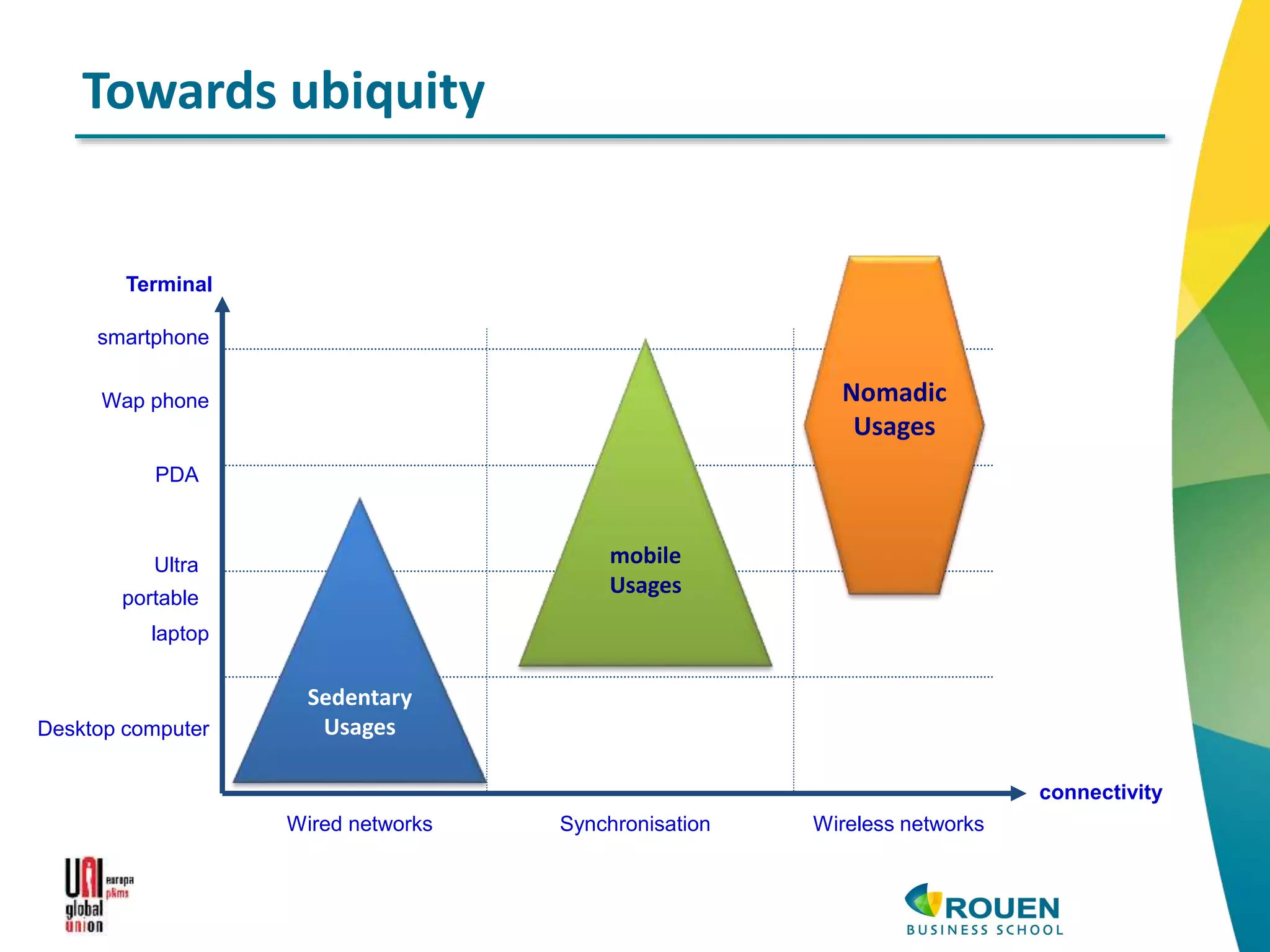
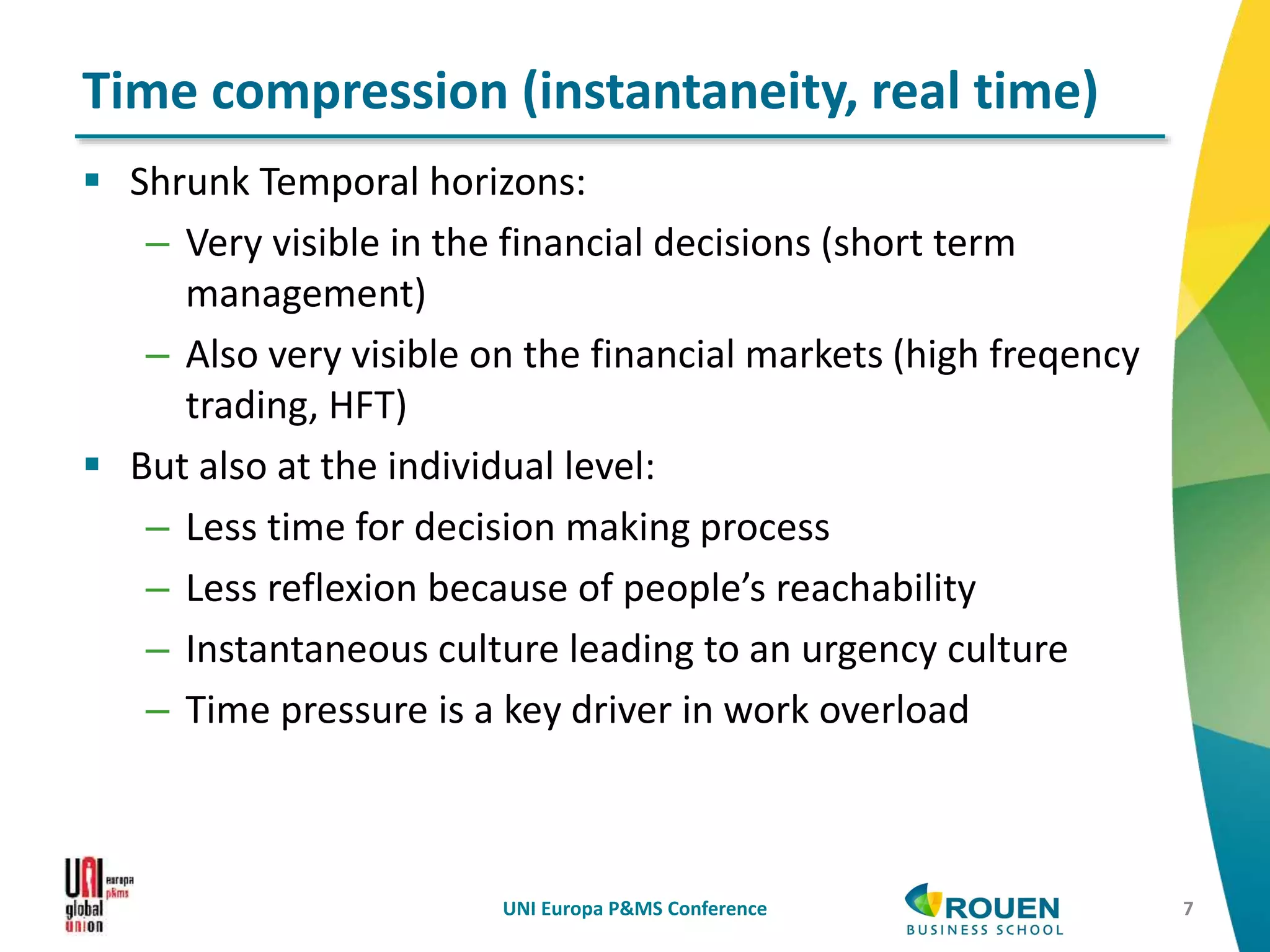
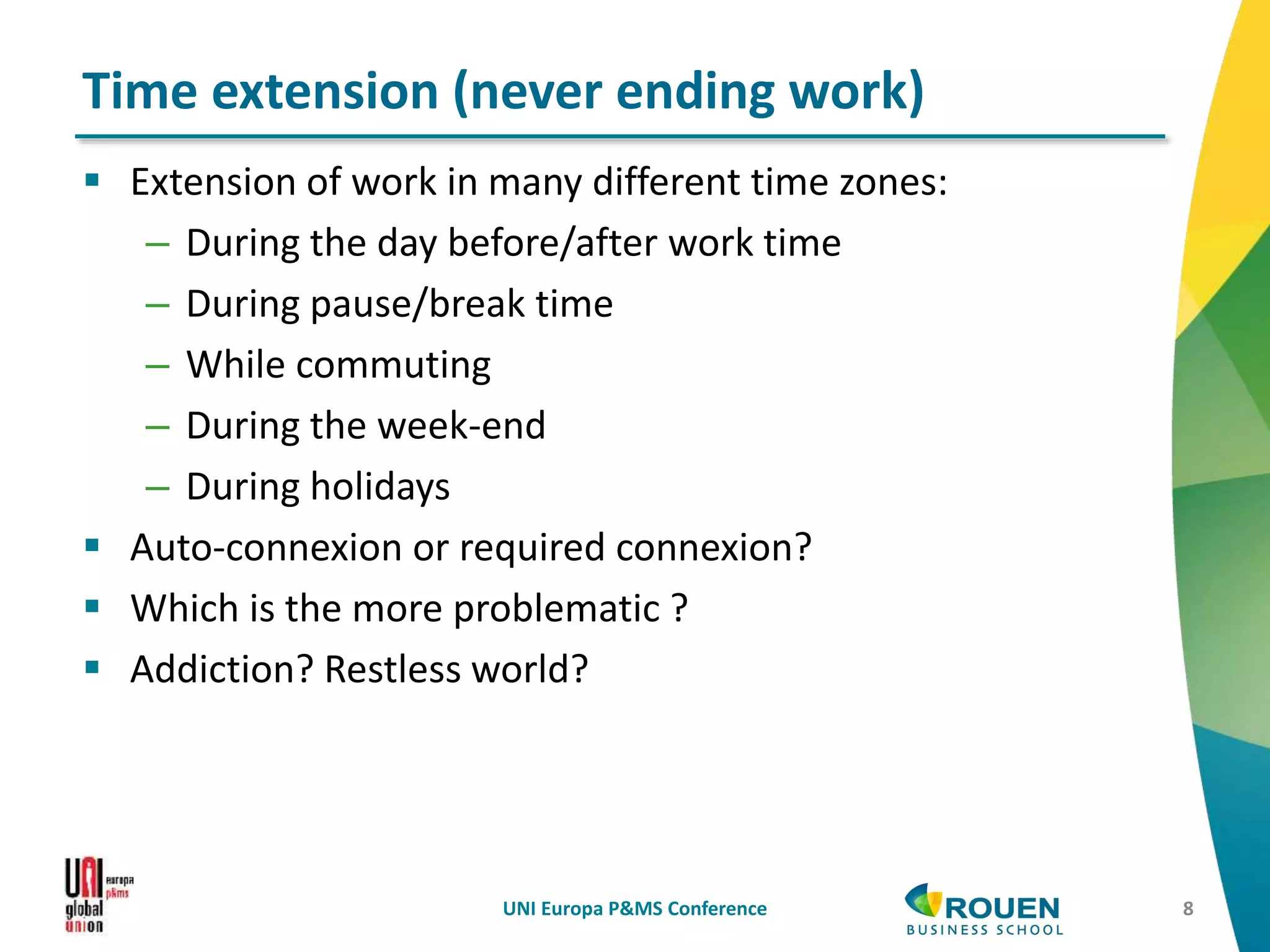
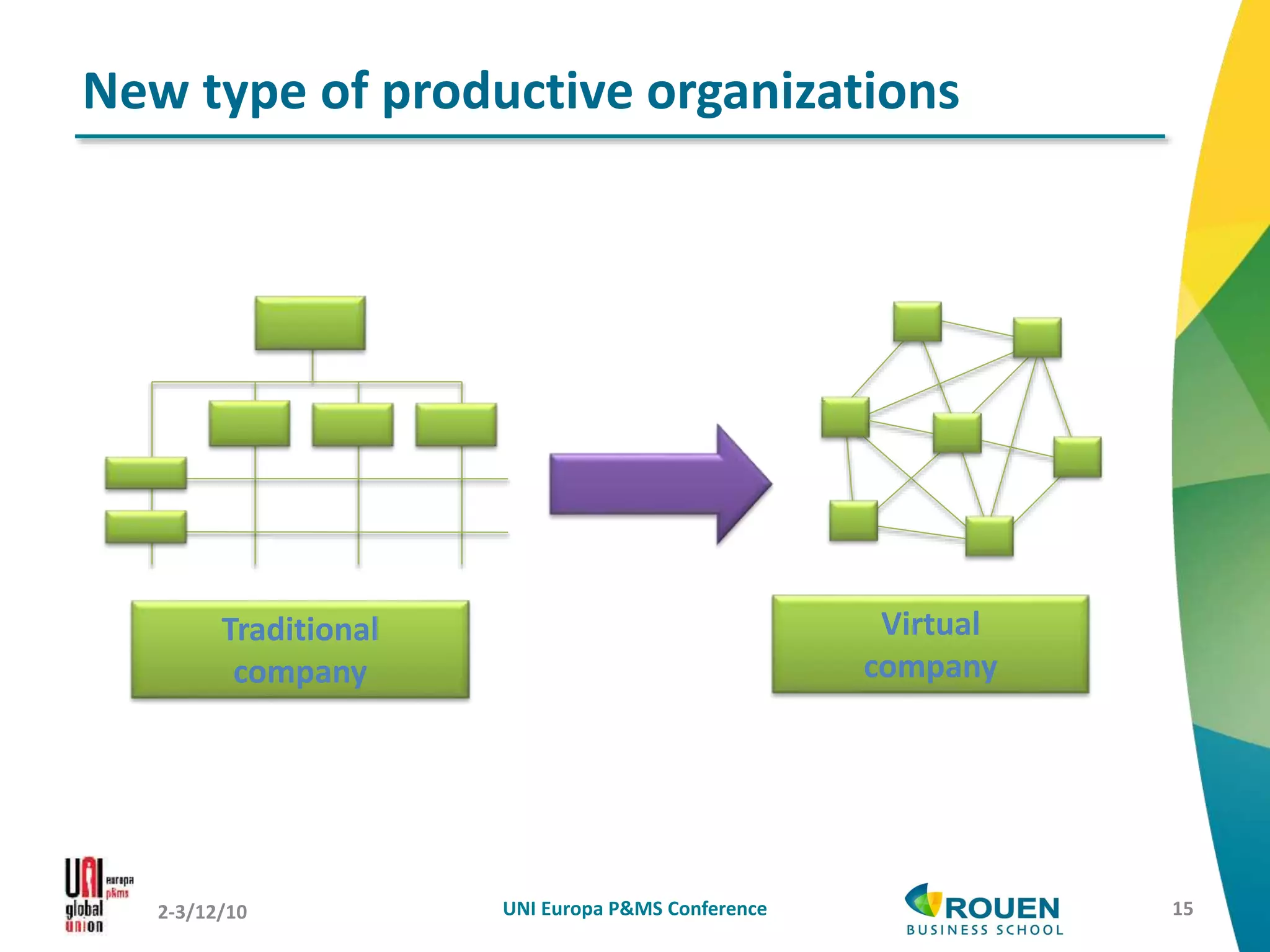
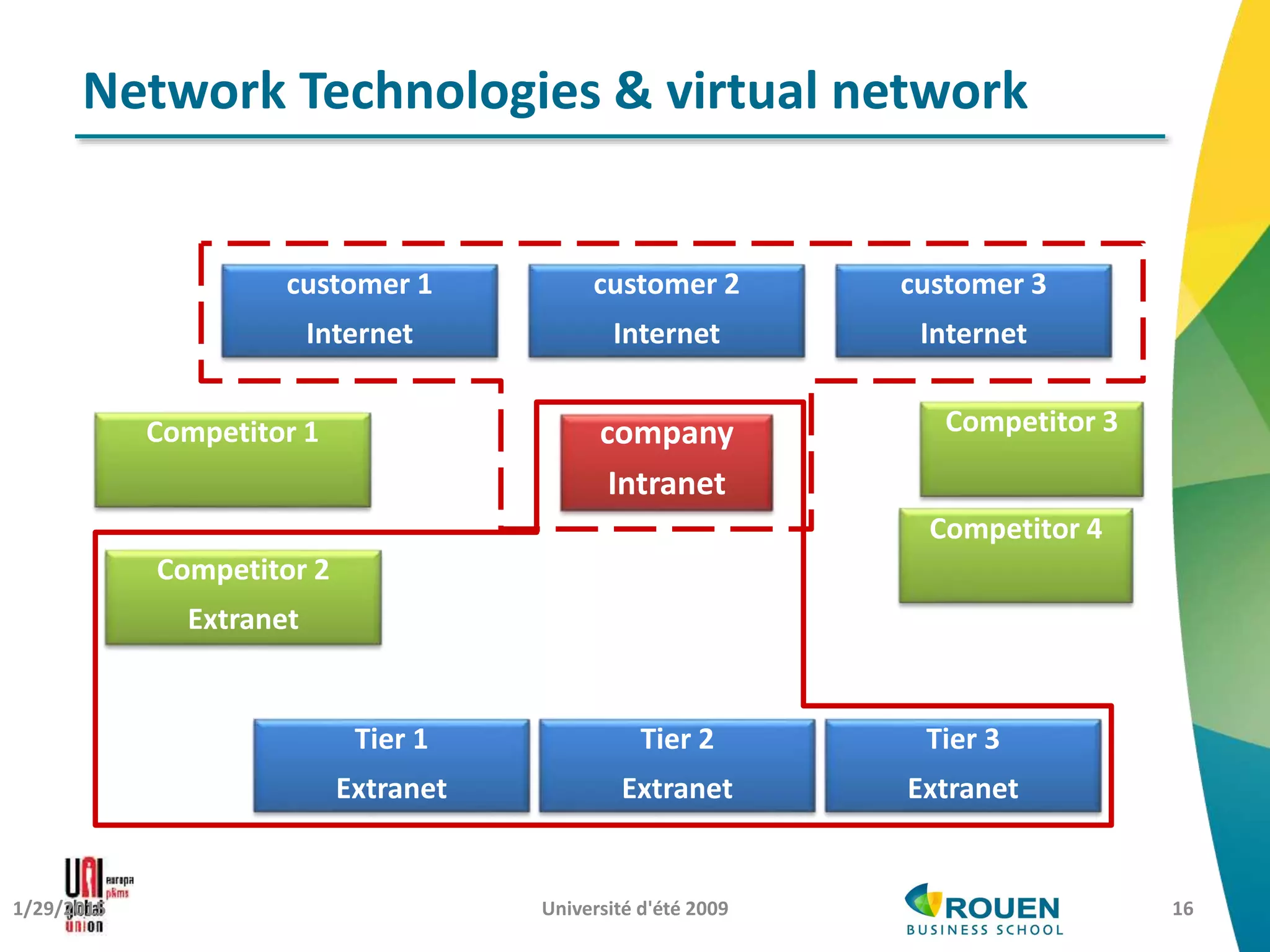
The document discusses how information and communication technologies (ICT) are reshaping the nature of work. It addresses both temporal and spatial effects of ICT. Temporally, ICT enables work to be done anytime and anywhere through increased connectivity and mobility. This has led to time compression with shorter decision-making windows, as well as time extension as work bleeds into personal hours. Spatially, ICT has driven communication costs to near zero, reinventing the local and global. Distance is compressed but not eliminated. ICT also enables new types of virtual and networked organizations that access distributed resources through electronic networks rather than relying primarily on internal physical resources. This digital revolution necessitates rethinking regulations around work to account for changes in