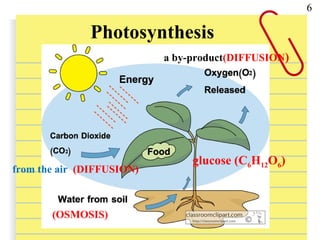
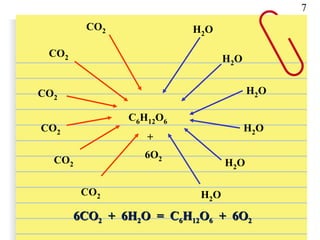
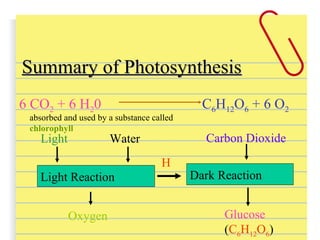
Van Helmont conducted an experiment where he planted a willow sapling in soil and measured the soil weight before and after 5 years of growth. He found that the tree had gained 74kg in weight but the soil had only lost 52g. This showed that the tree's food came from water alone, not the soil. However, he overlooked the role of carbon dioxide from the air, which plants use along with water during photosynthesis to produce their own food in the form of glucose.