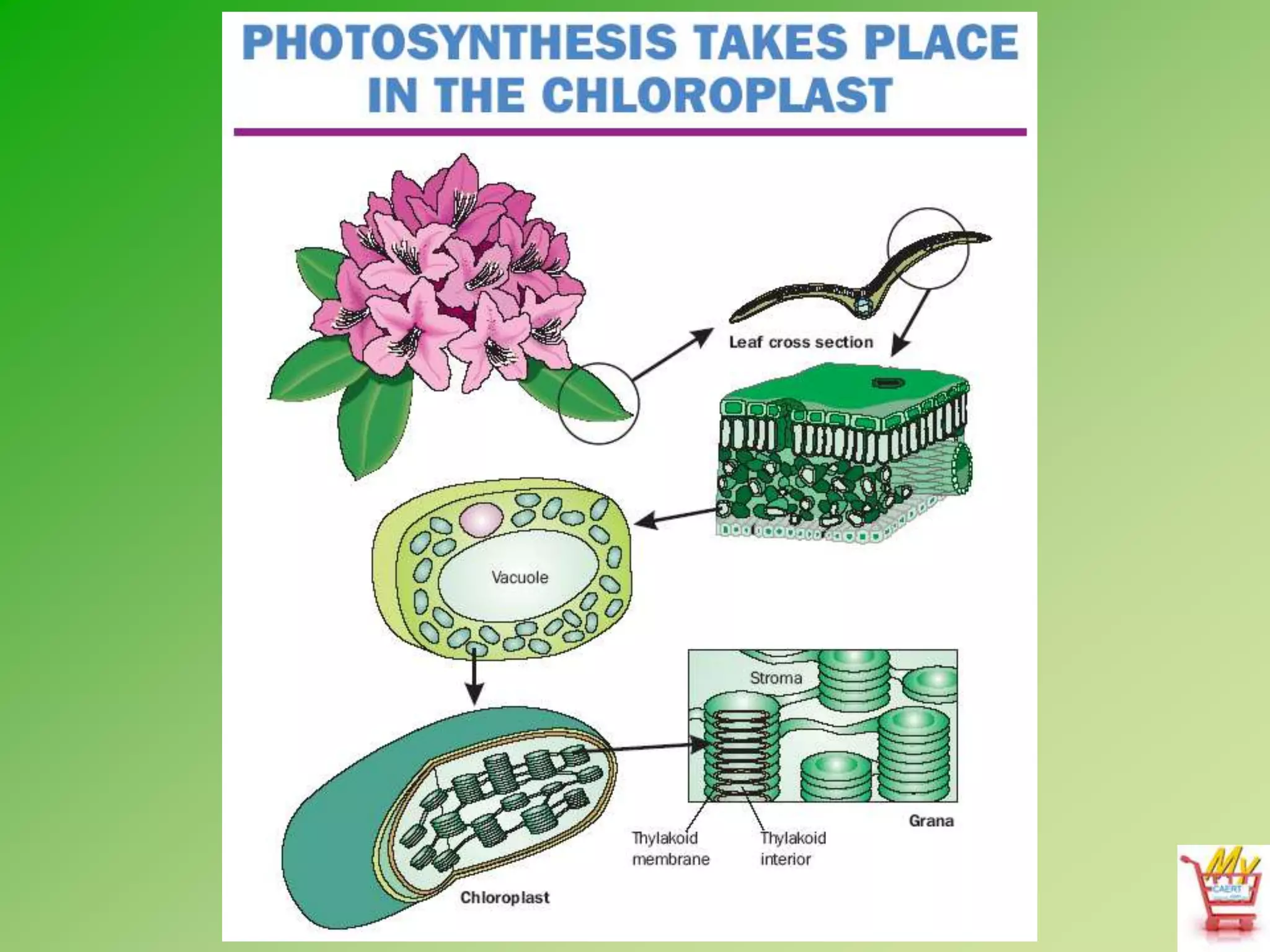
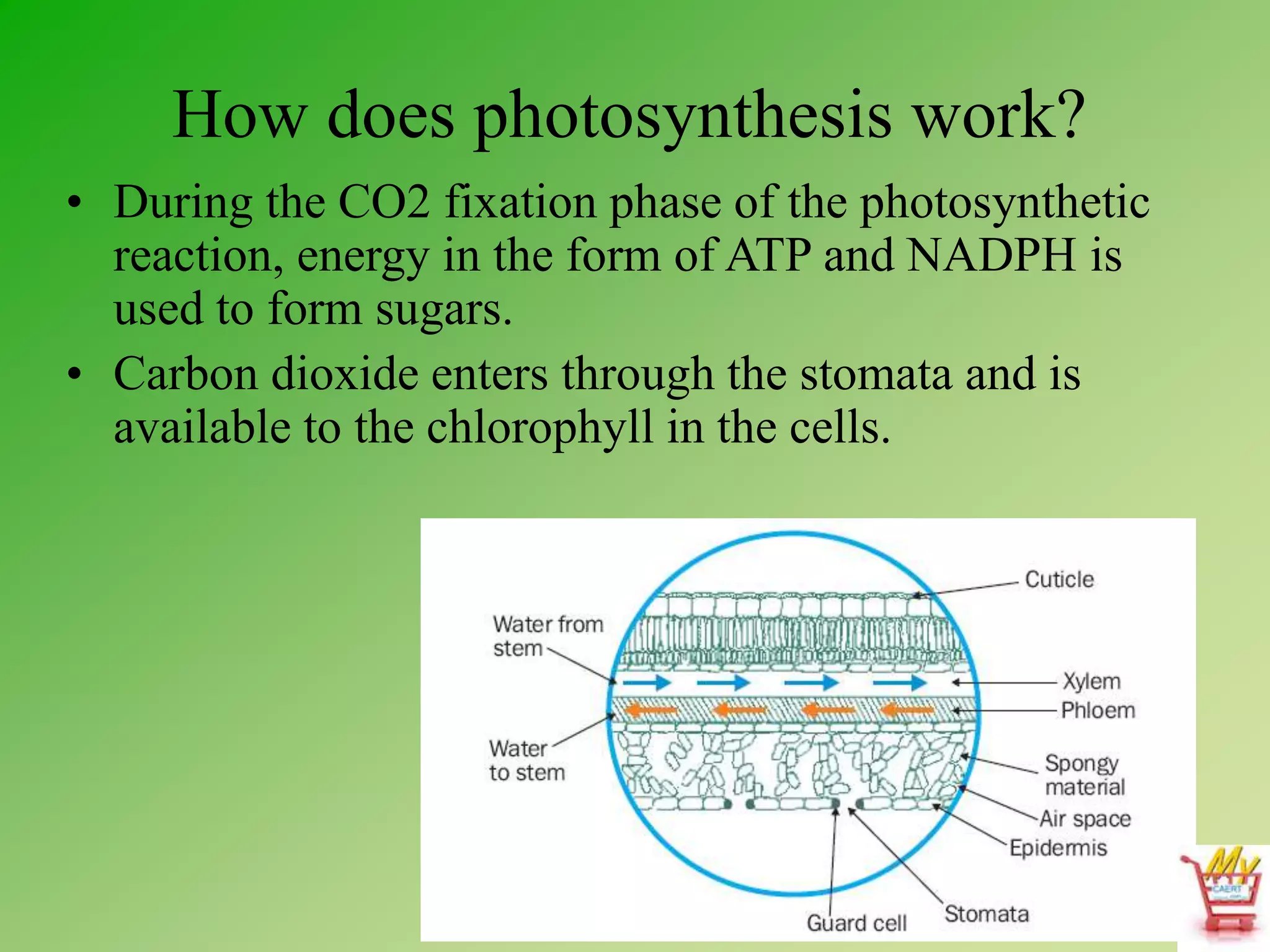
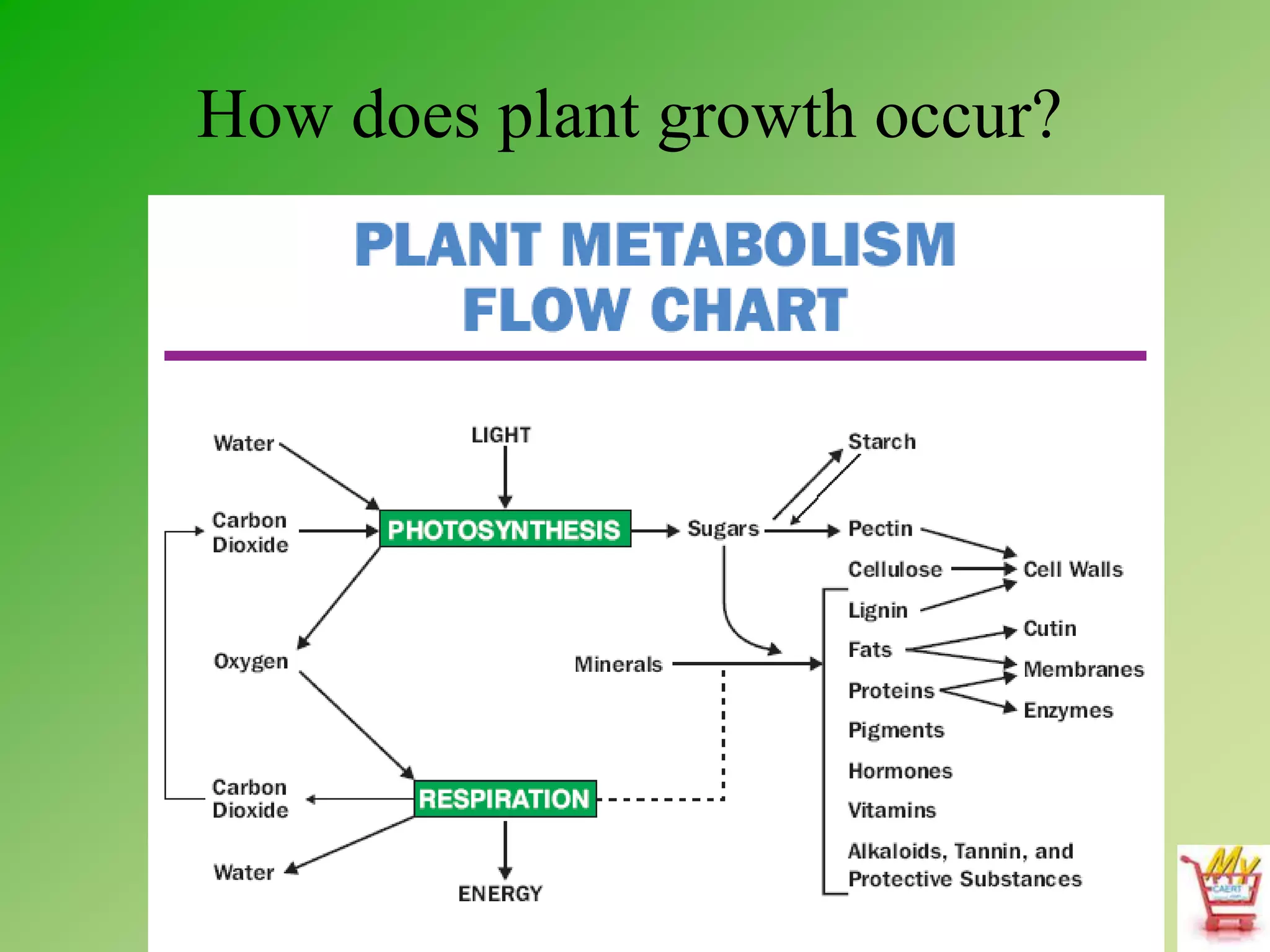
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are important plant processes. Photosynthesis uses energy from sunlight to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water. This fuels plant growth and also produces oxygen as a byproduct. Cellular respiration breaks down sugars to release the stored energy, producing carbon dioxide and water. Plant growth occurs through metabolic processes that use enzymes to break down and rebuild molecules. These plant processes are essential to human life as they produce oxygen, food, fuel, and play a role in rainfall and climate regulation.