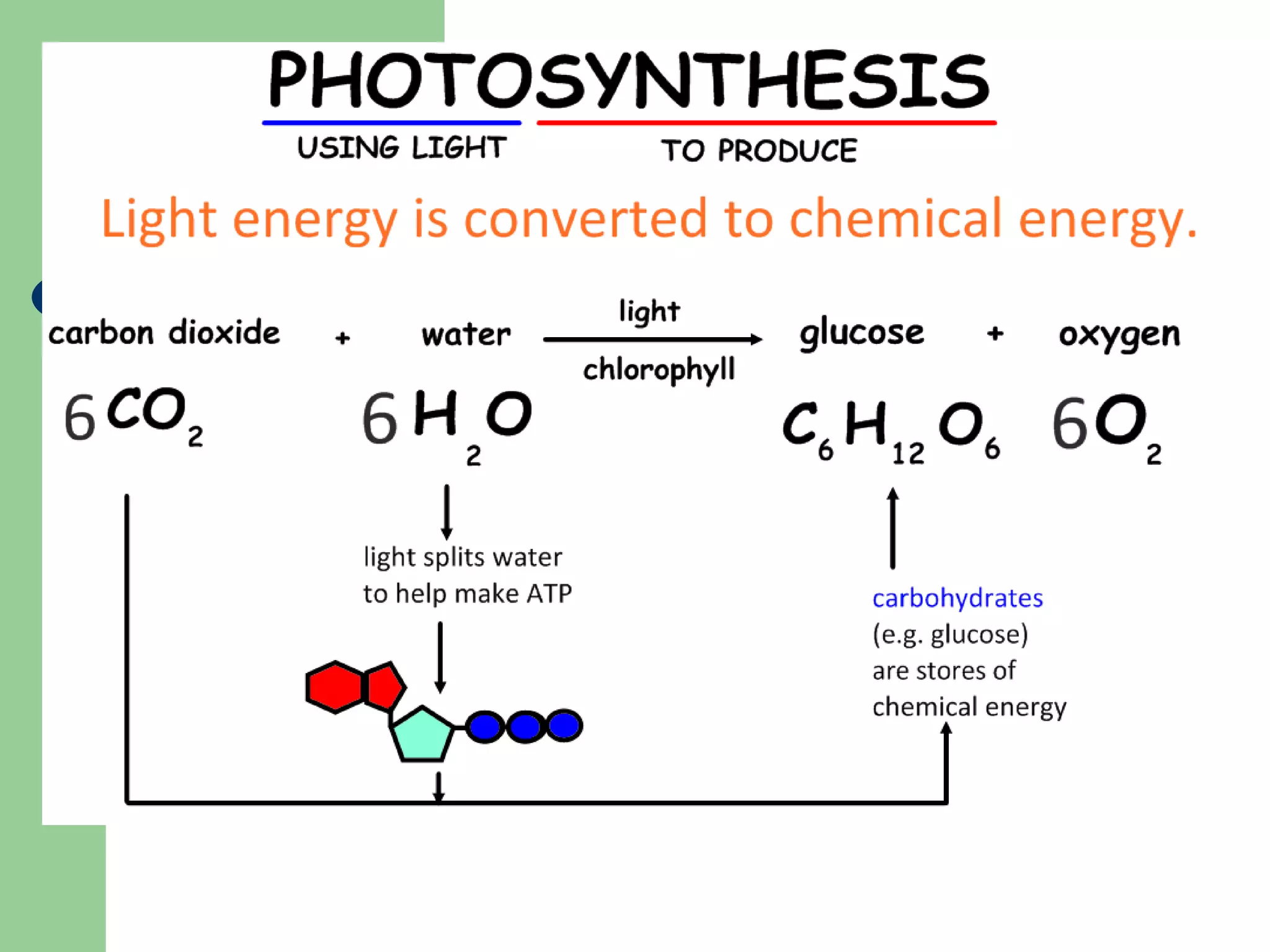
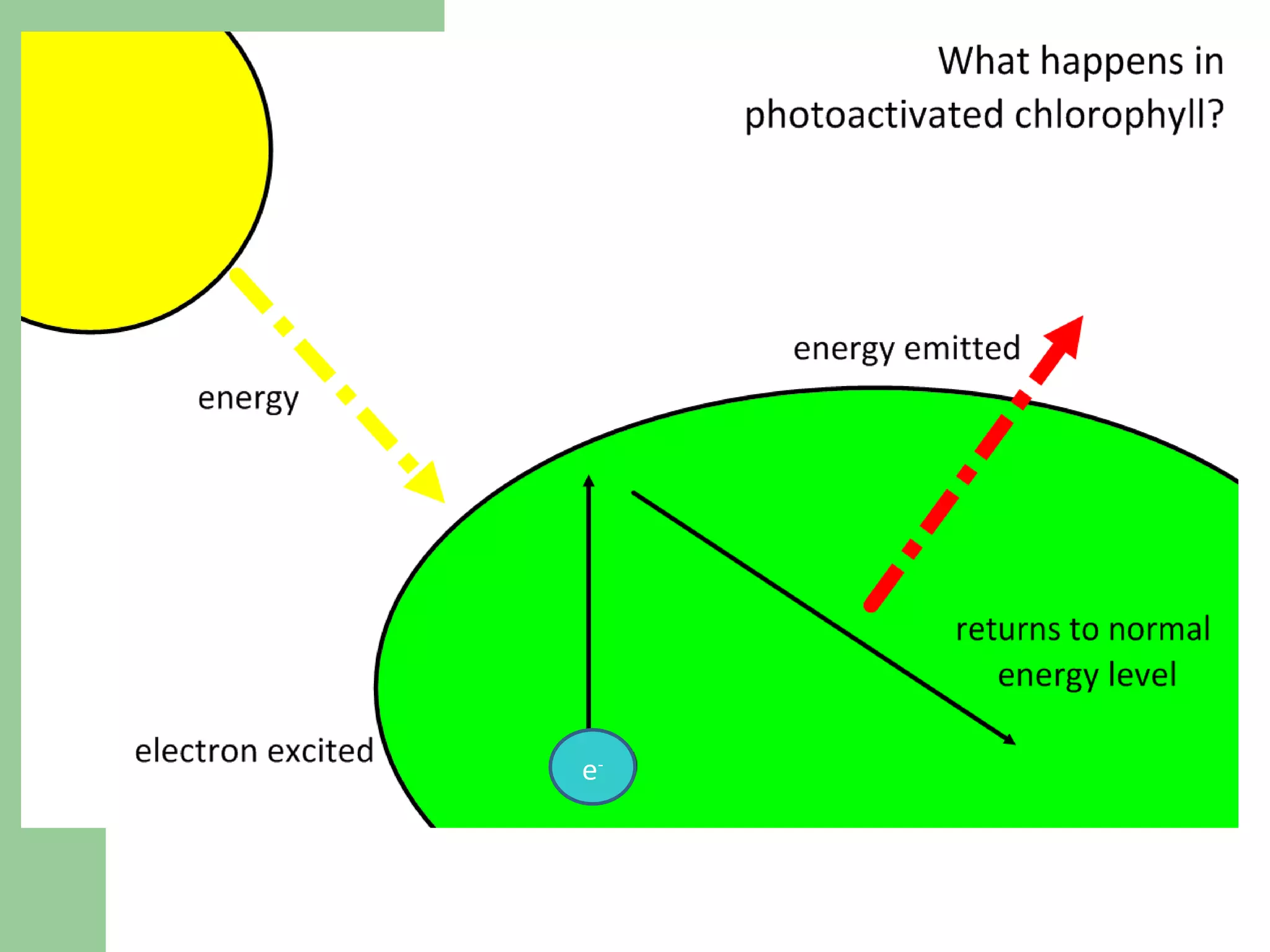
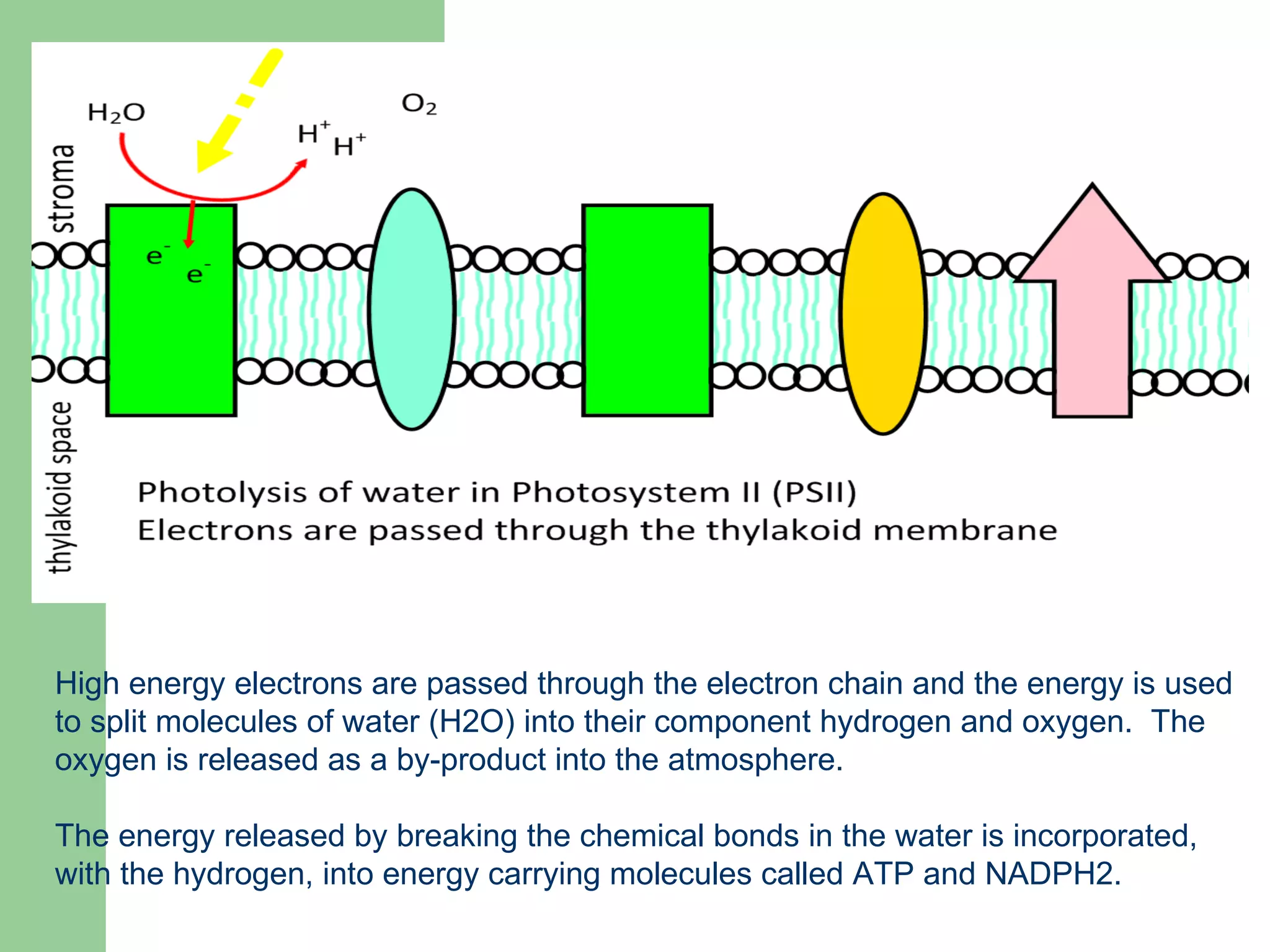
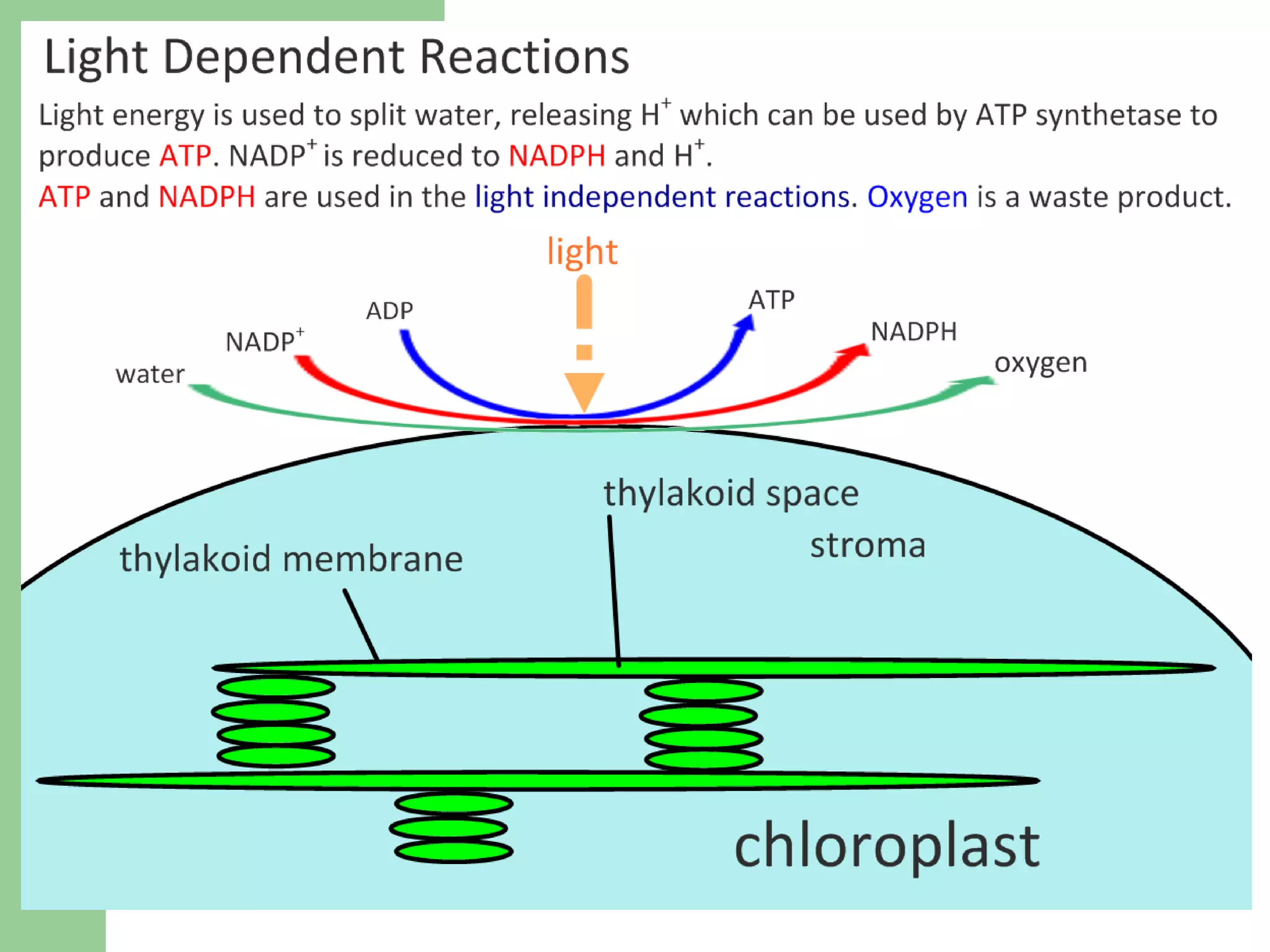
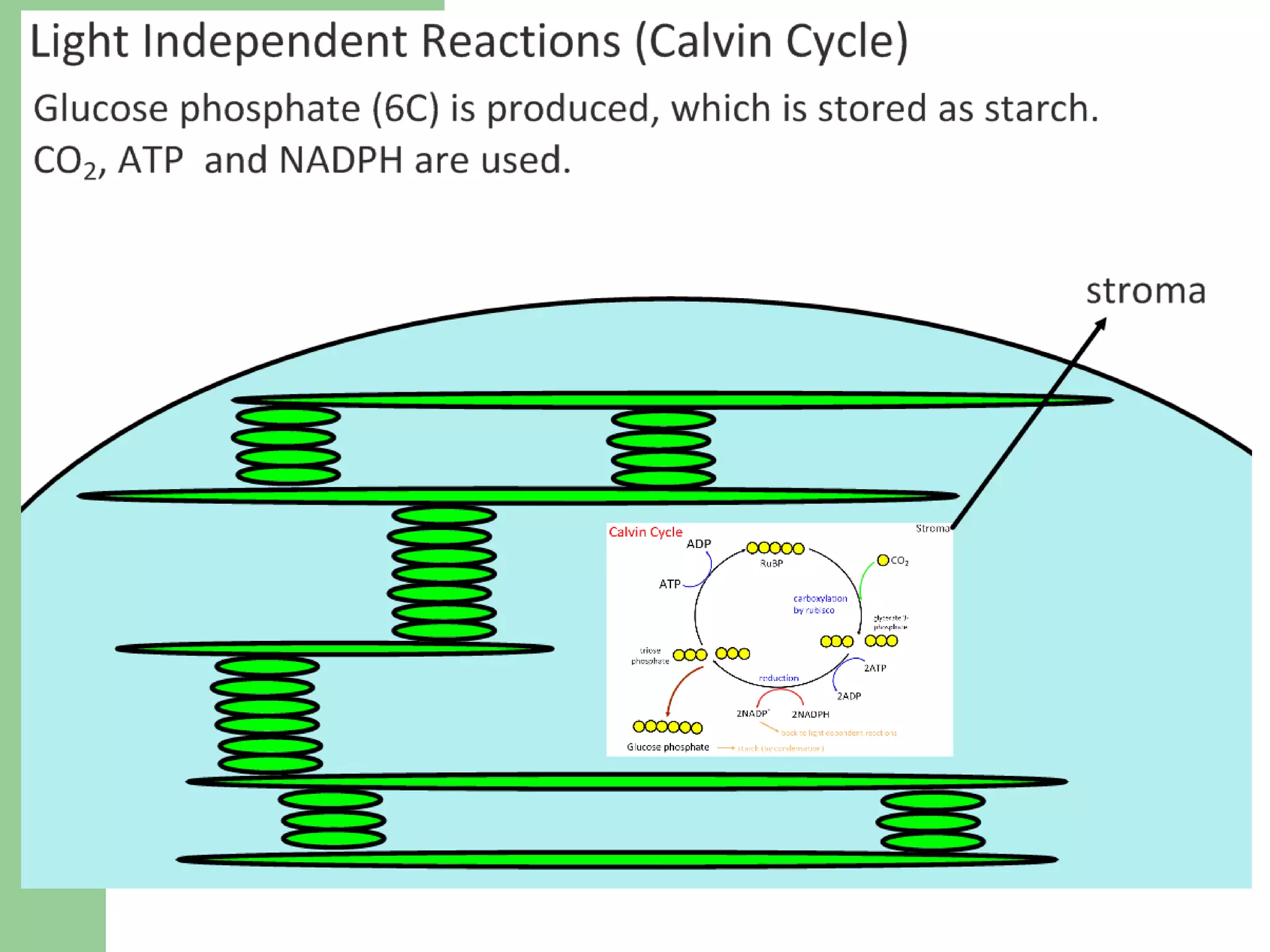
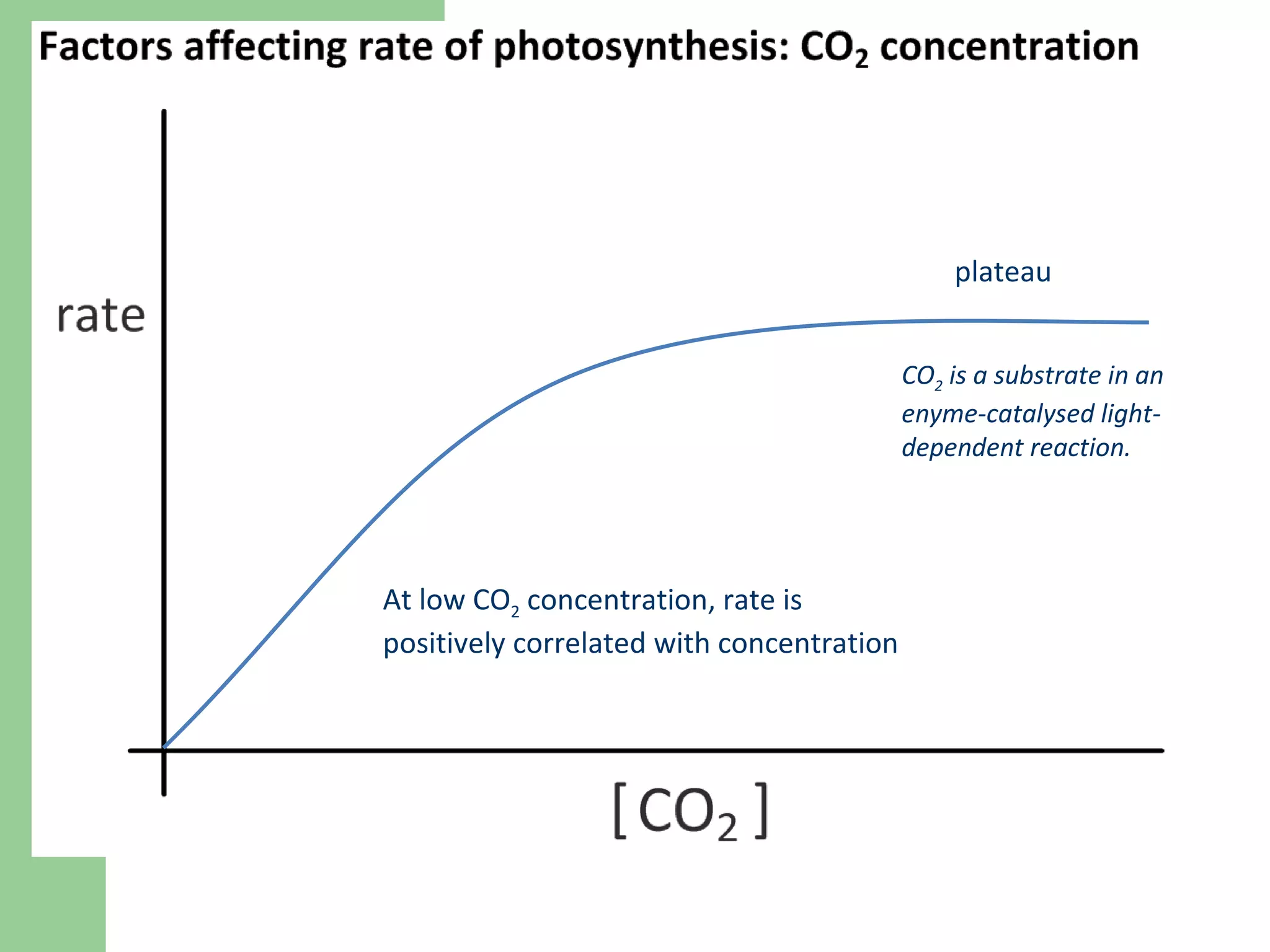
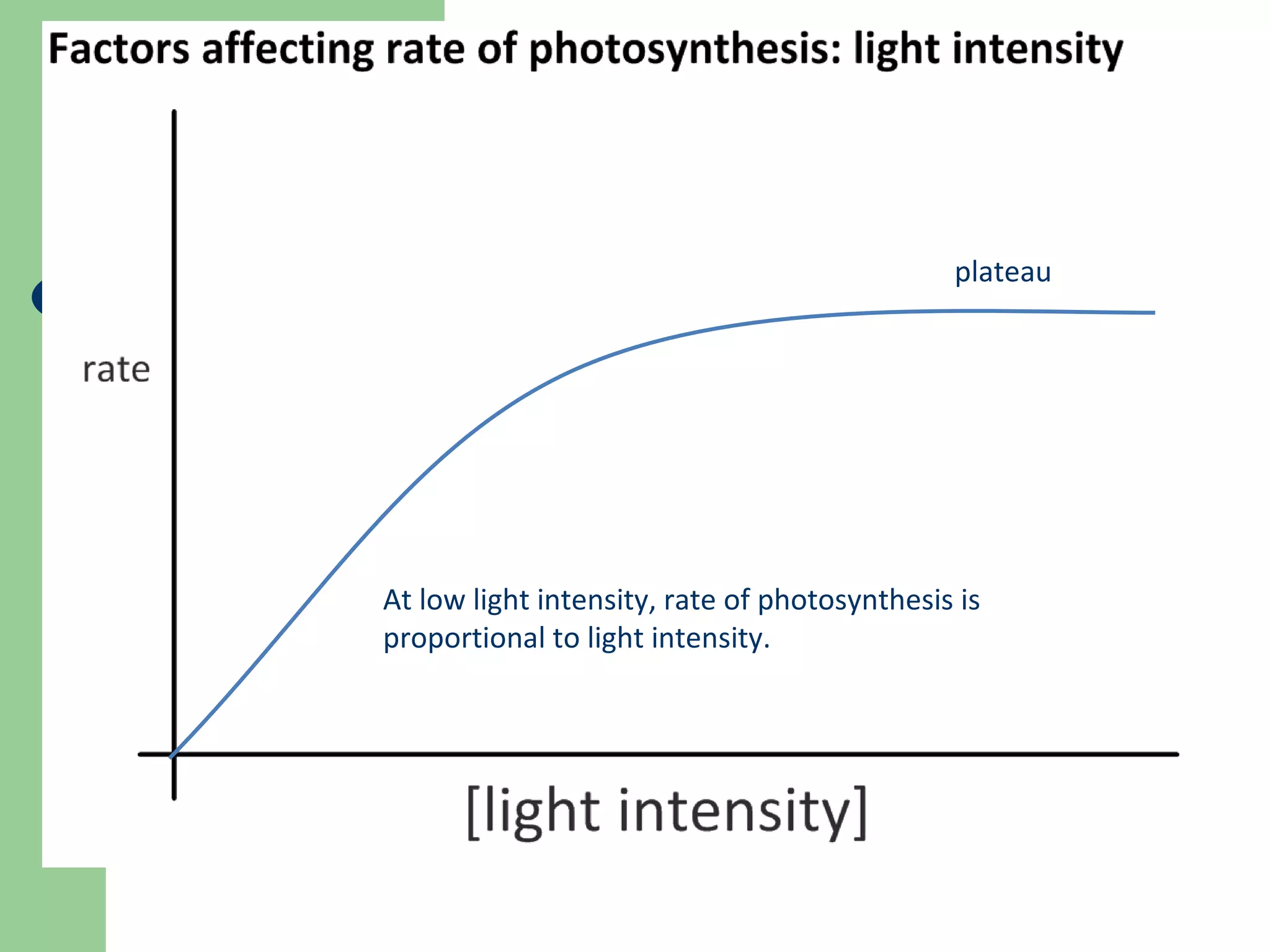
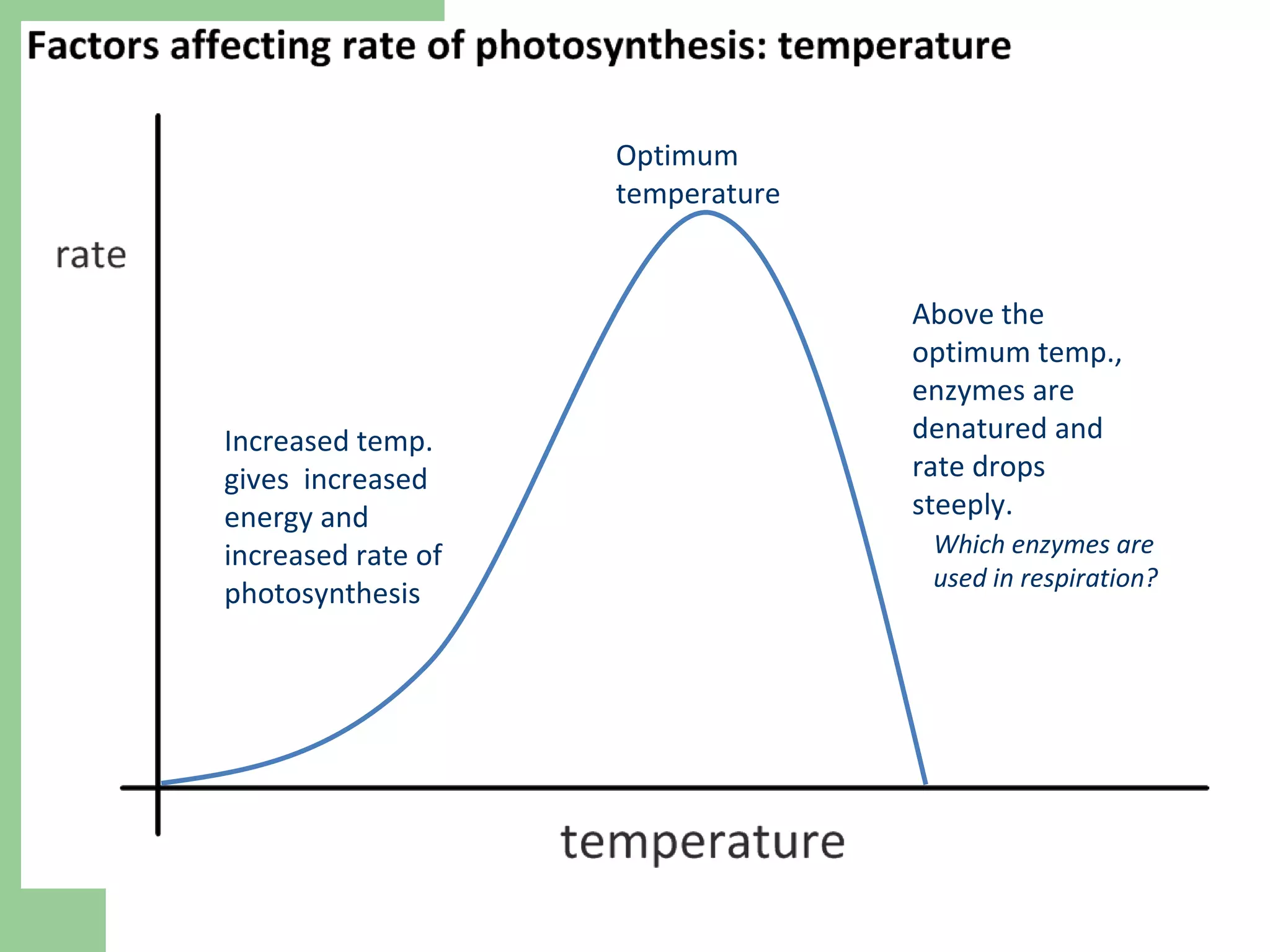
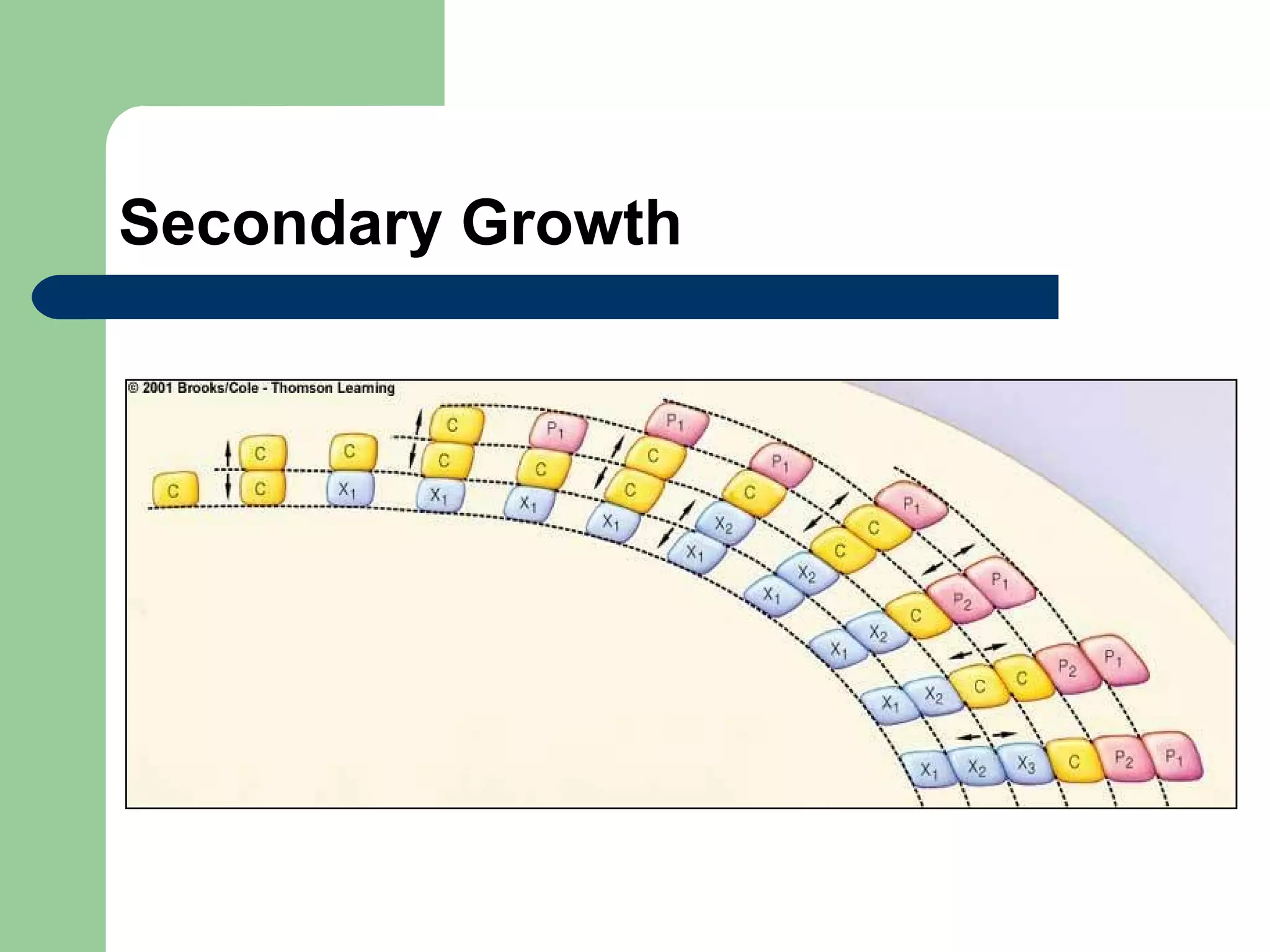
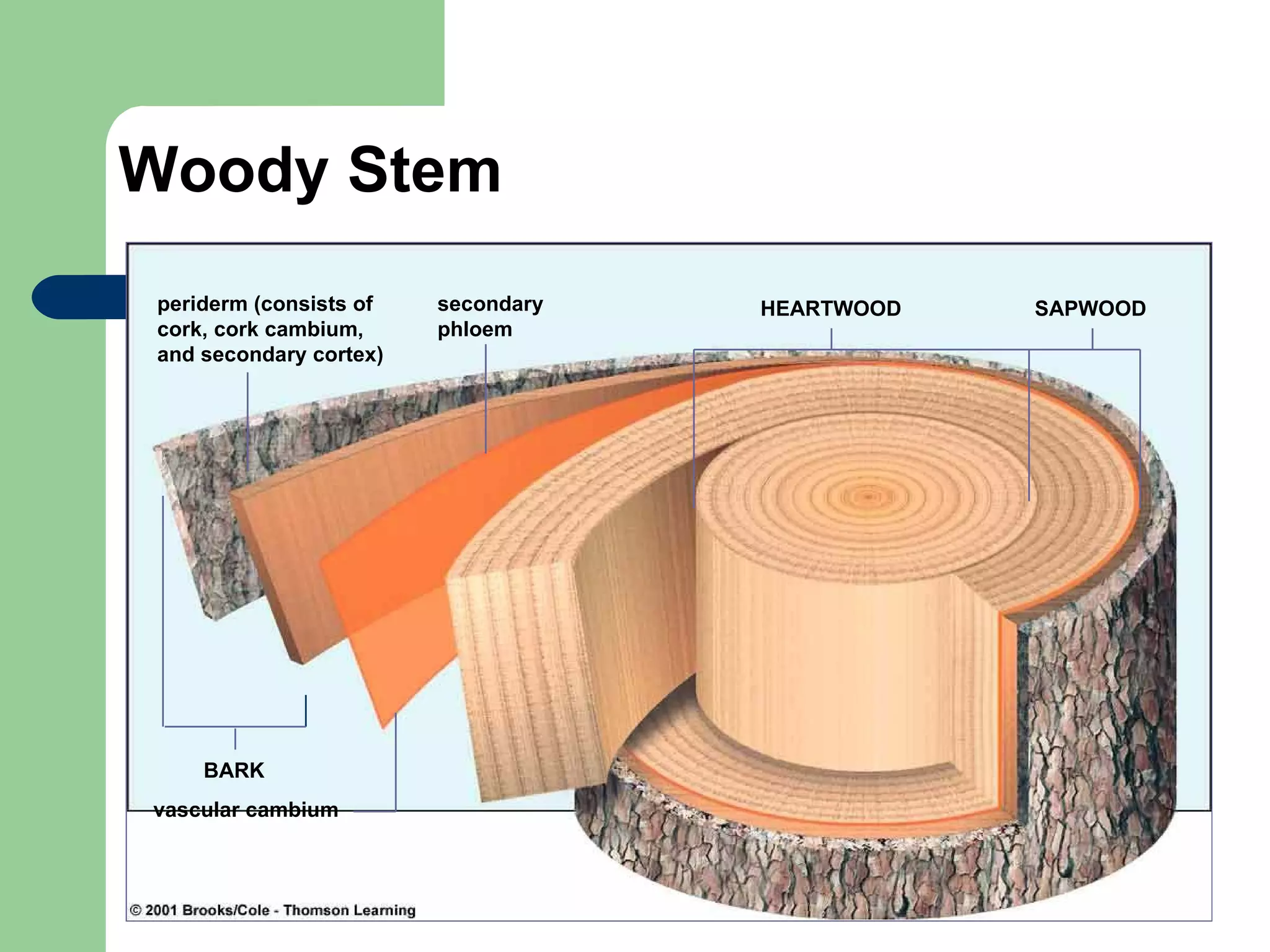
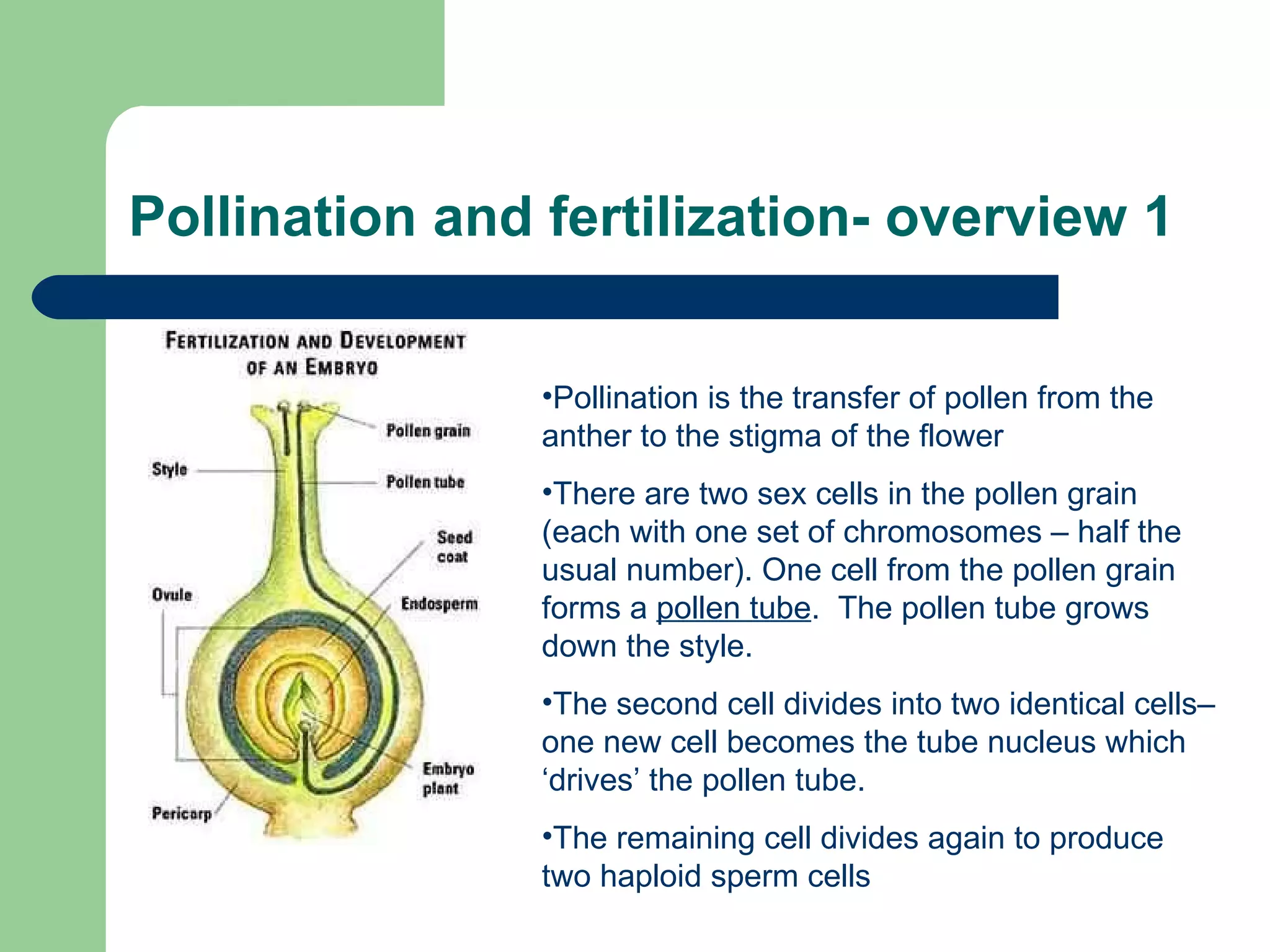
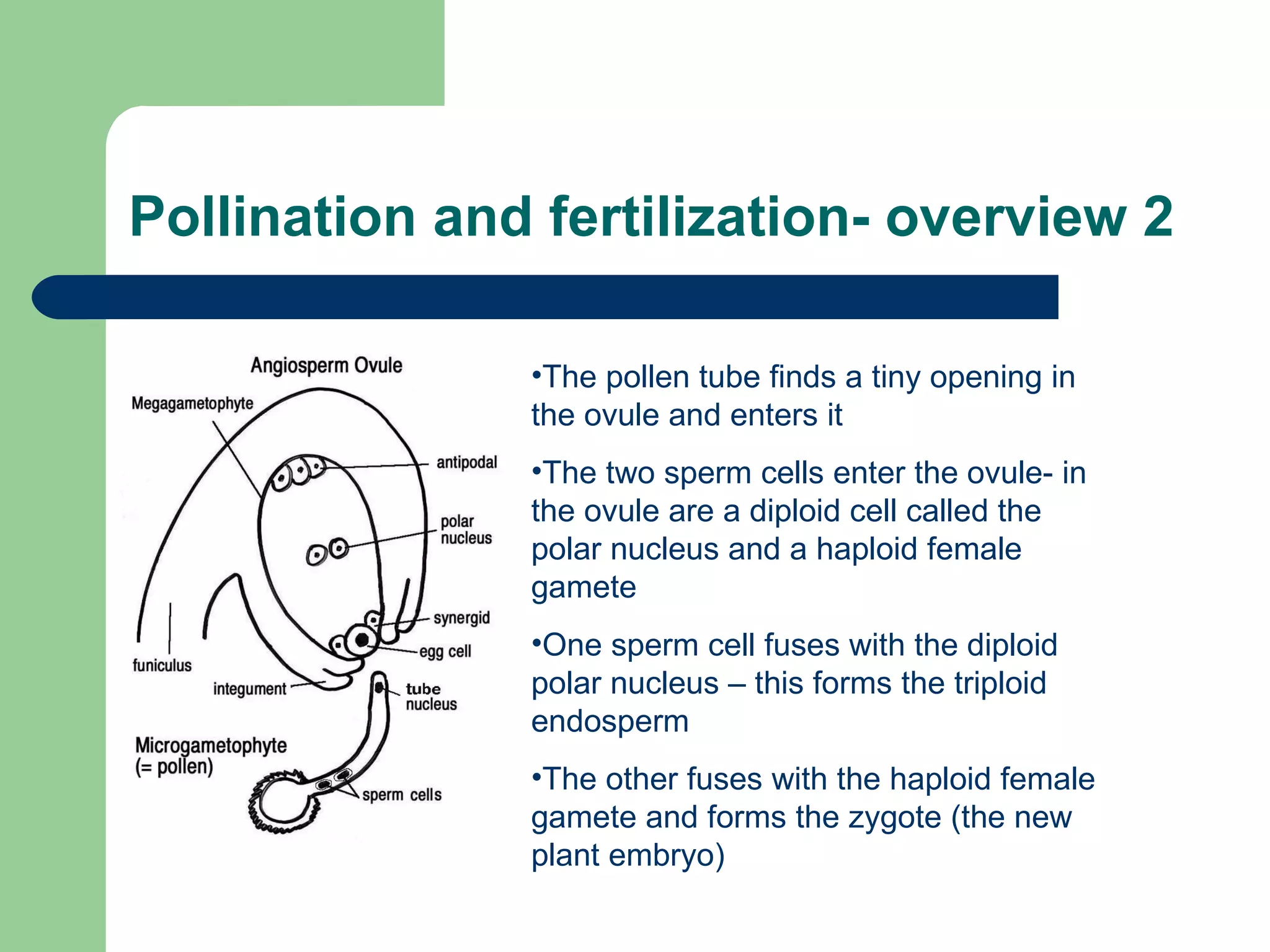
This document provides an overview of topics to be covered in RHS Level 2 Certificate Week 10, including photosynthesis, respiration, secondary thickening, and pollination/fertilization. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen through light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Secondary thickening occurs in woody stems and results in the growth of secondary xylem and phloem tissues. Pollination involves the transfer of pollen from anther to stigma, and fertilization is the fusion of sperm and egg cells within the ovule leading to seed formation.