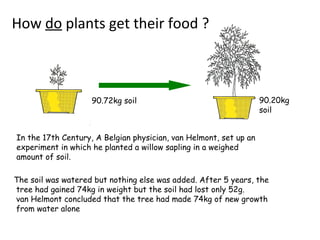
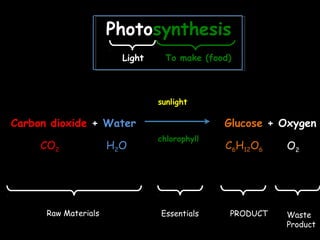
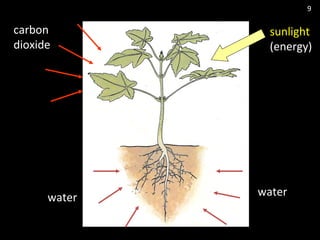
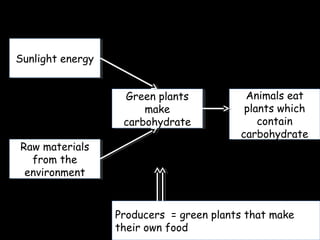
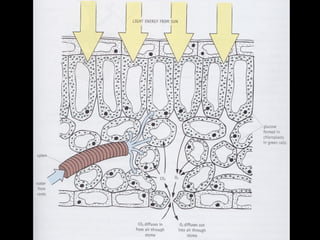
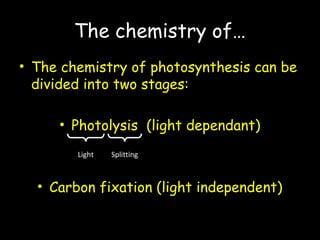
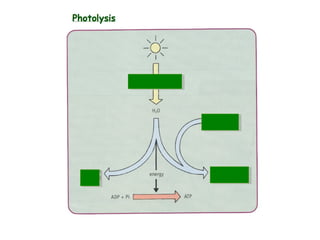
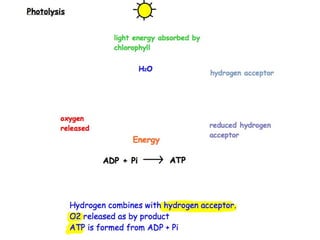
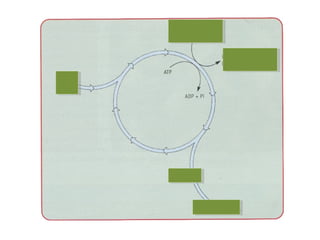
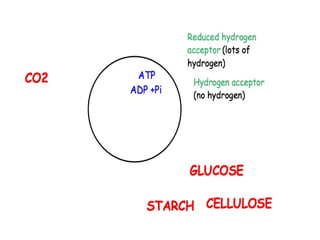
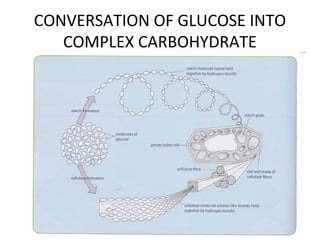
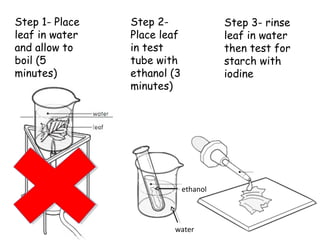
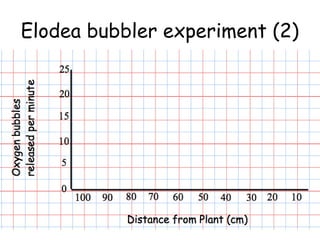
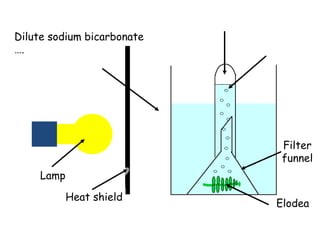
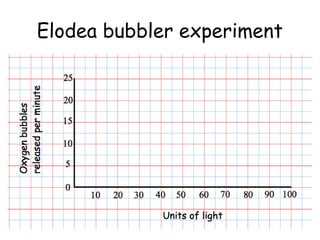
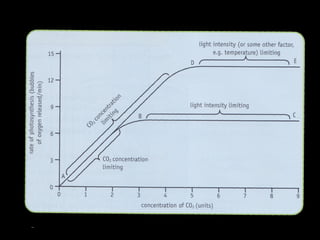
The document discusses photosynthesis and the factors that affect its rate. It explains that the three limiting factors of photosynthesis are light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature. Graphs show how the rate levels off or declines when these factors become limited. Horticulture can help reduce these limiting effects by providing extra lighting to greenhouses, increasing temperature which also releases more carbon dioxide, and allowing for increased and earlier crop yields under more controlled conditions.