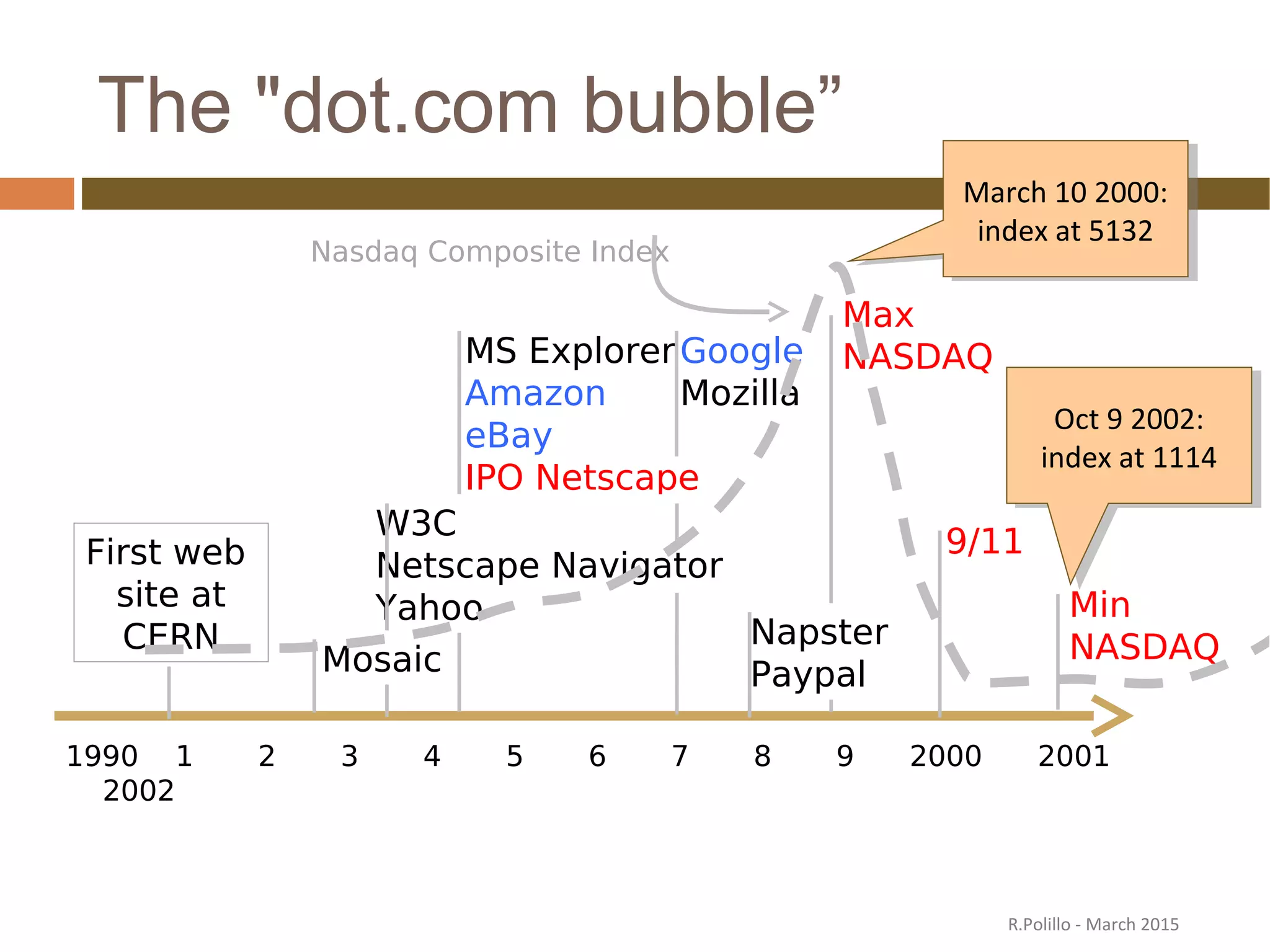
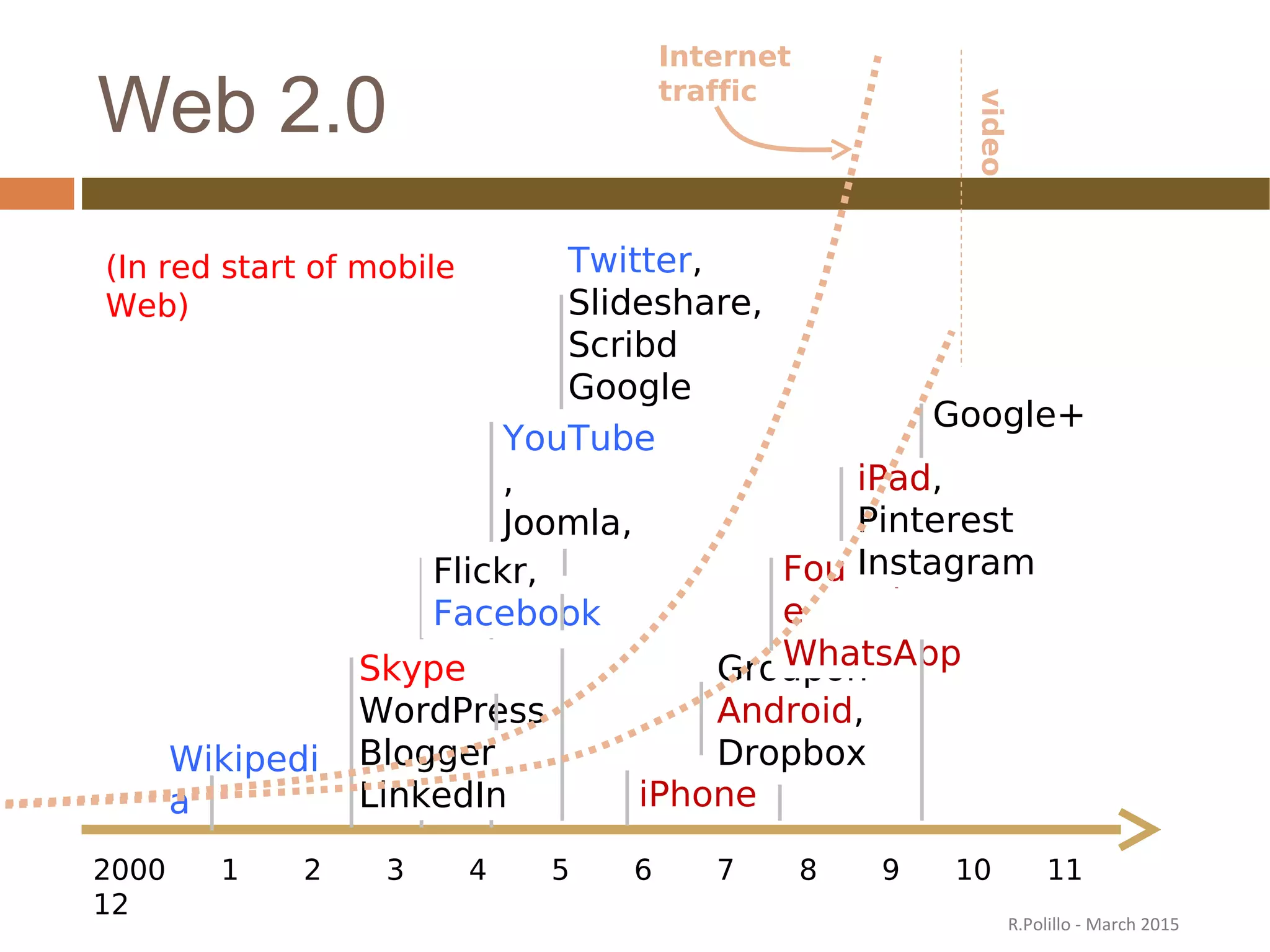
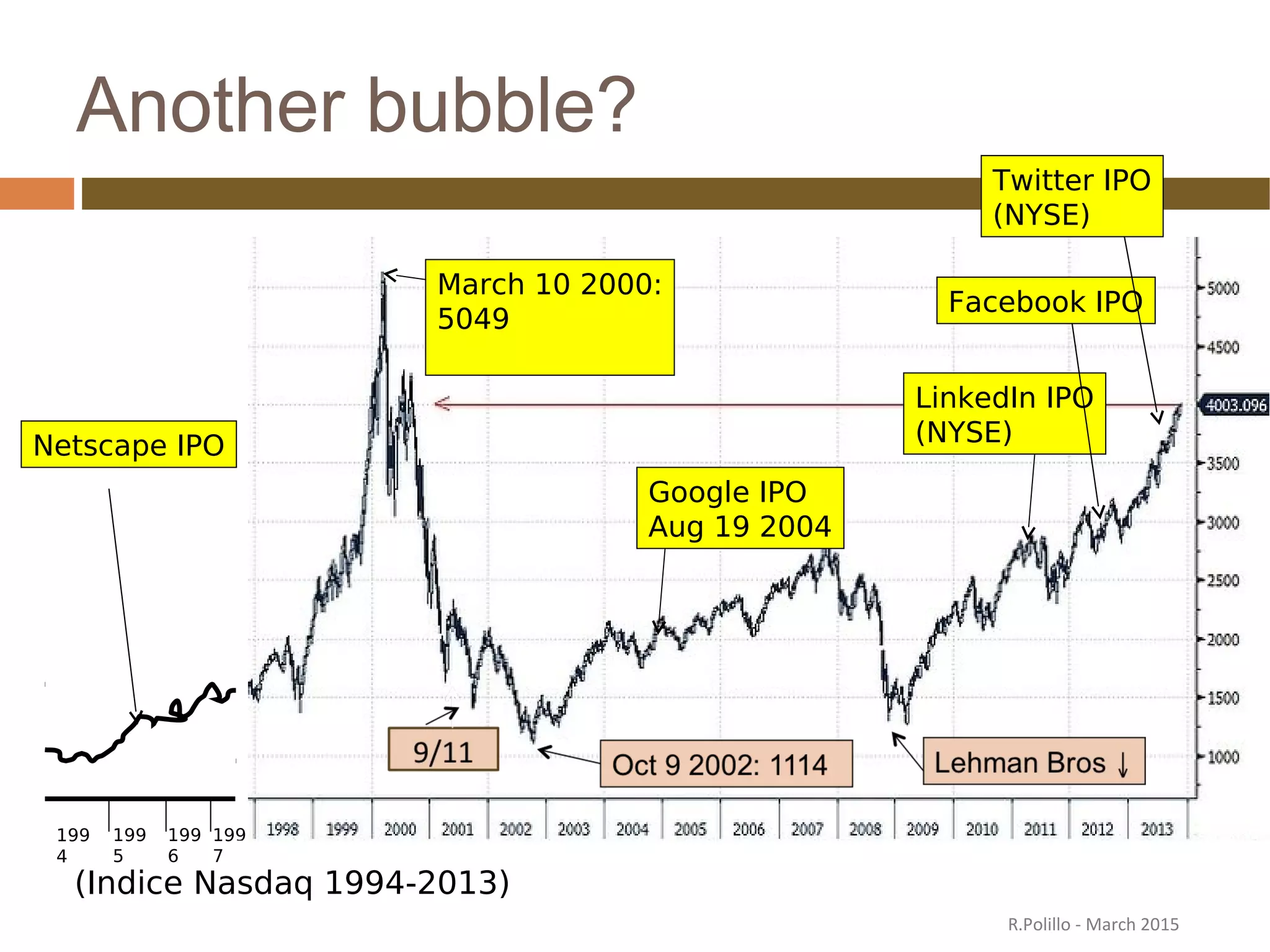
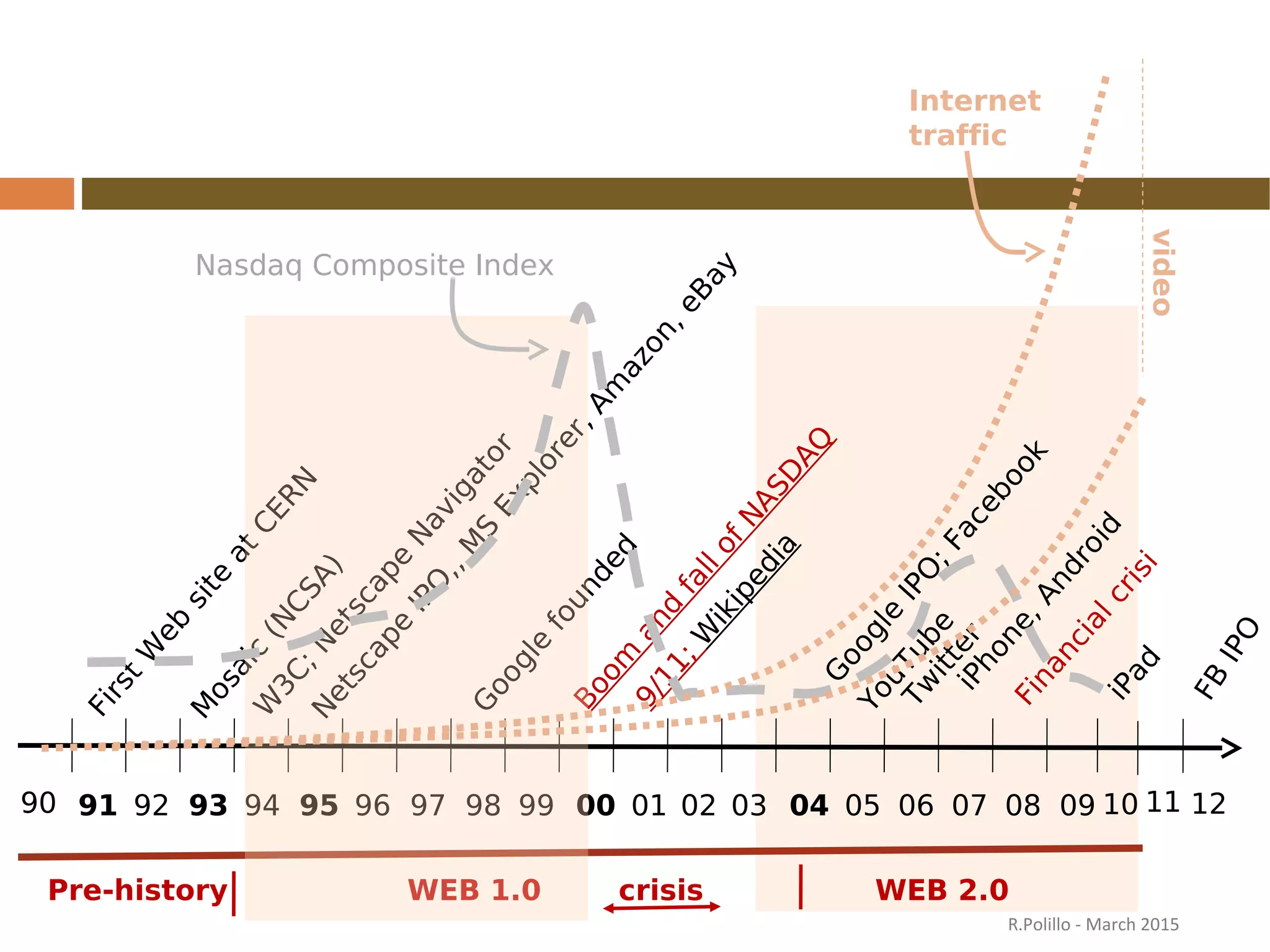
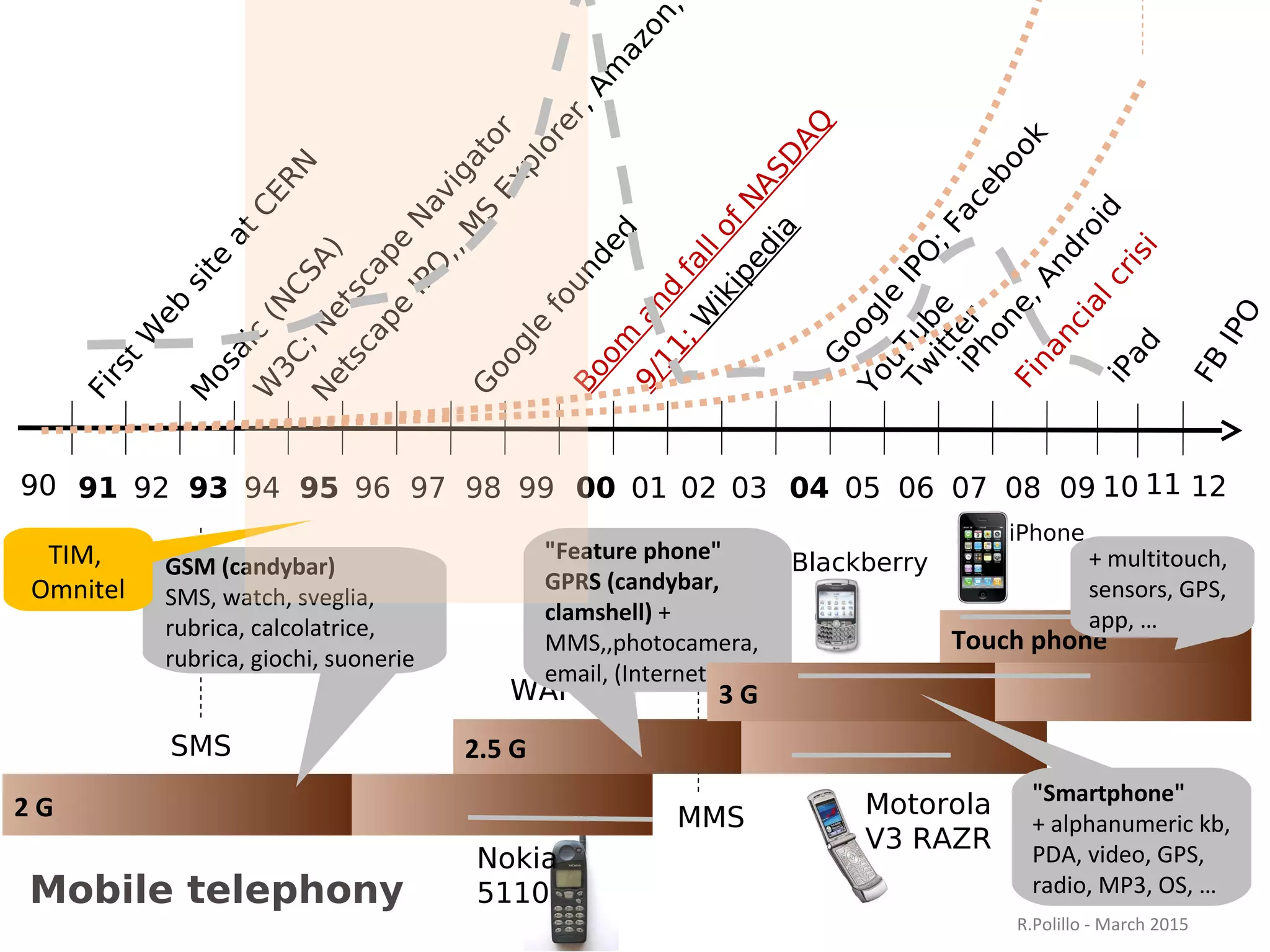
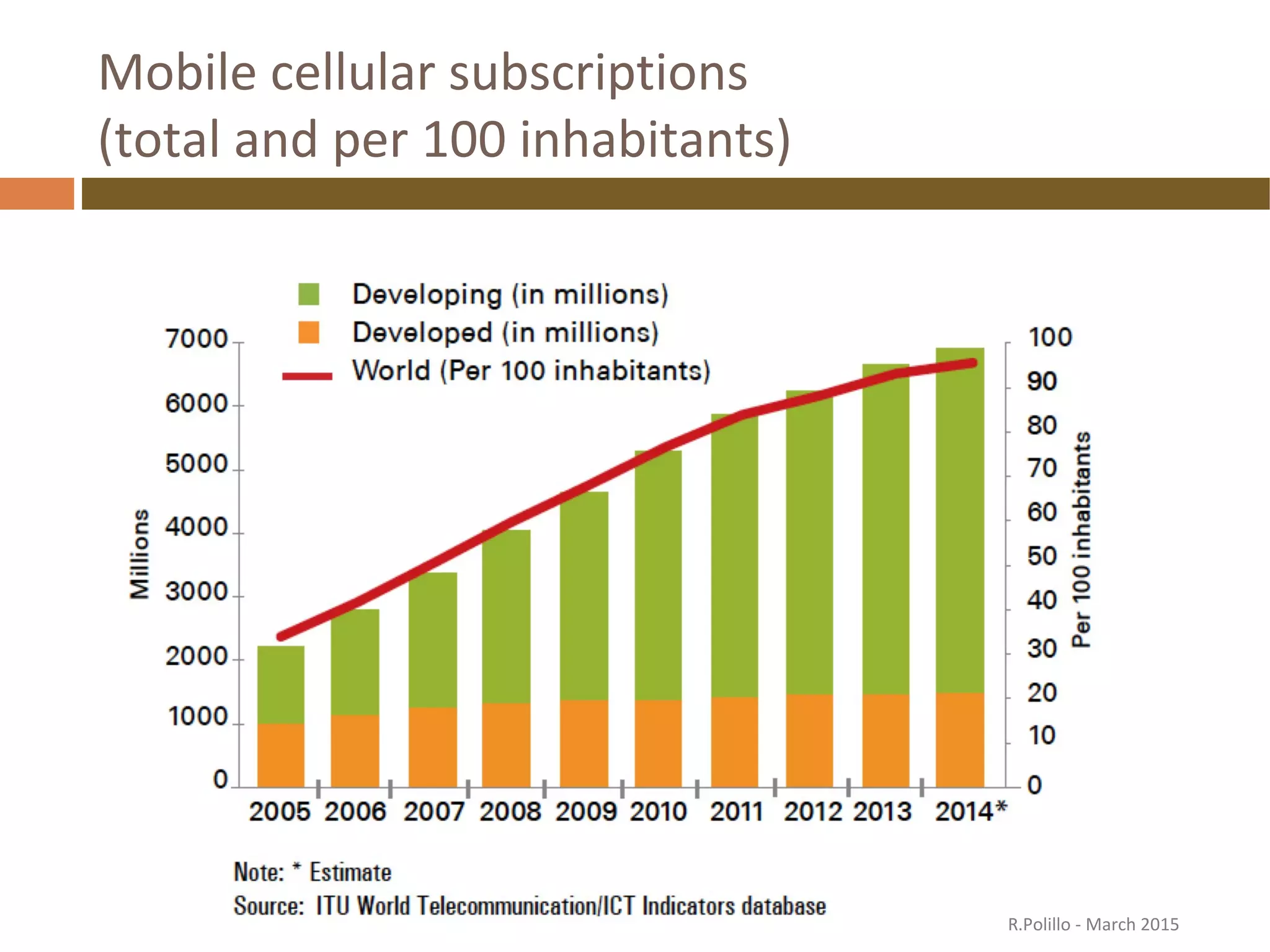
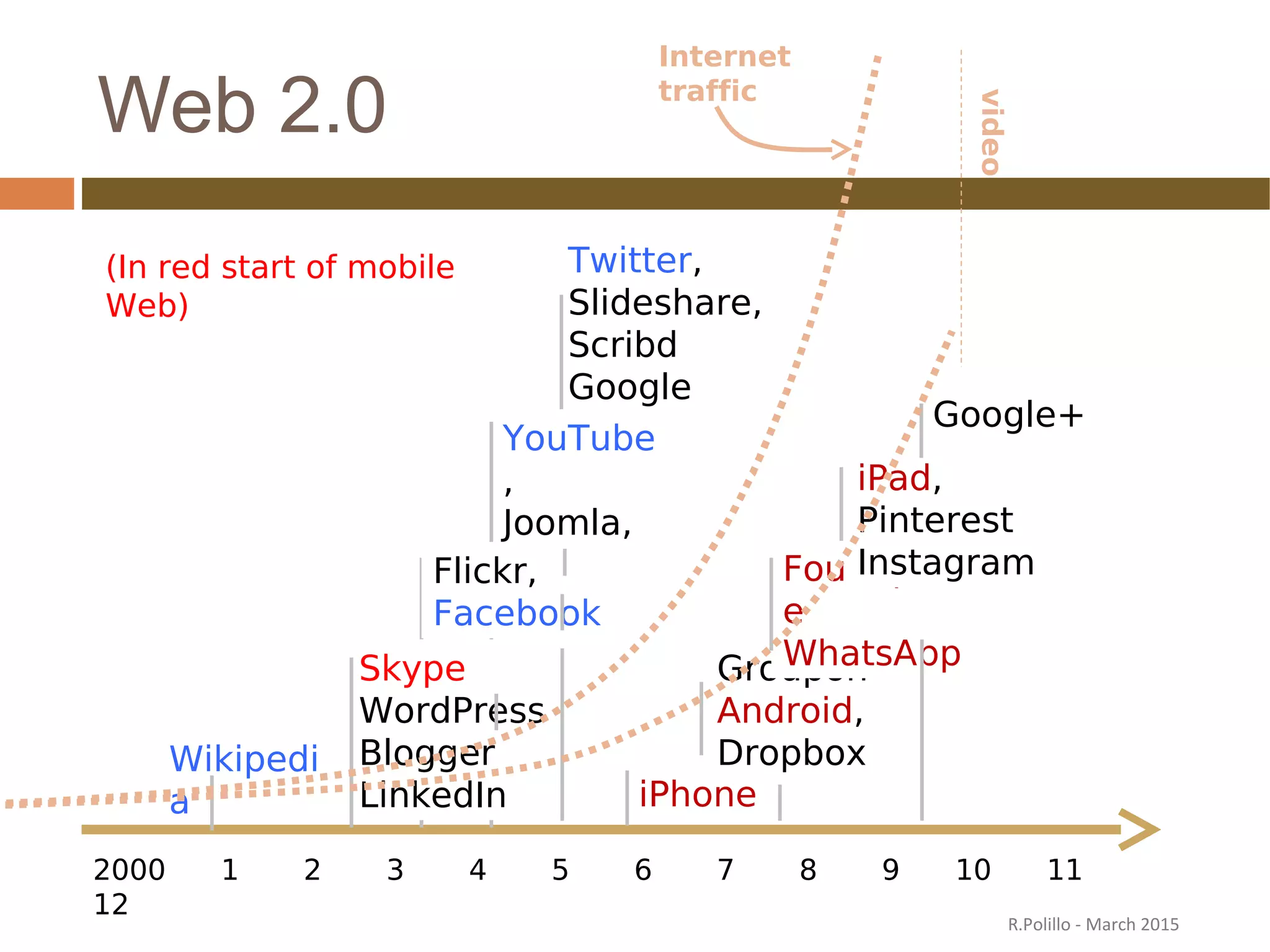
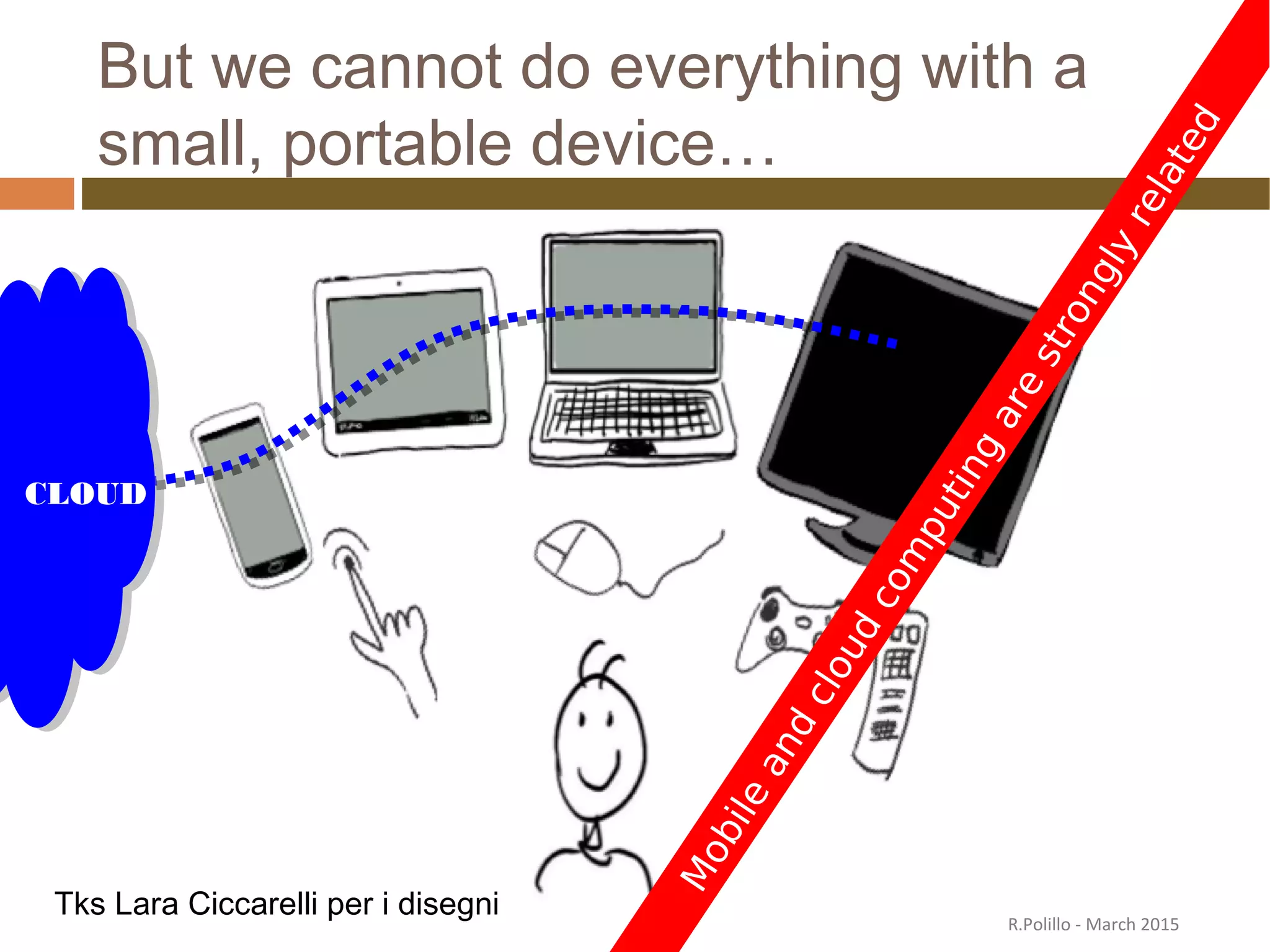
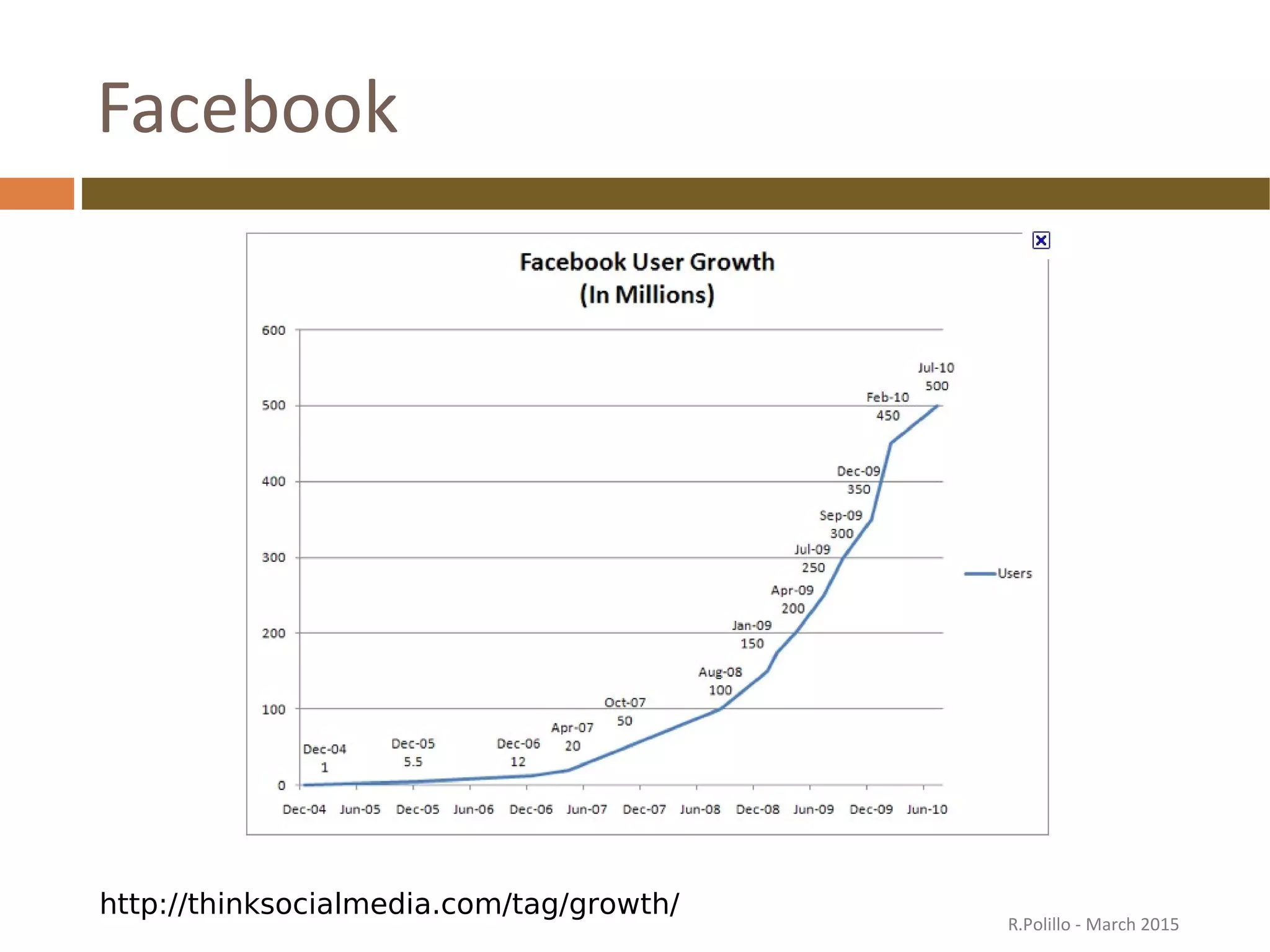
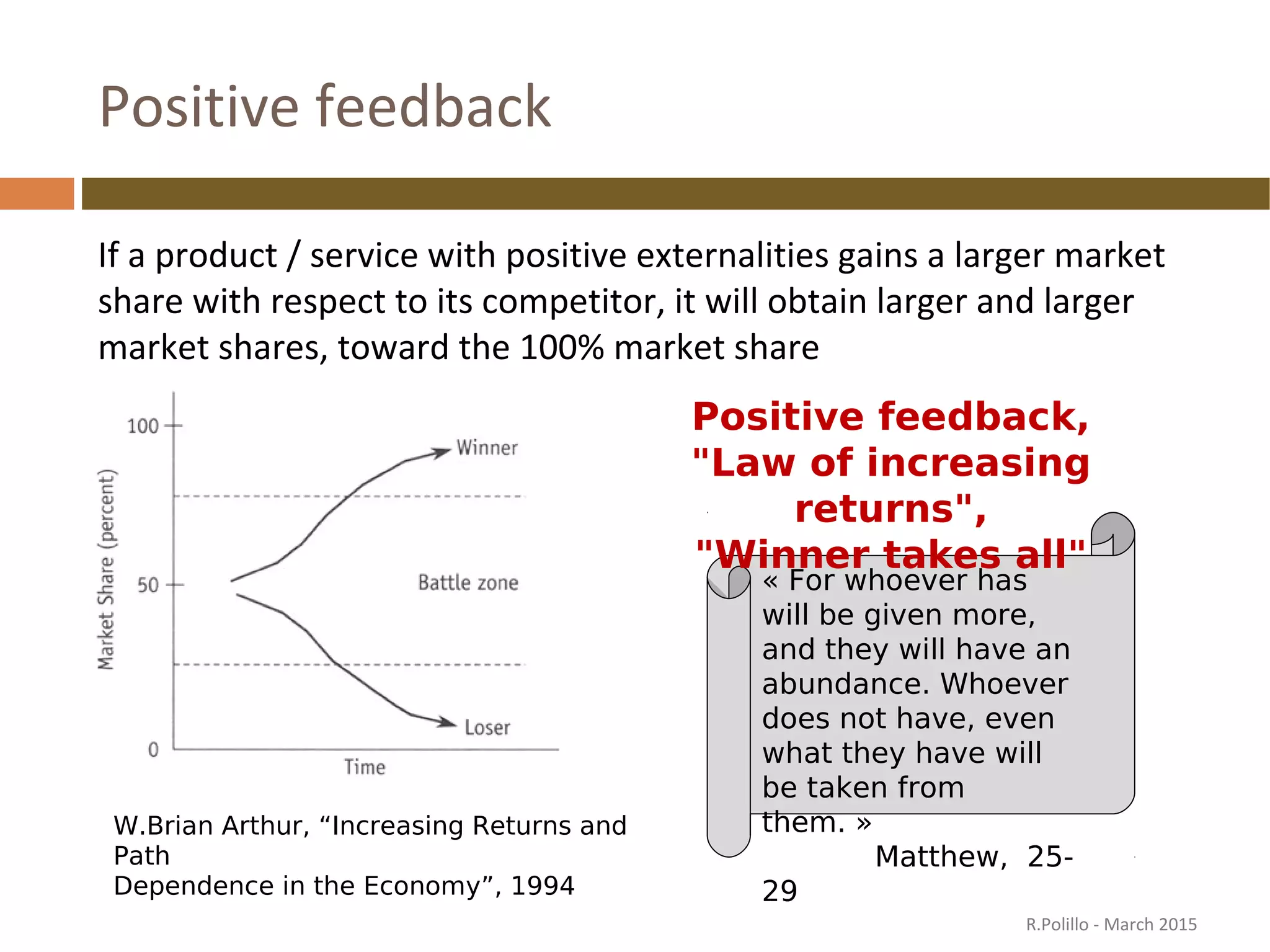
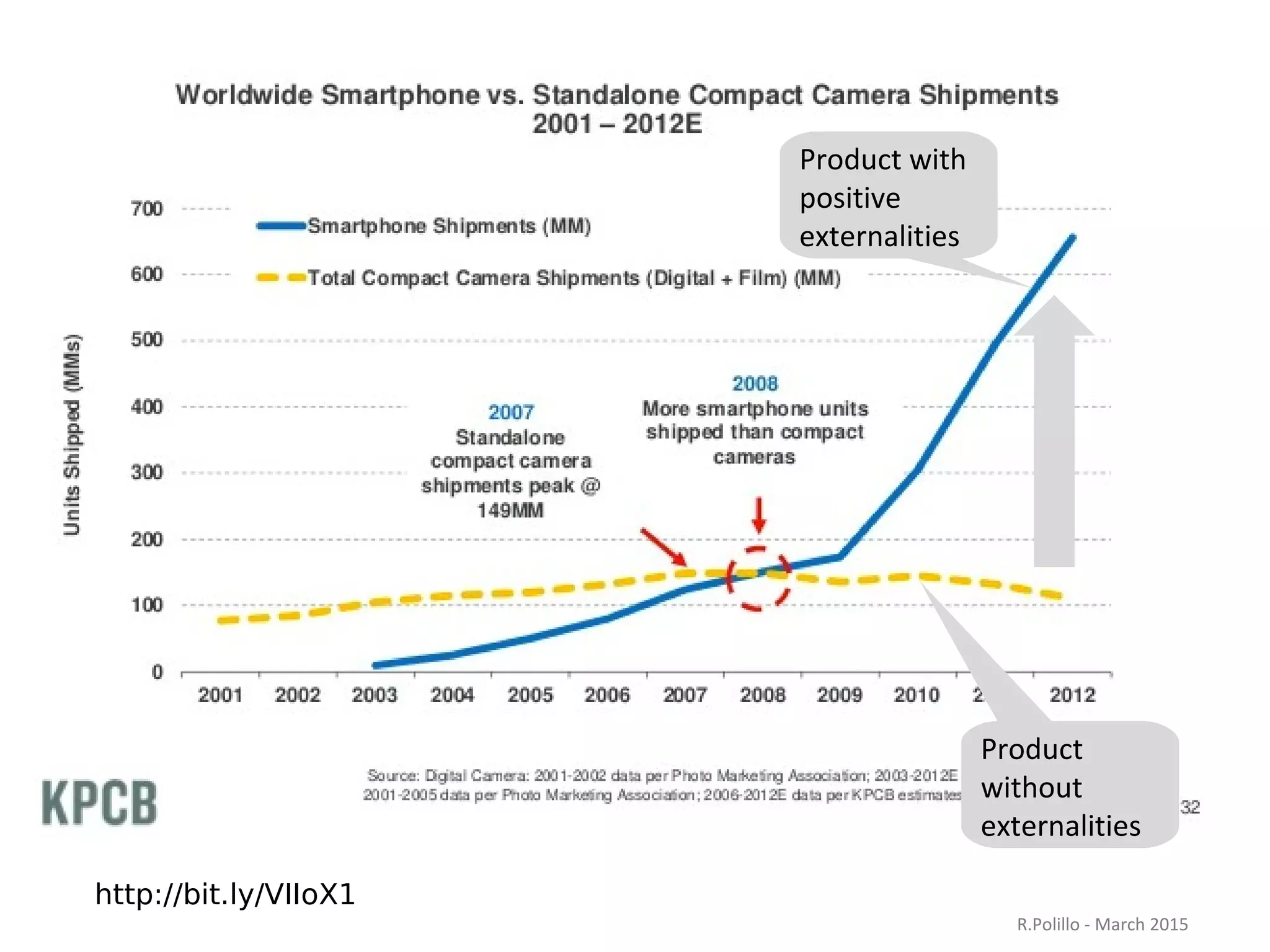
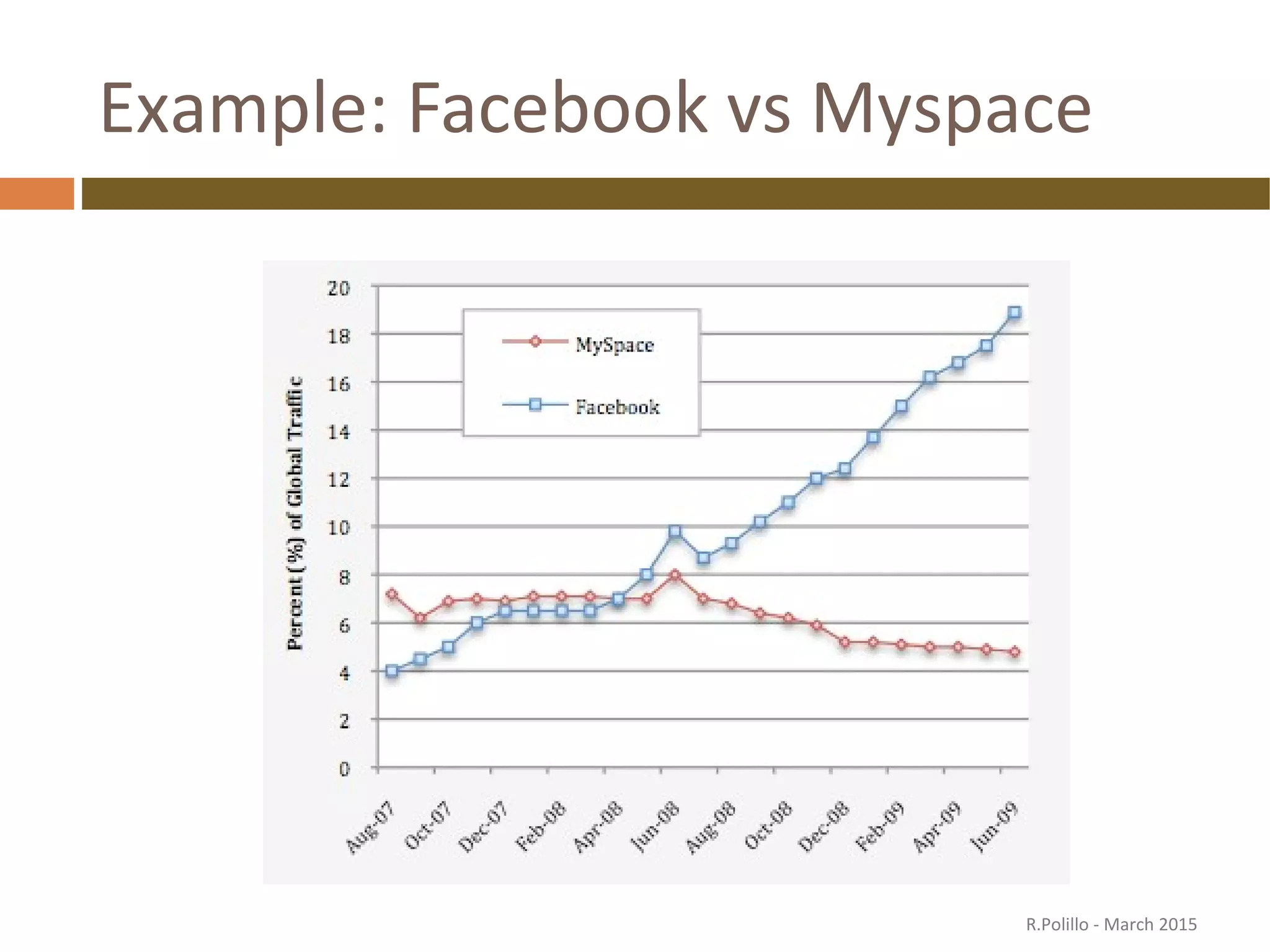
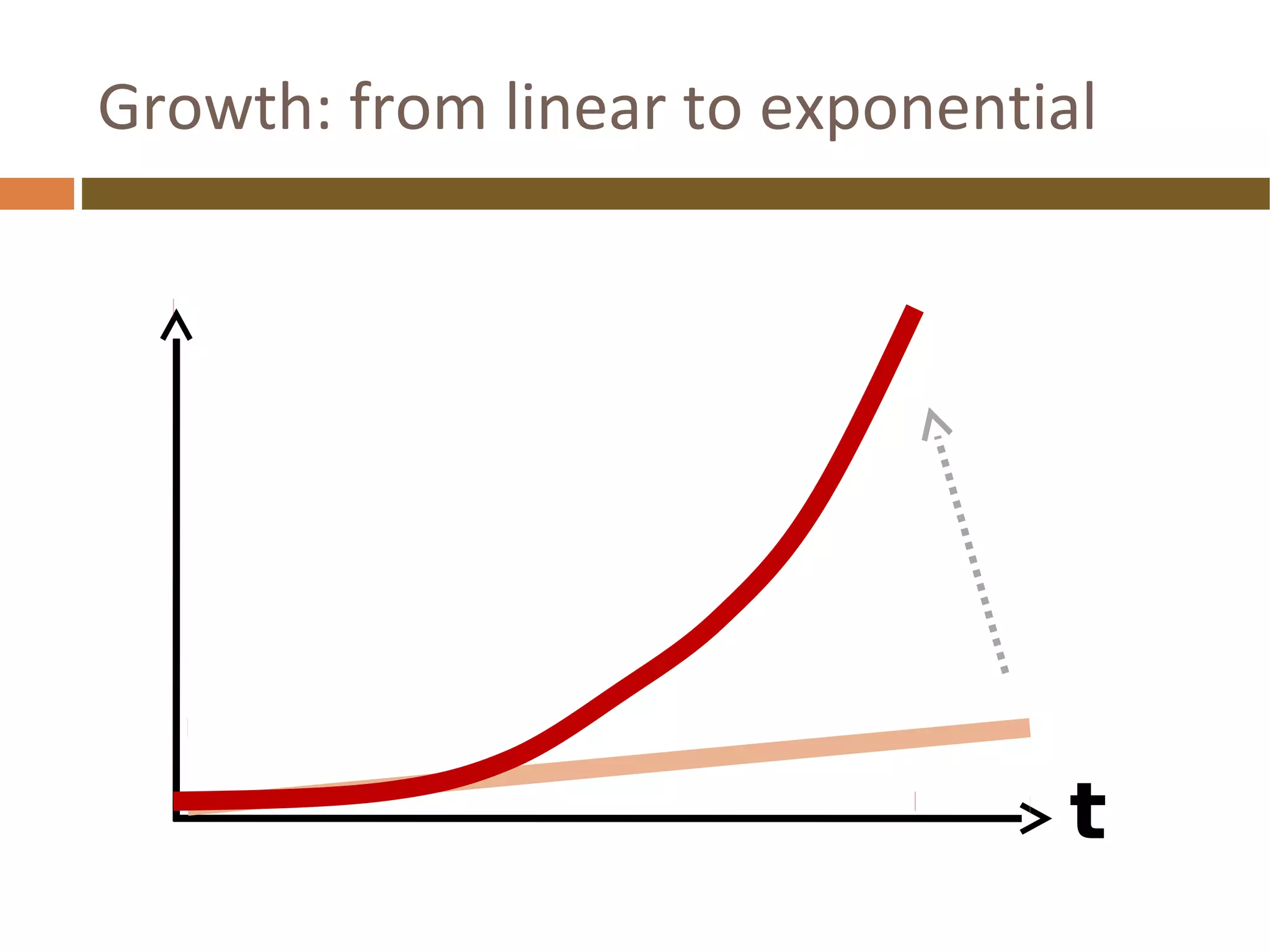
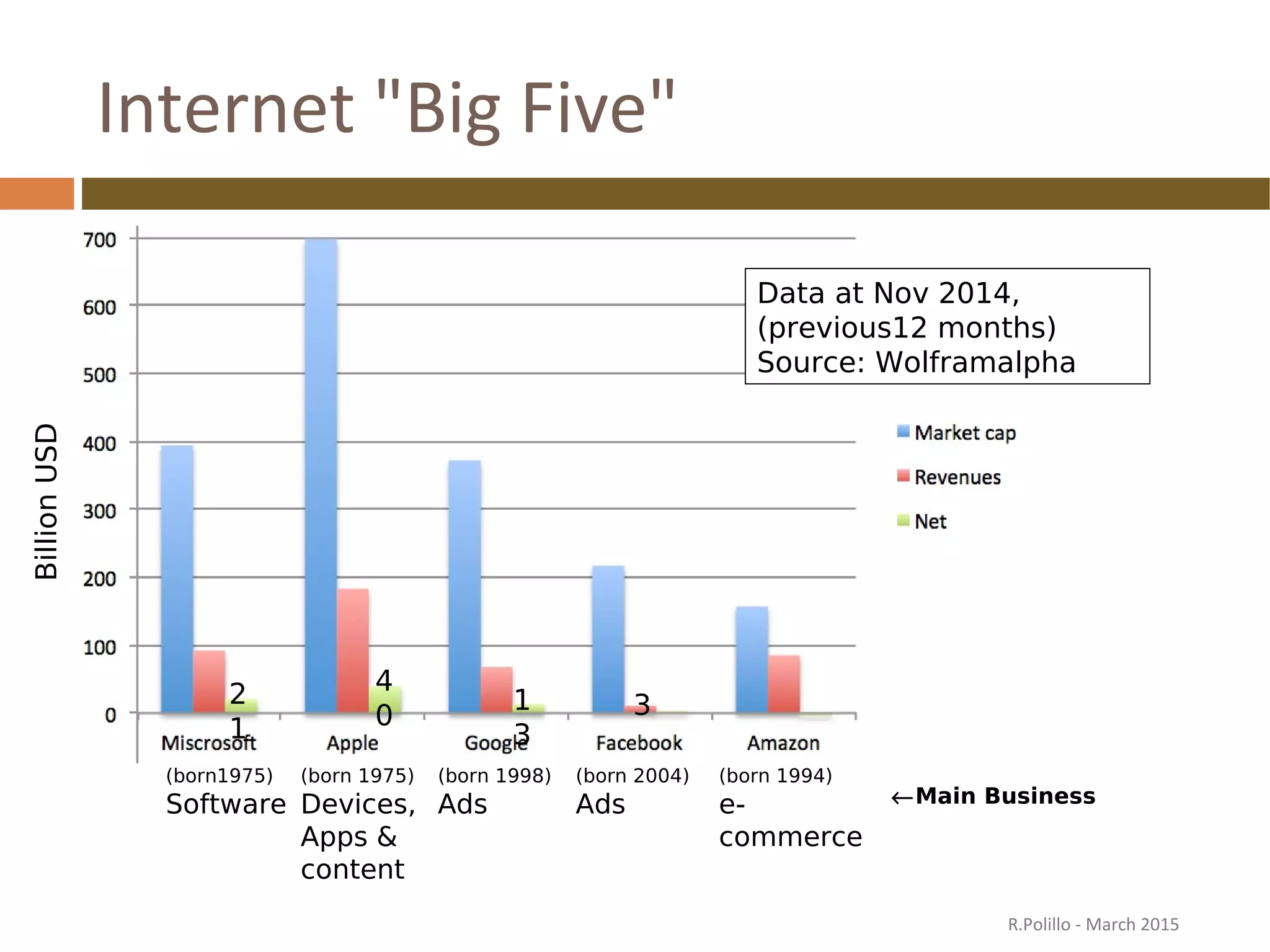
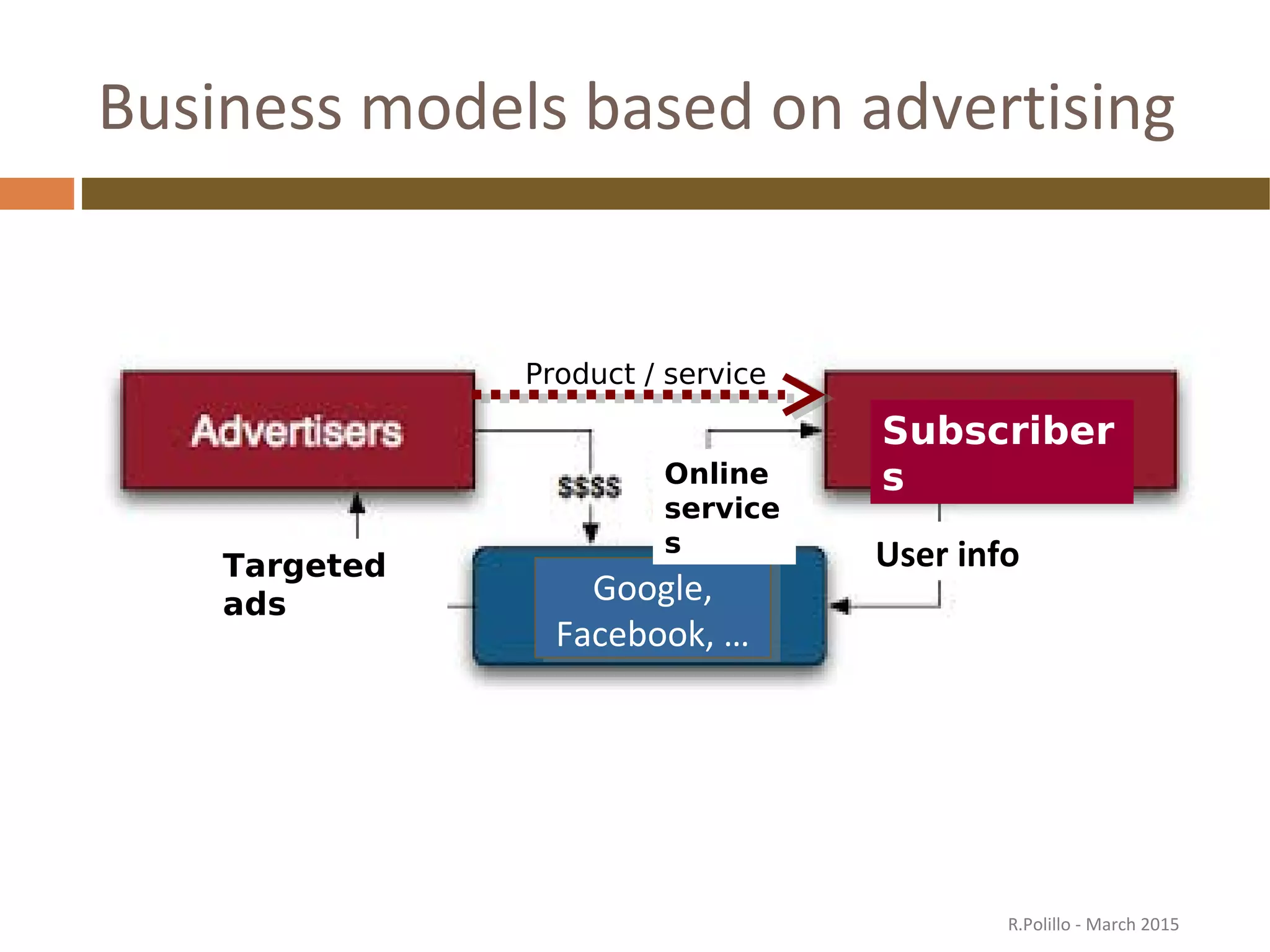
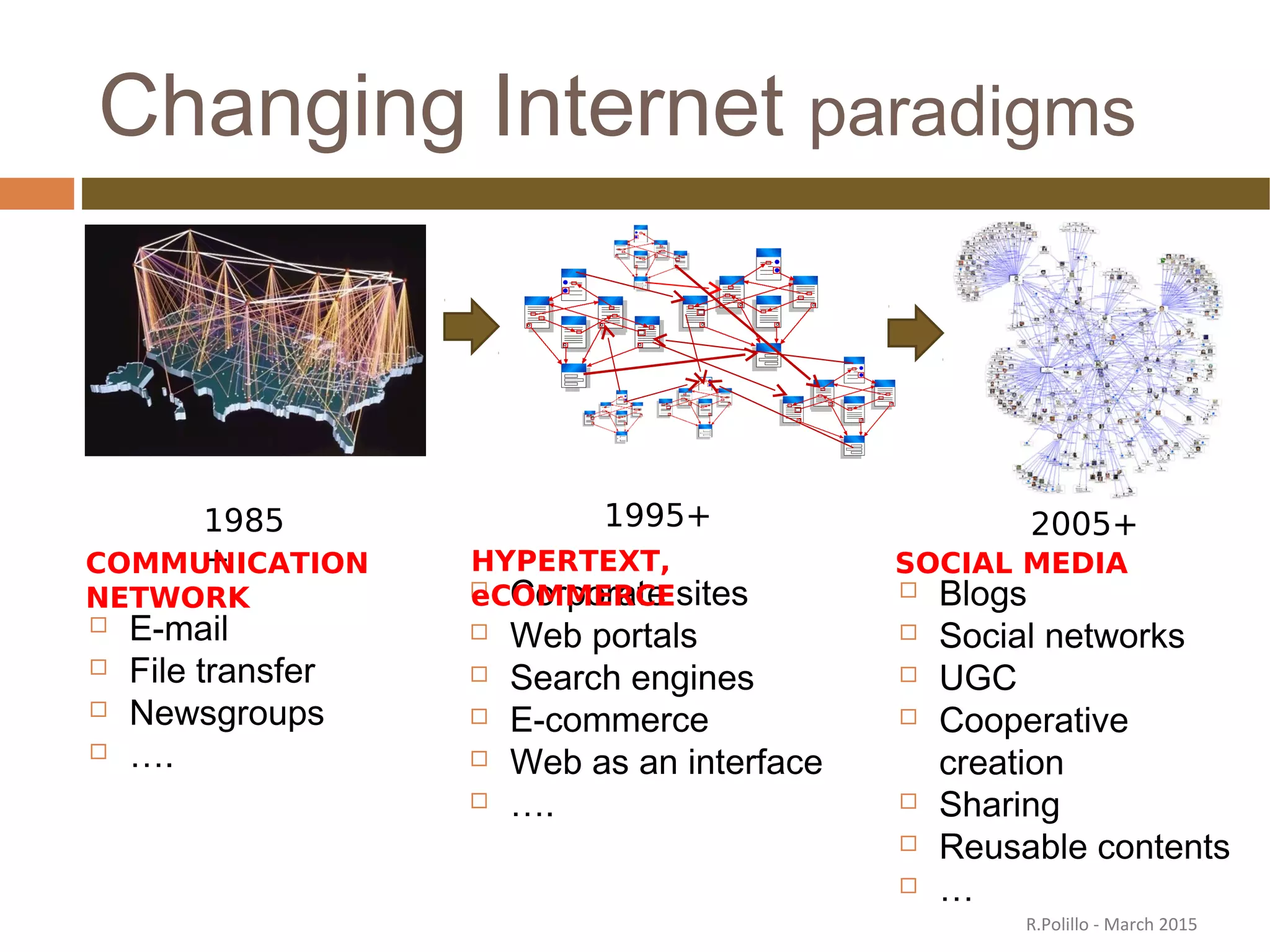
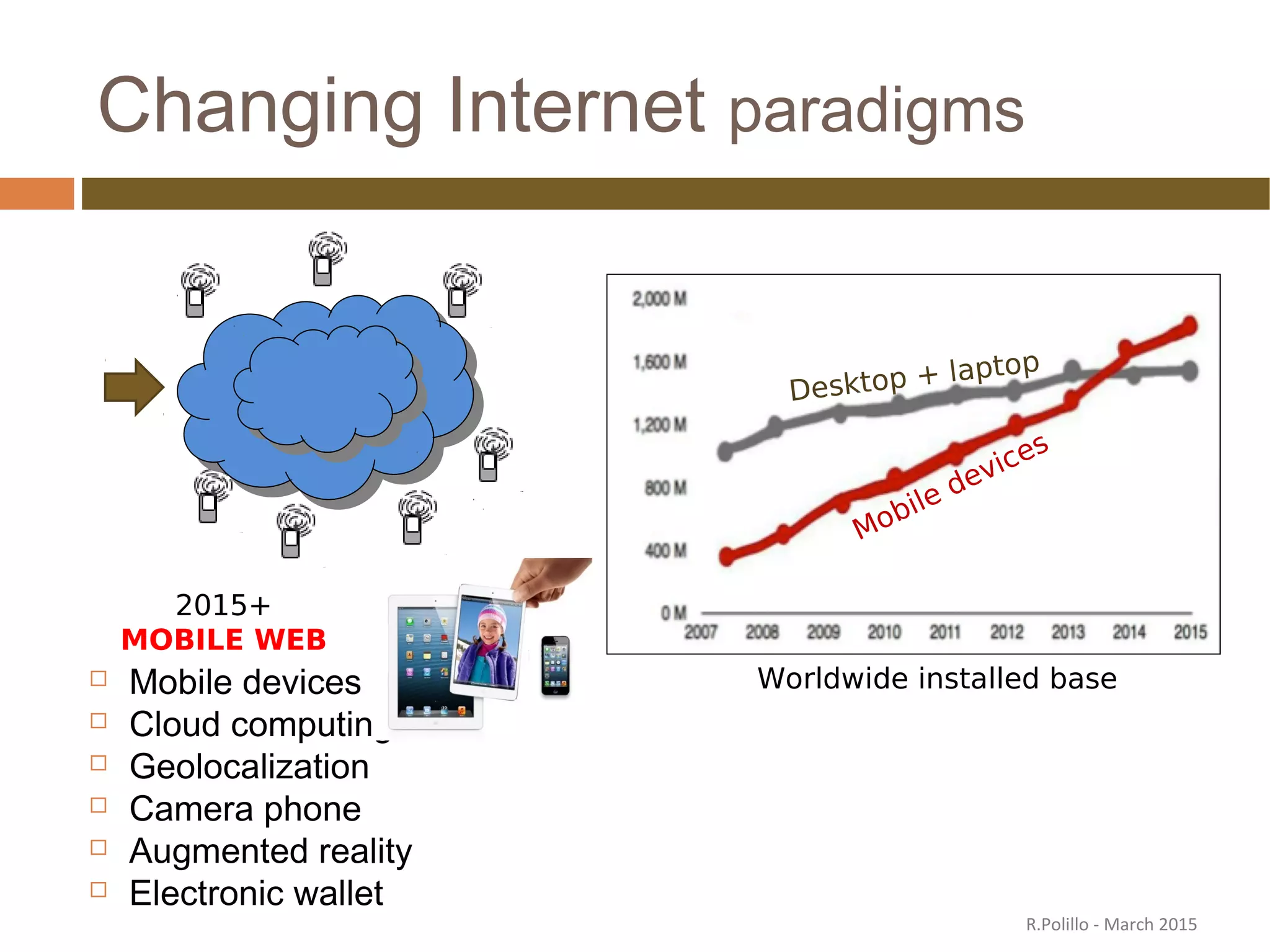
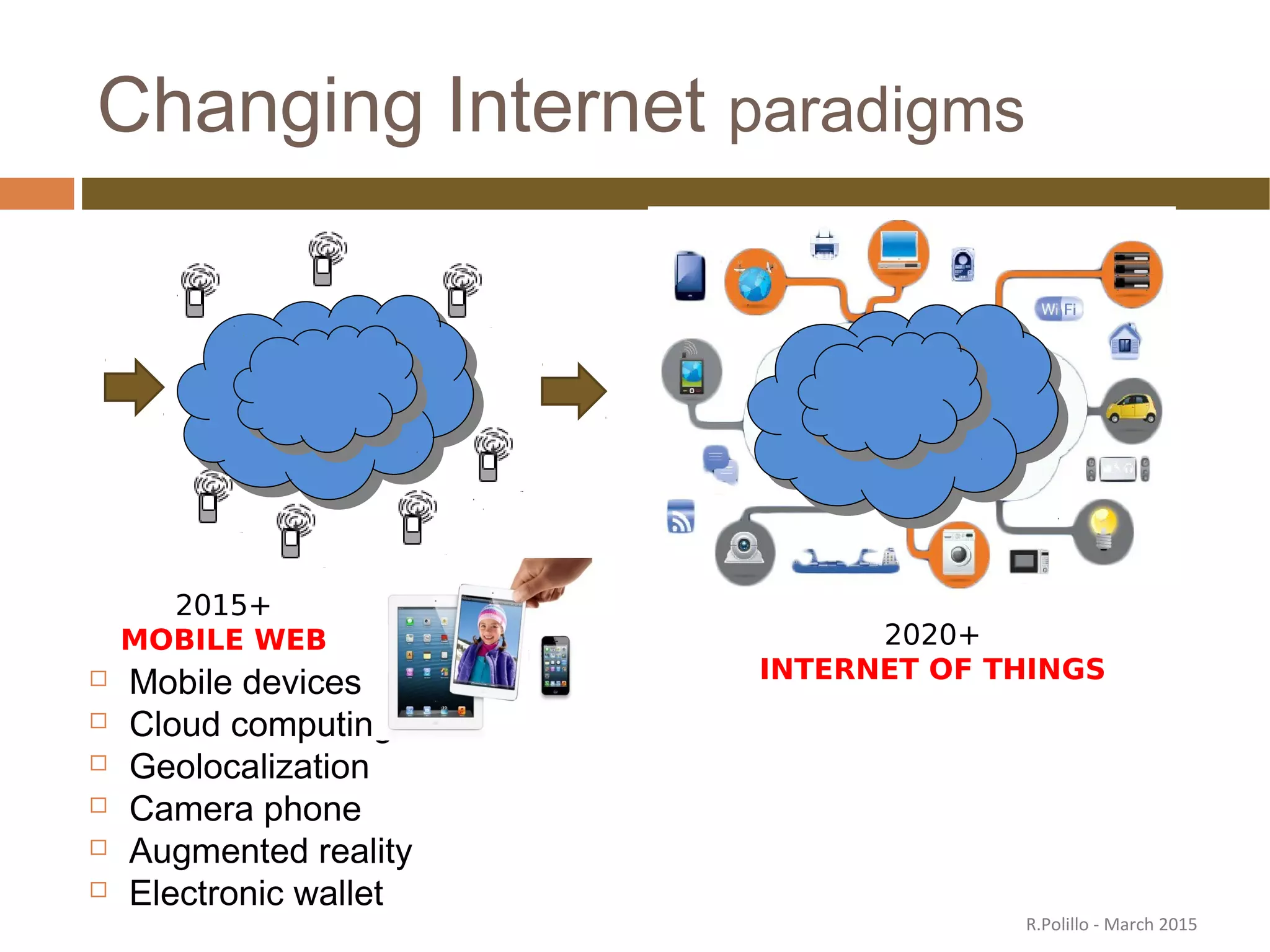
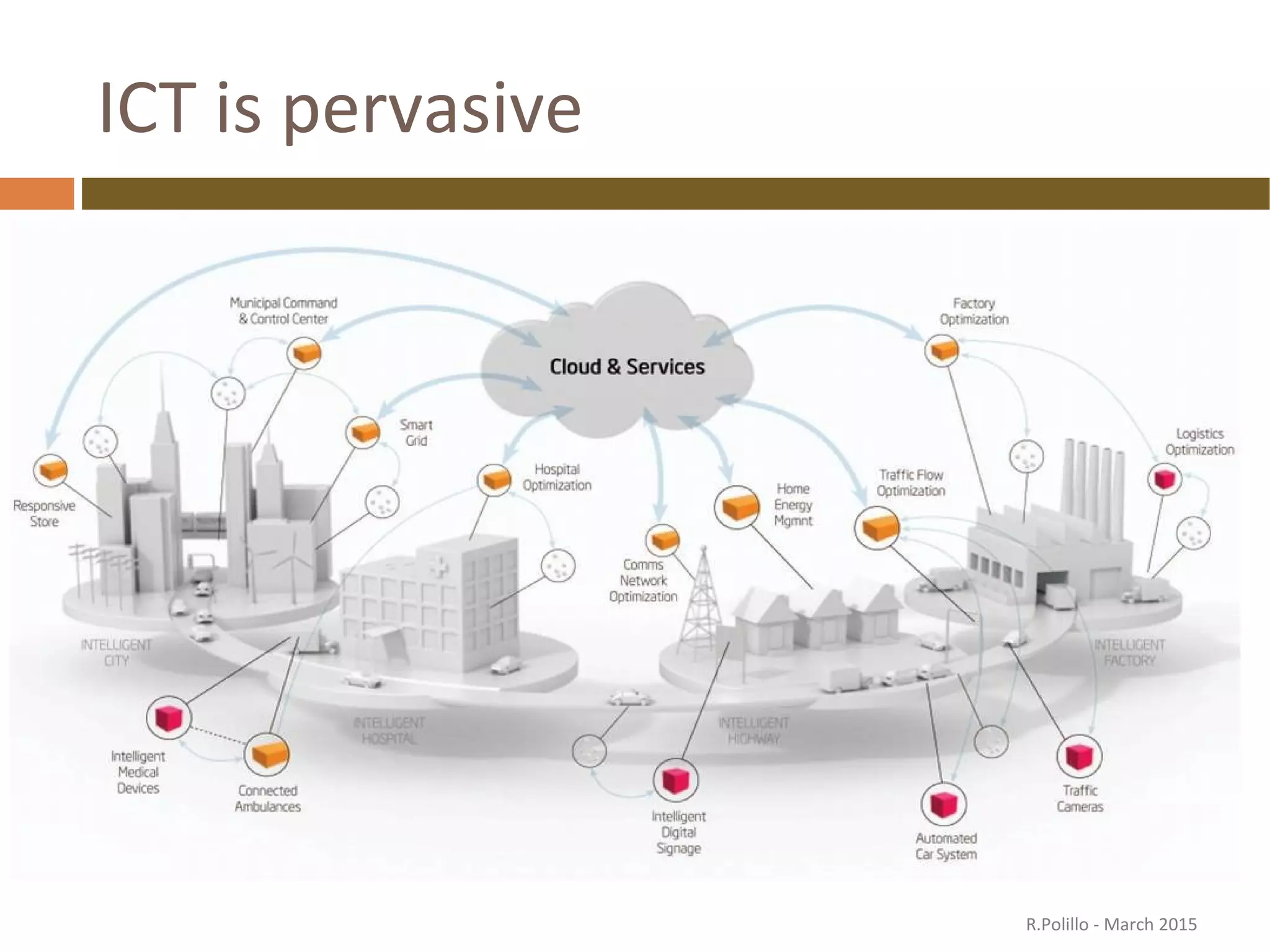
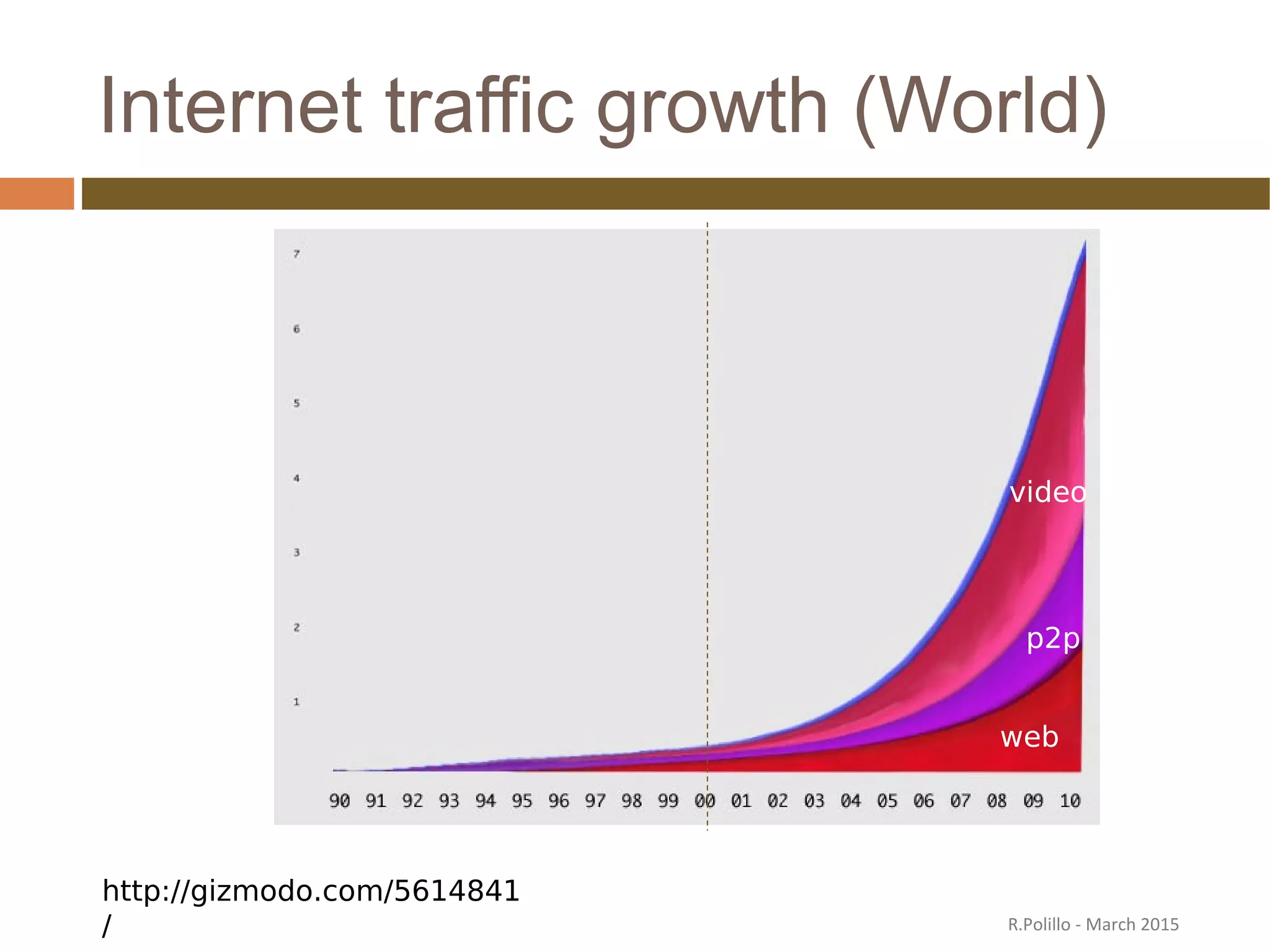
The document discusses the evolution of the web from its inception in 1991 to present-day developments, highlighting key milestones such as the transition from static web pages to dynamic social media platforms. It covers the major driving forces behind these changes, including technology, market trends, user behavior, and the impact of mobile devices and cloud computing. It also addresses potential future implications, such as issues regarding privacy, information reliability, and the effects of technological growth on employment.




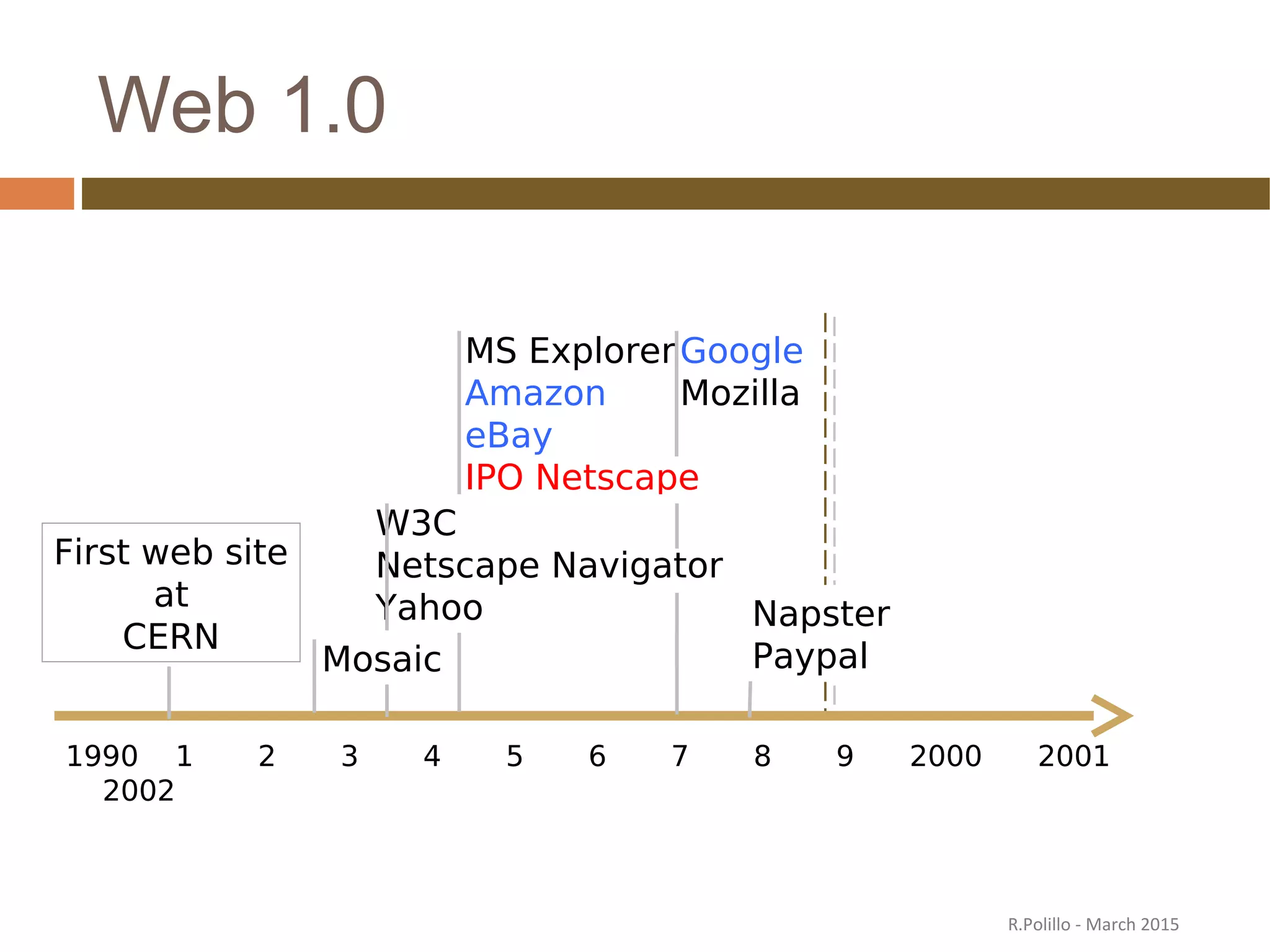

![Web 1.0 Typical applications
Corporate Web sites
Portals and search engines
eCommerce
[Corporate portals]
R.Polillo - March 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webevolution-urbeur-150323124030-conversion-gate01/75/The-Web-evolution-and-perspective-12-2048.jpg)