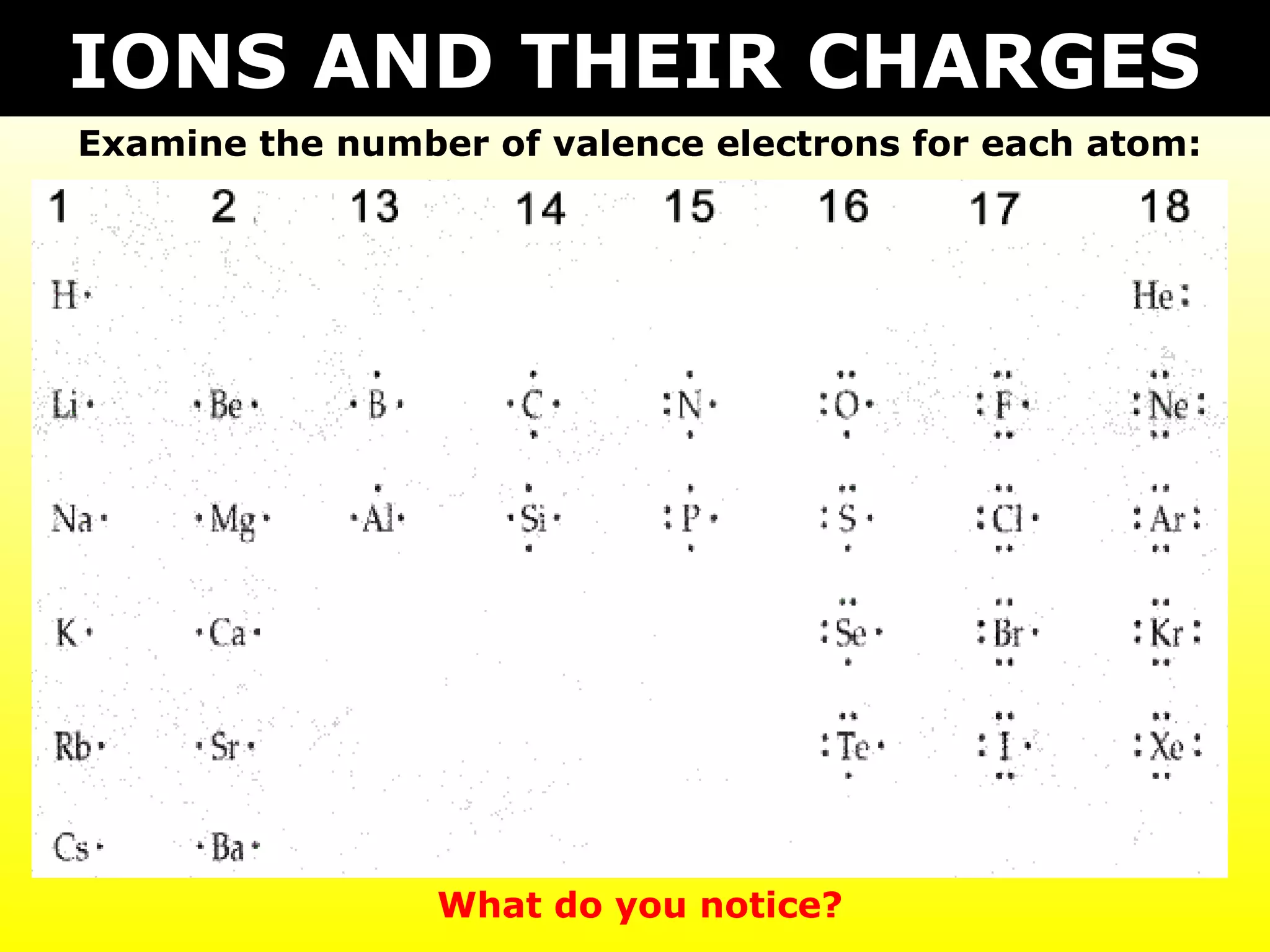
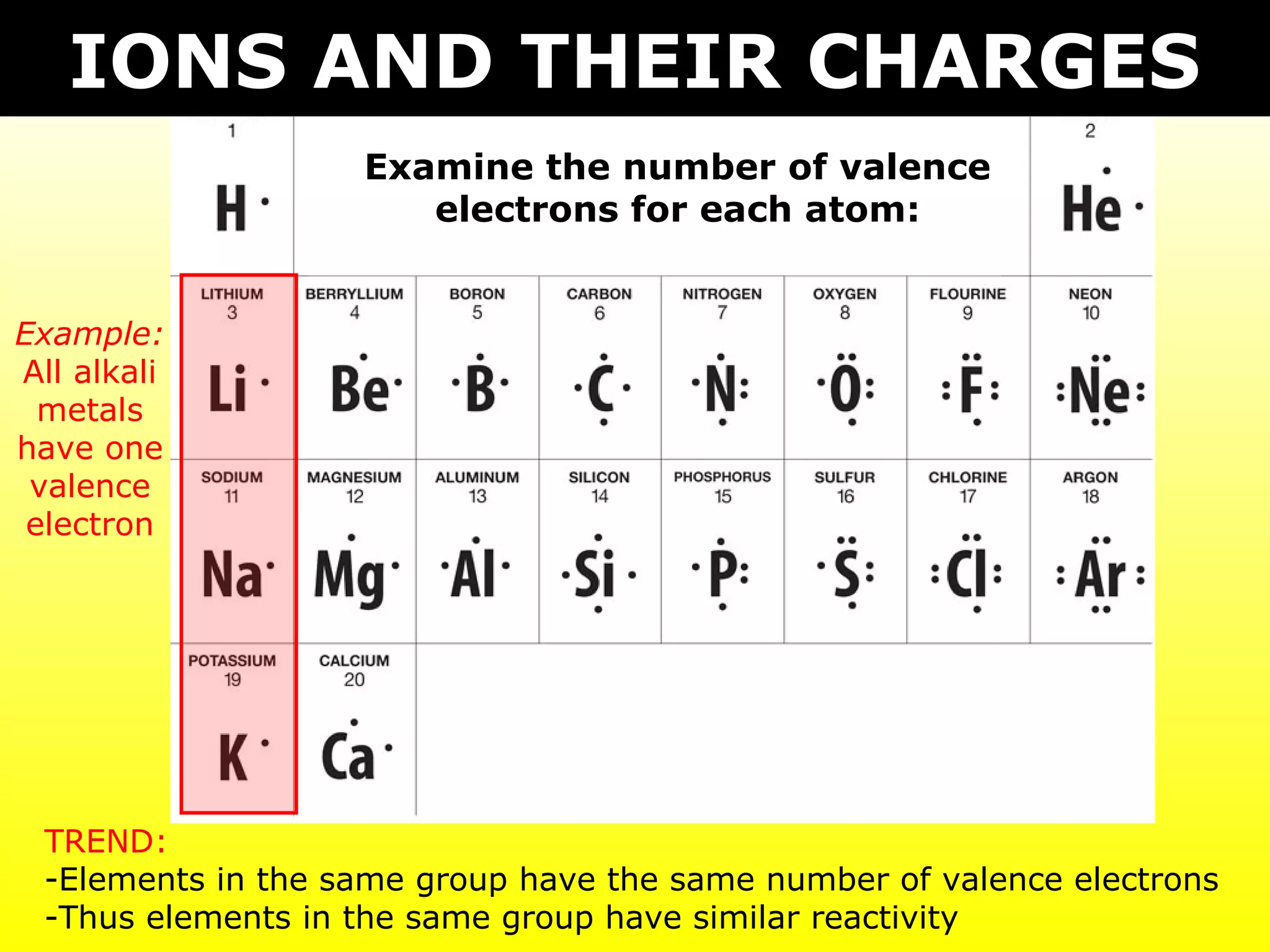
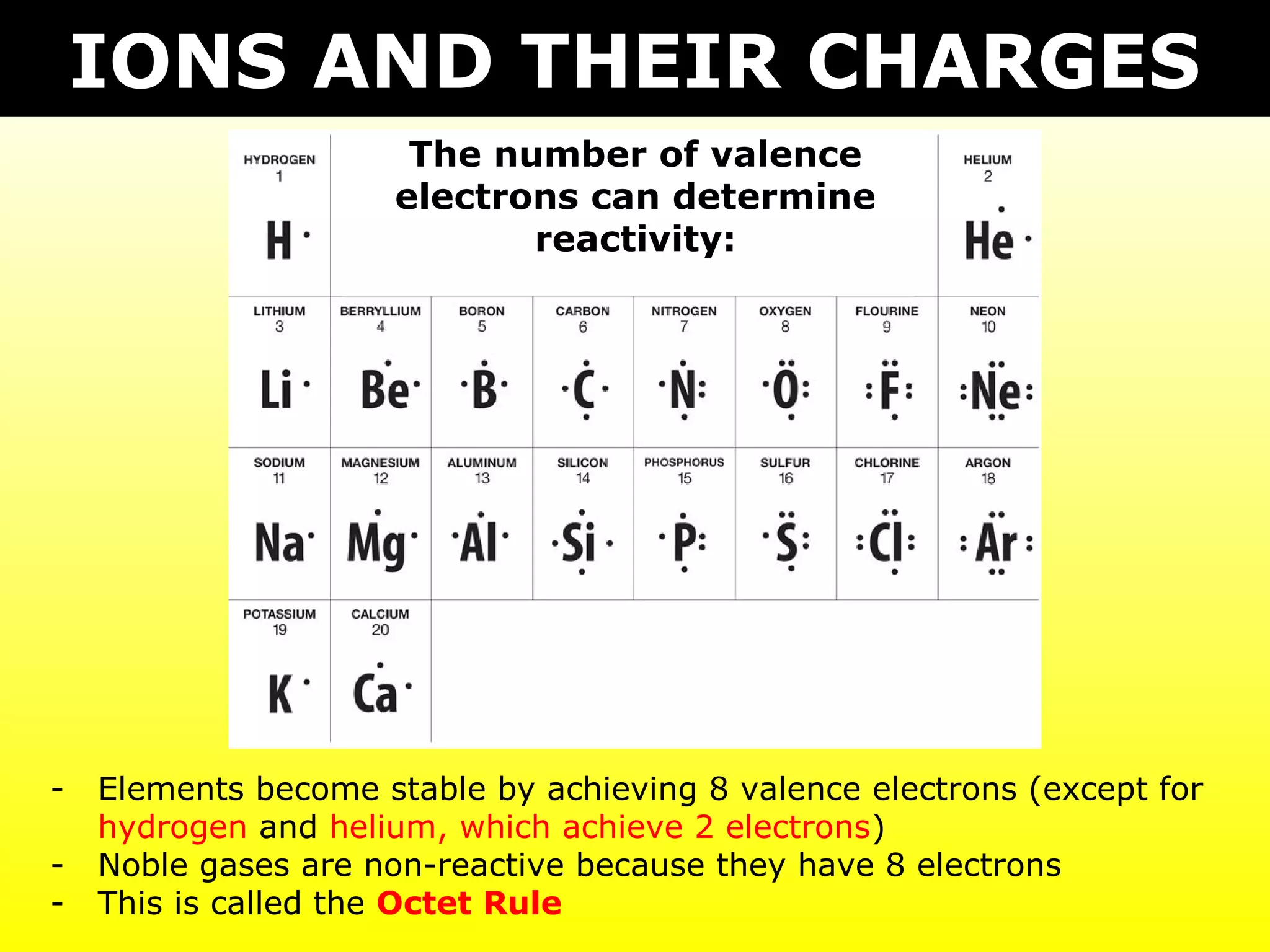
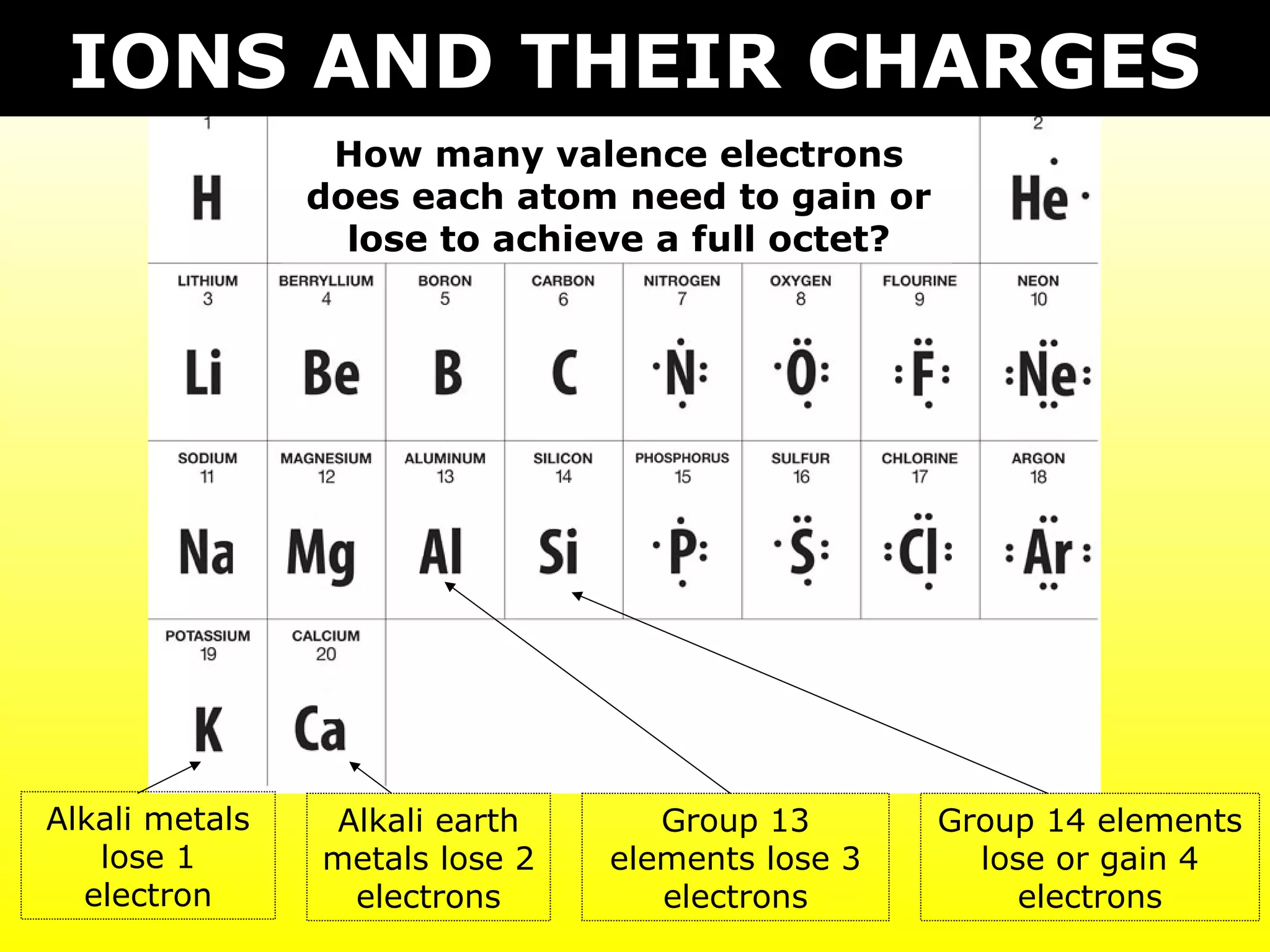
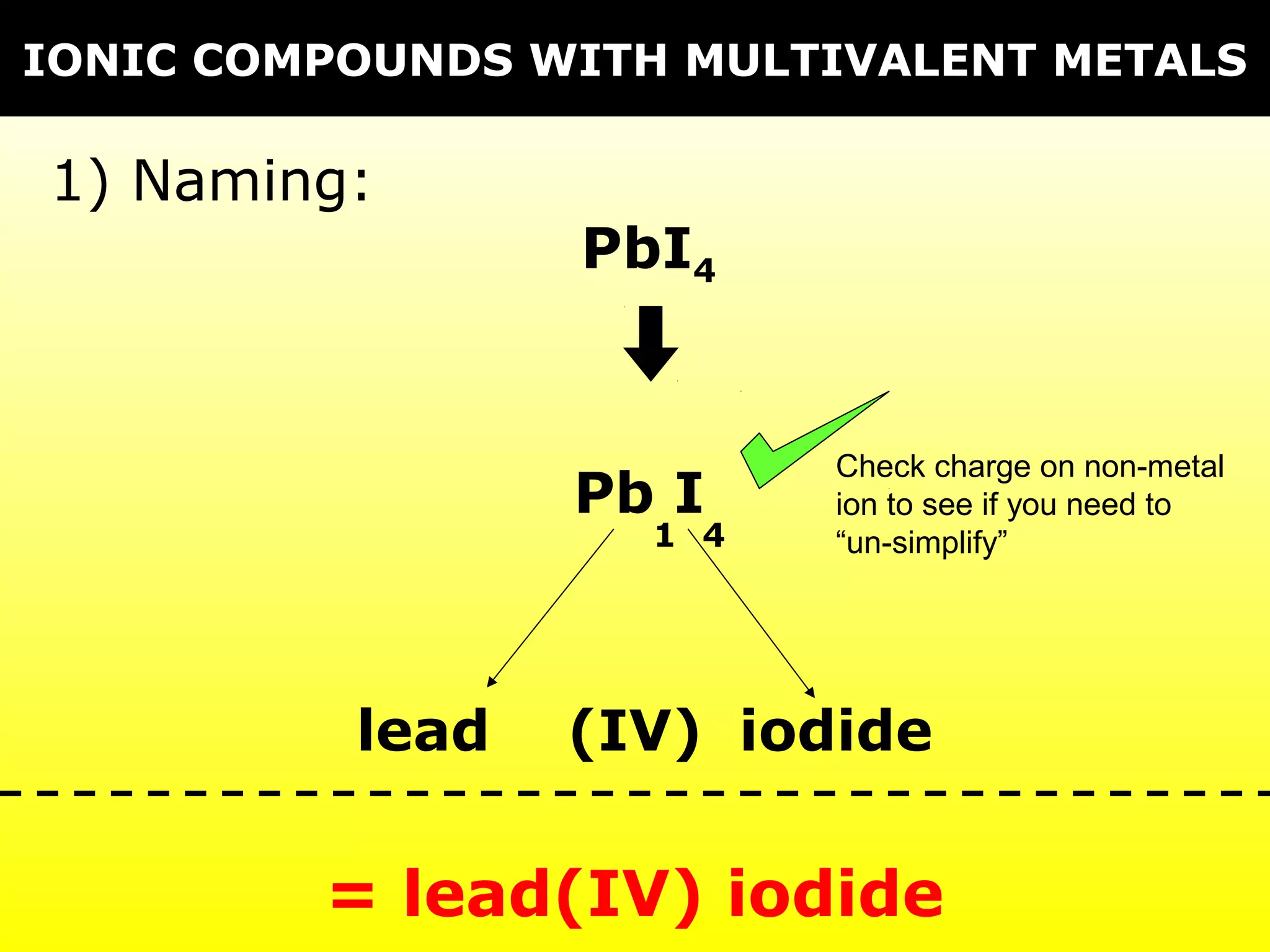
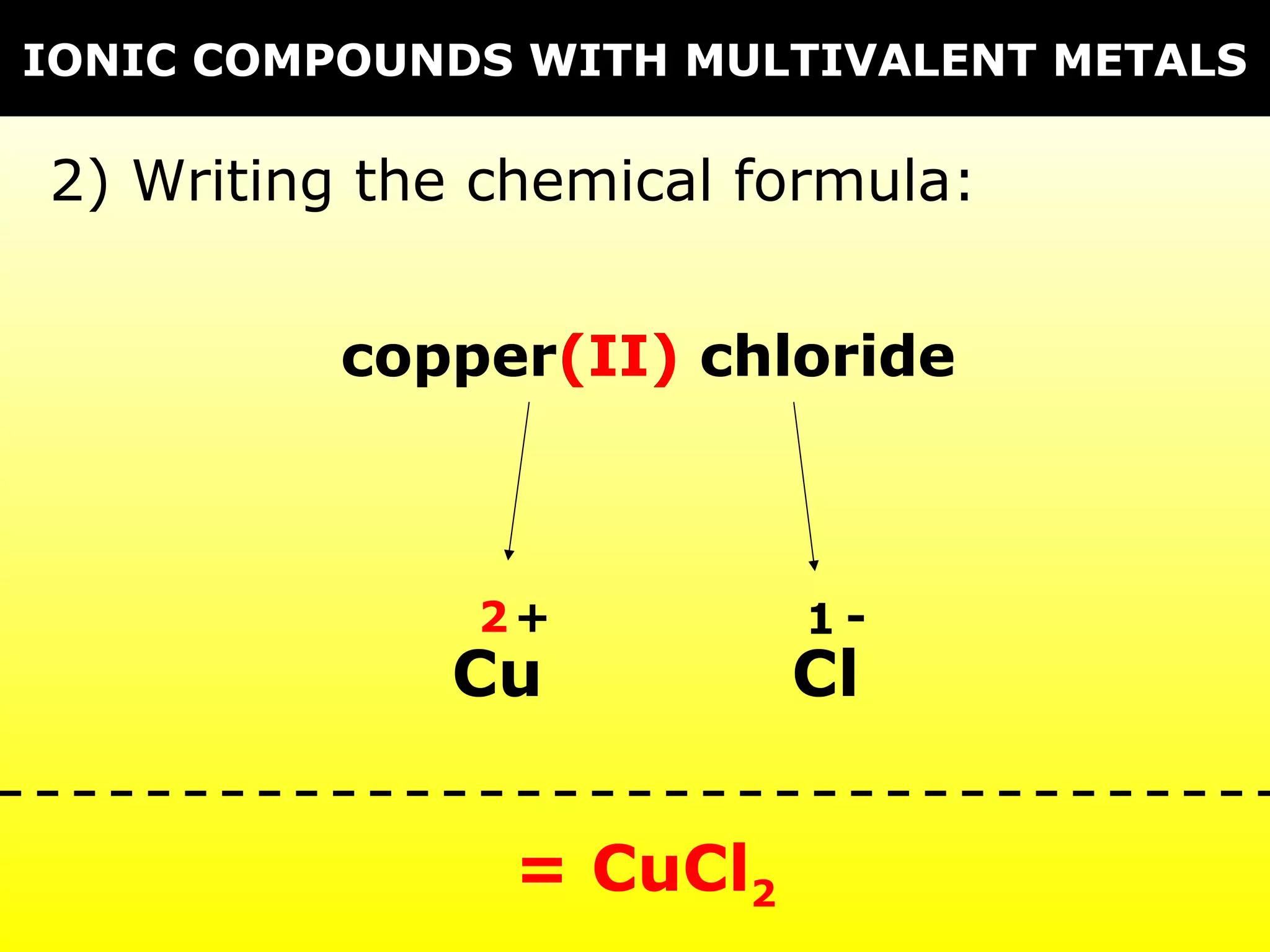
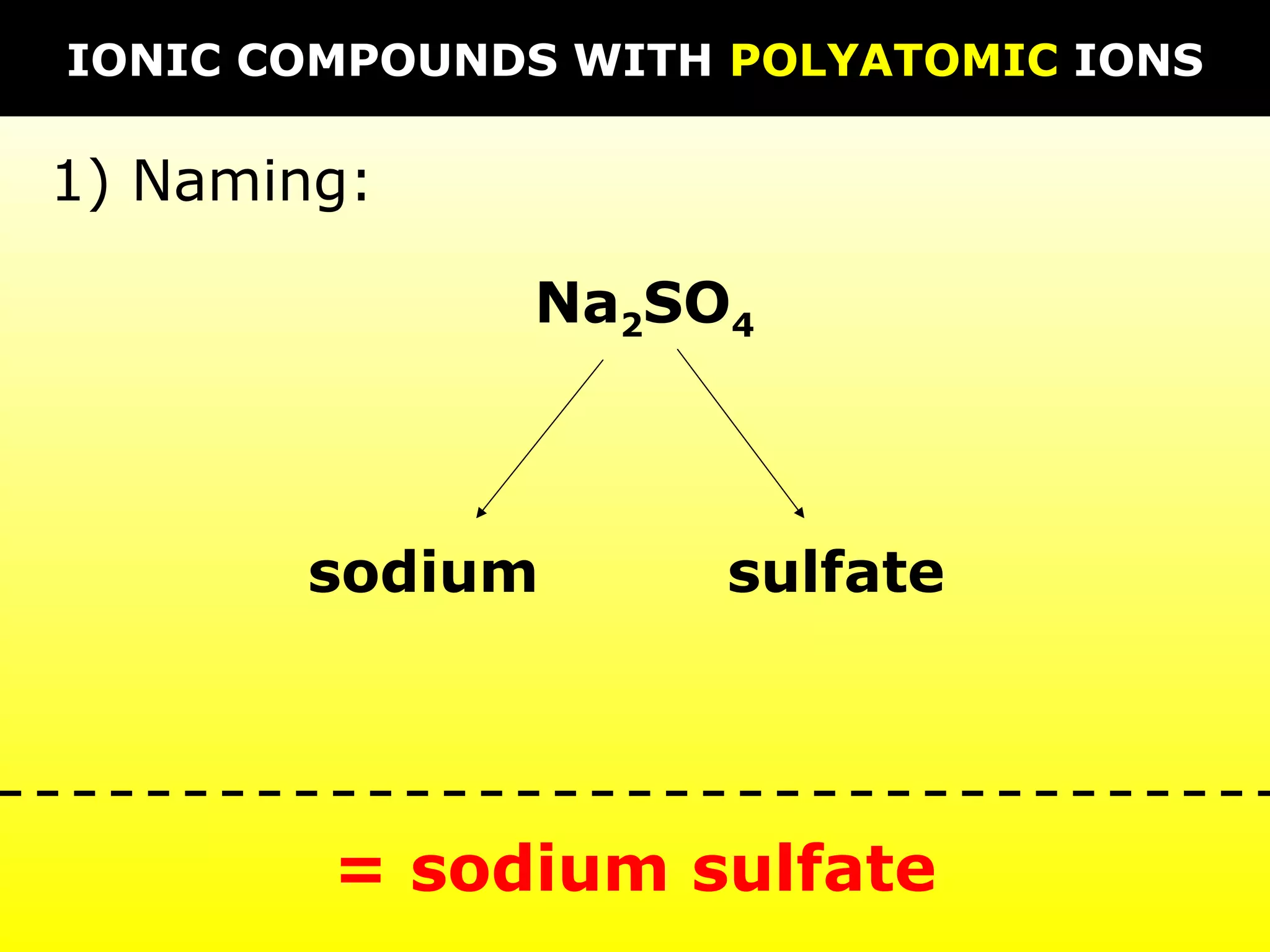
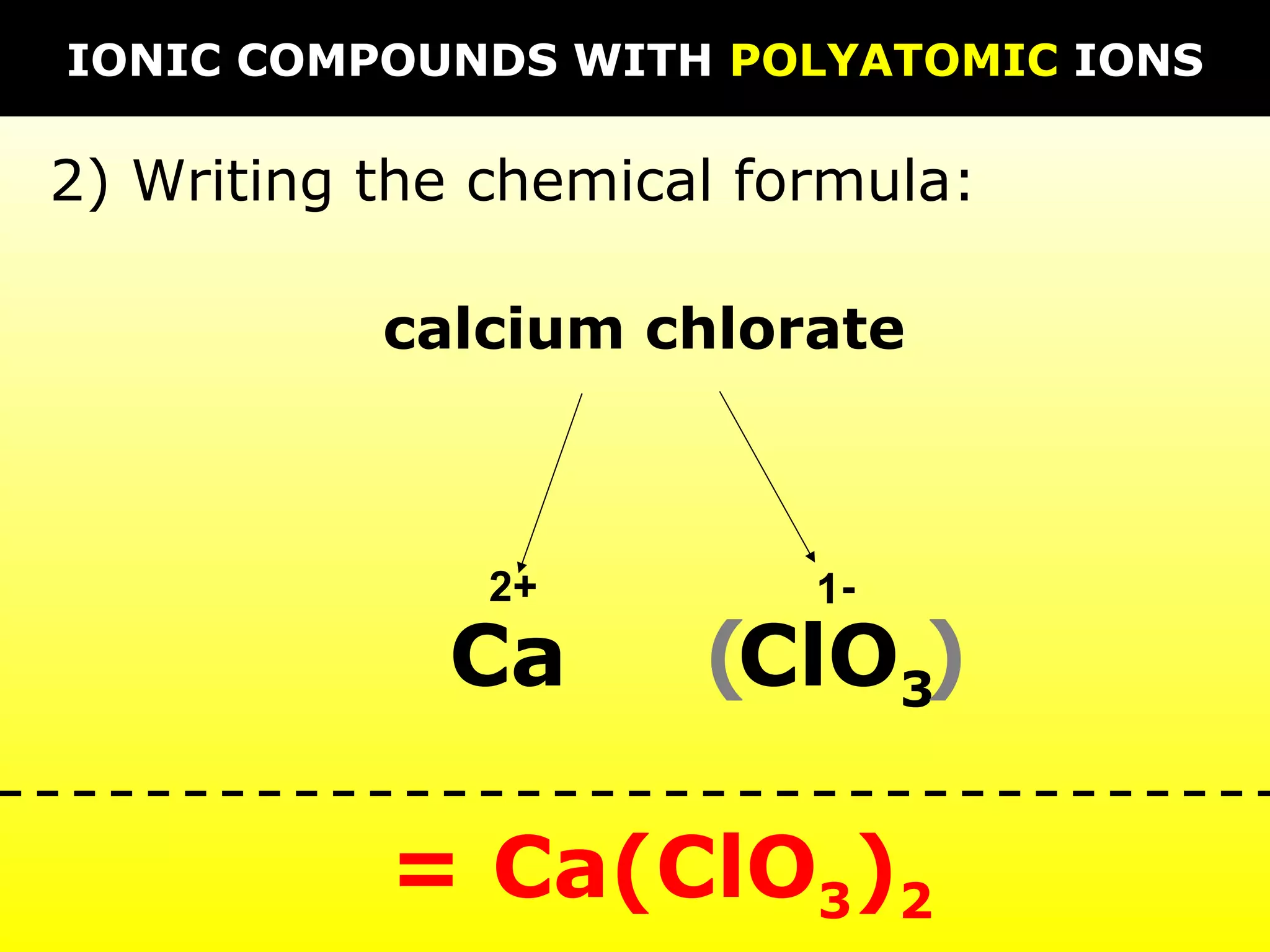
The document discusses naming and writing formulas for different types of compounds including:
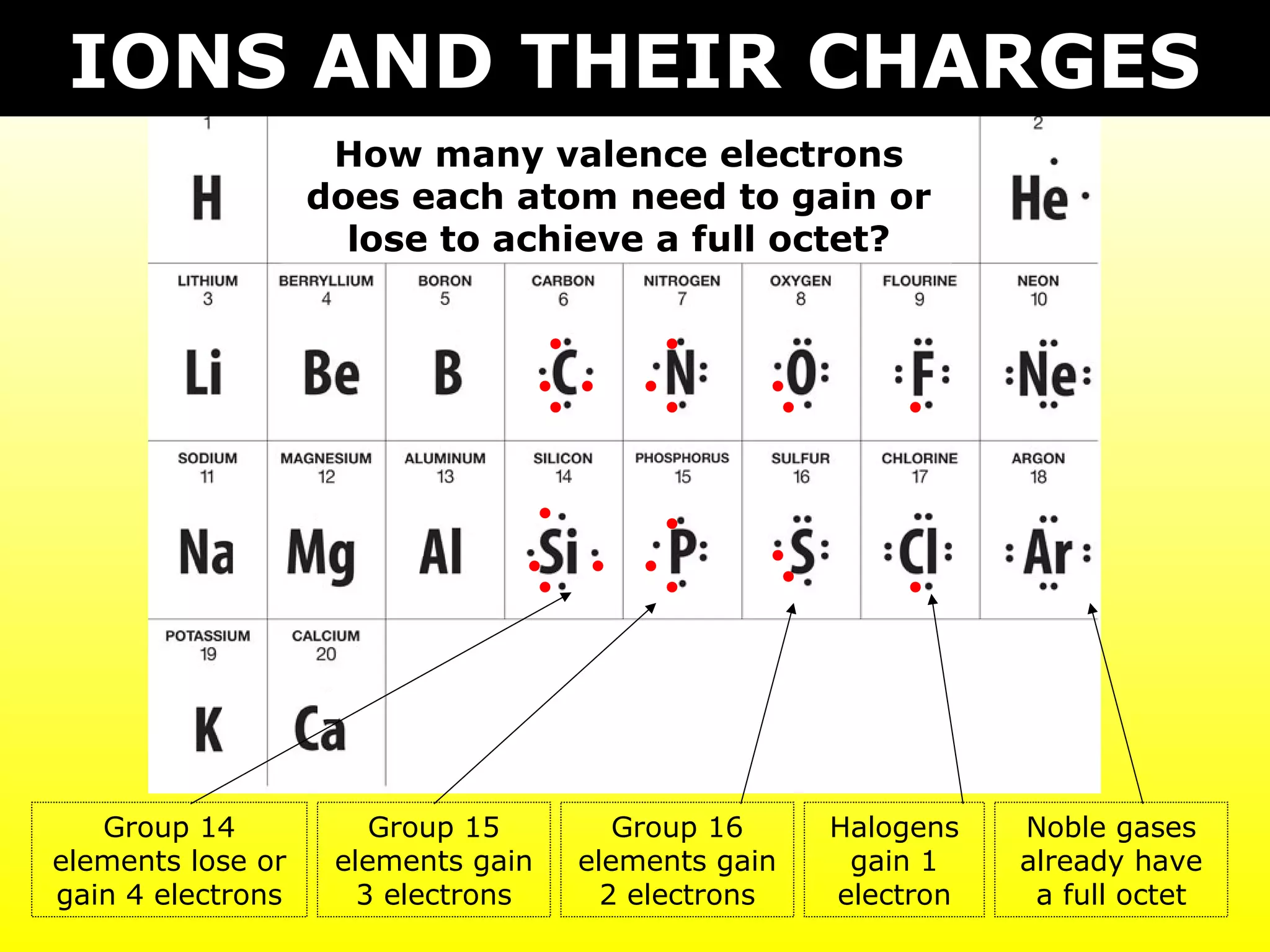
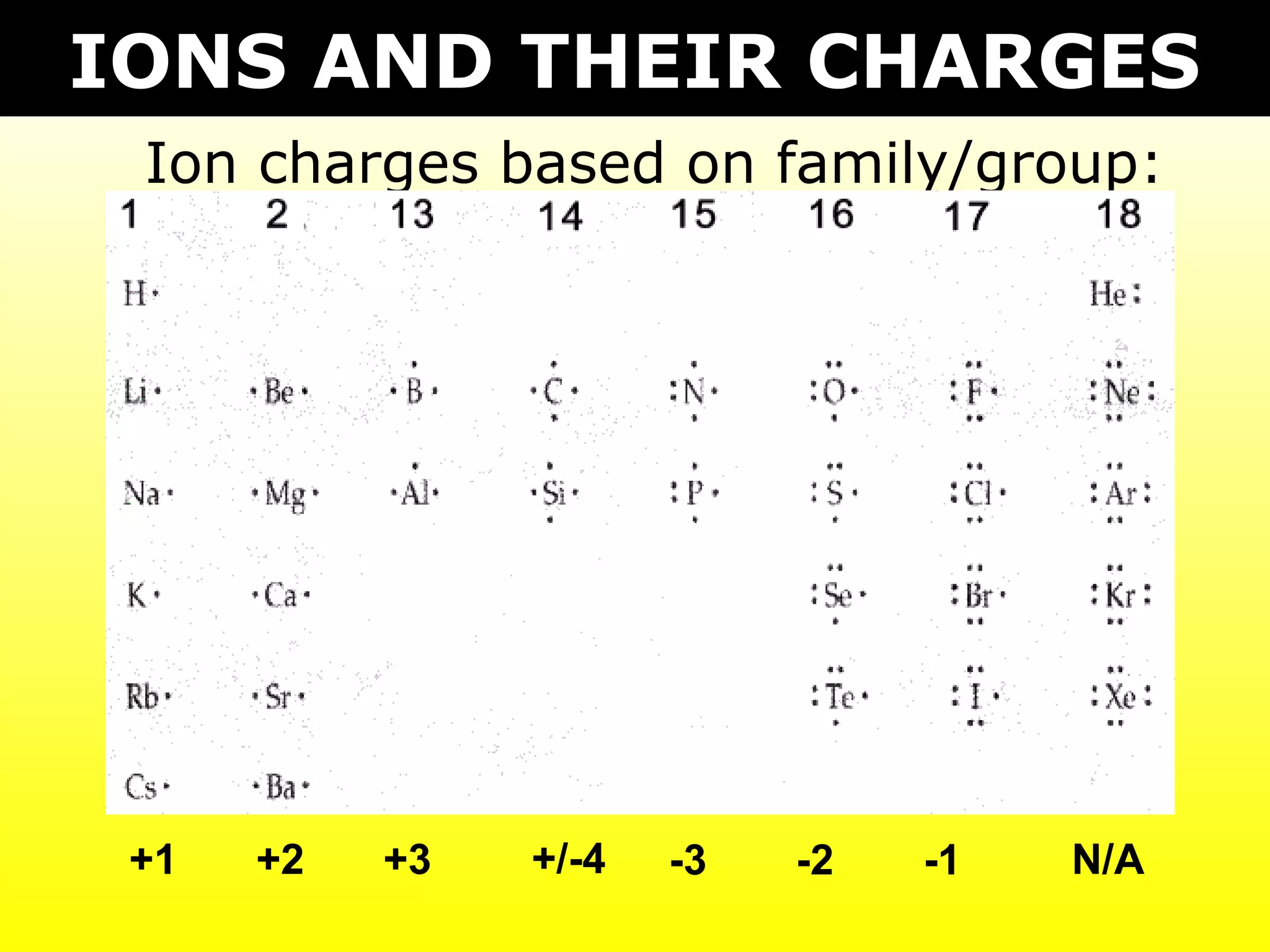
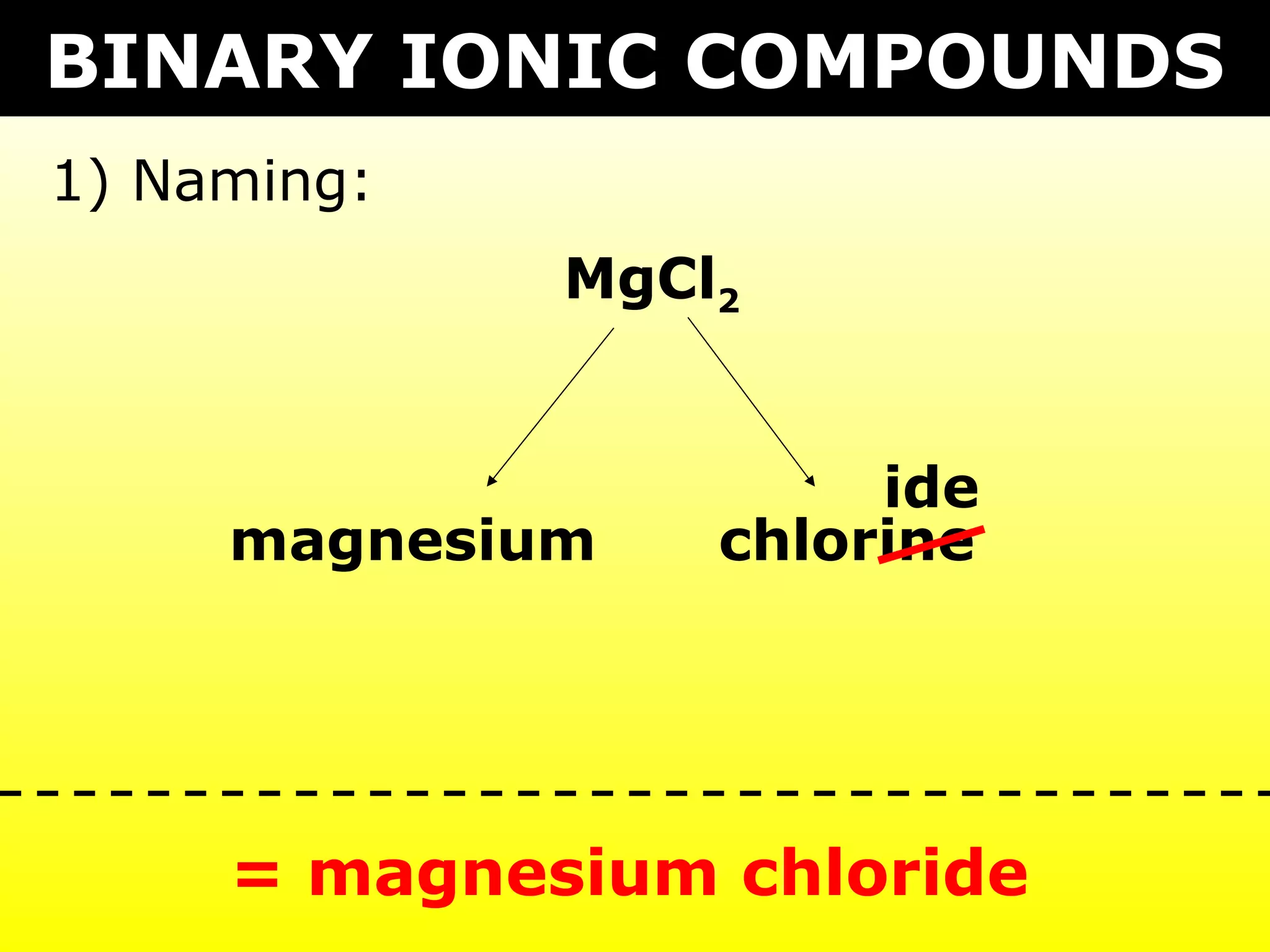
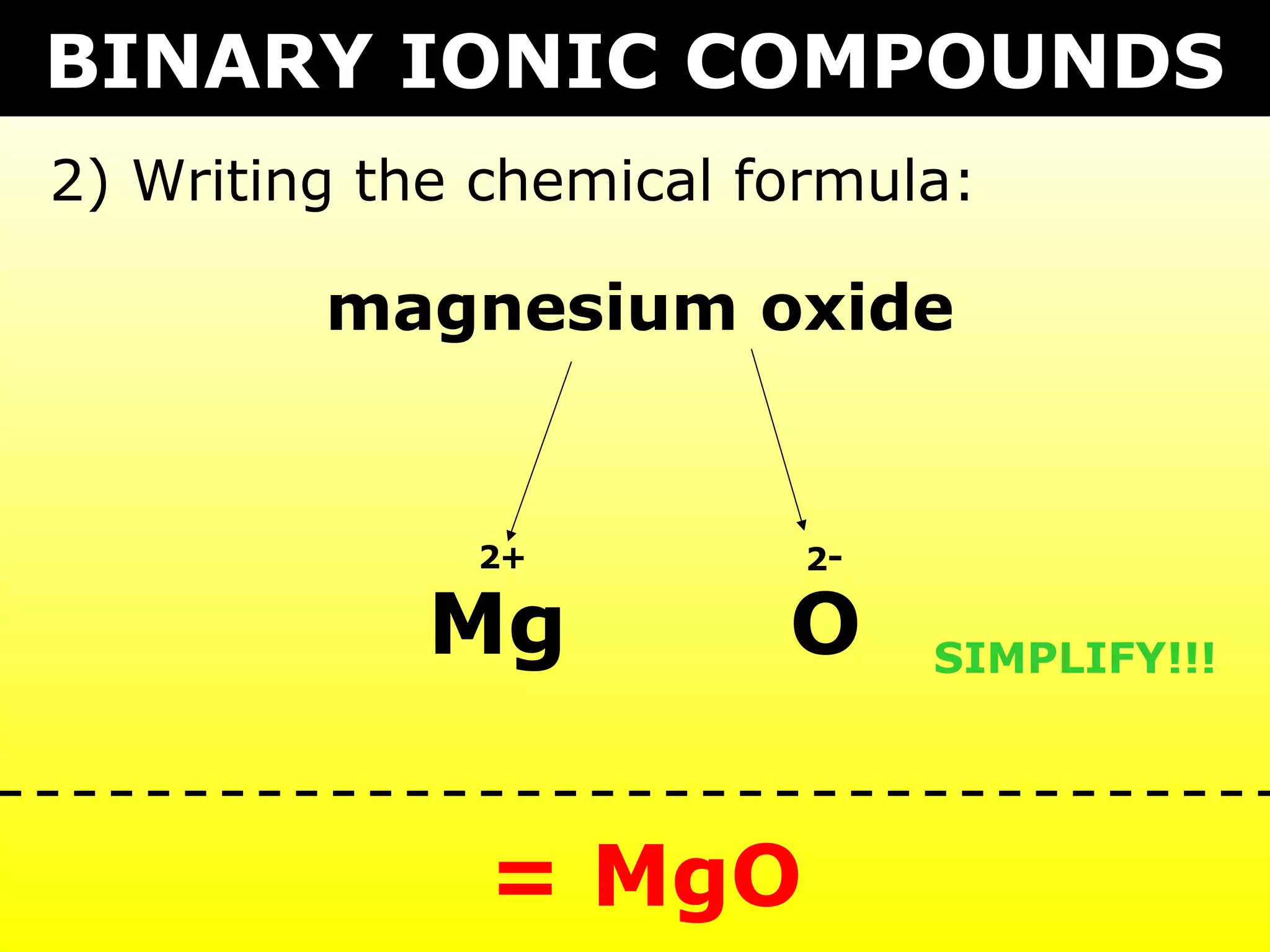
- Ionic compounds formed between metals and nonmetals by gaining or losing valence electrons to achieve stable octets.
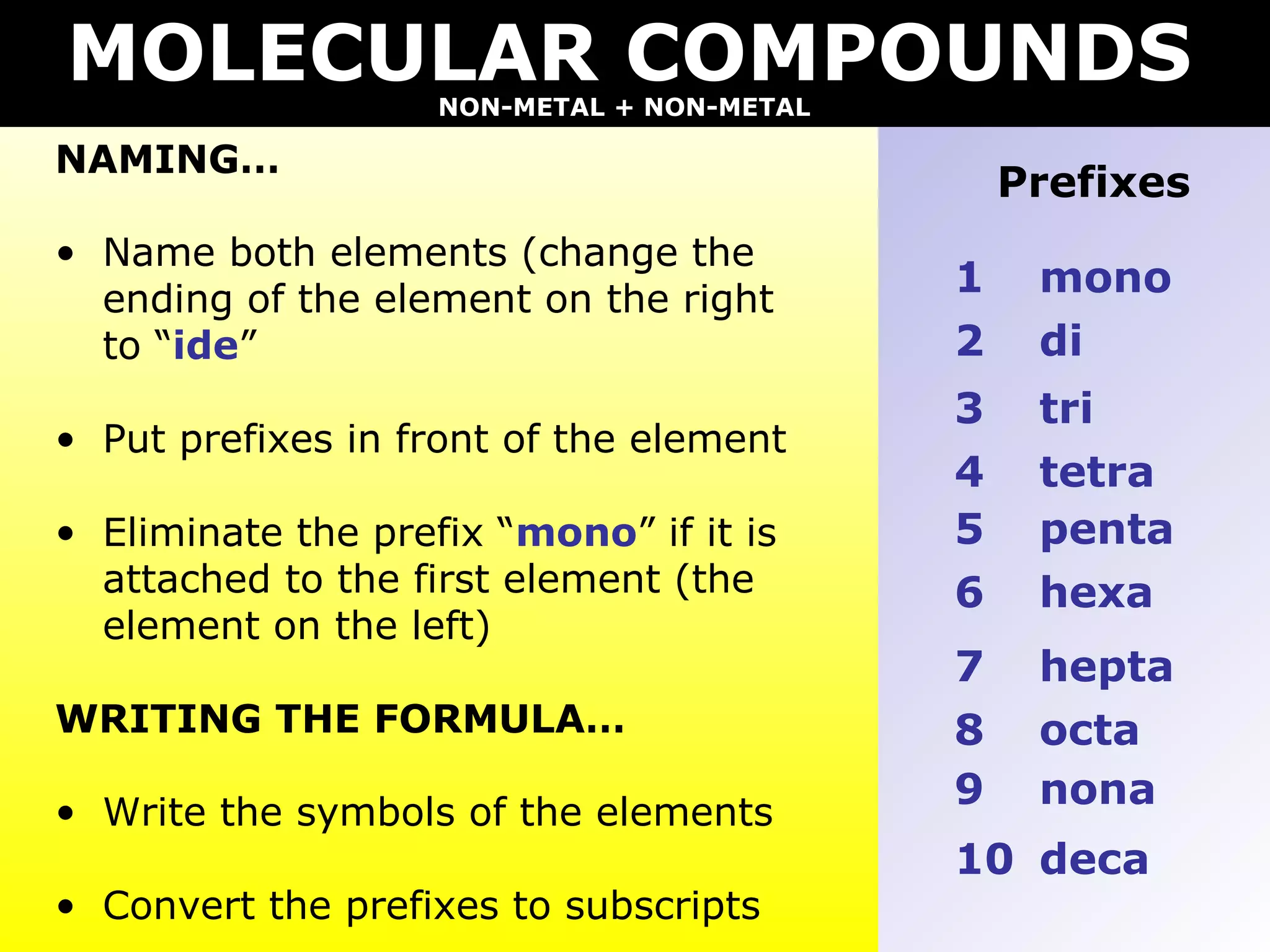
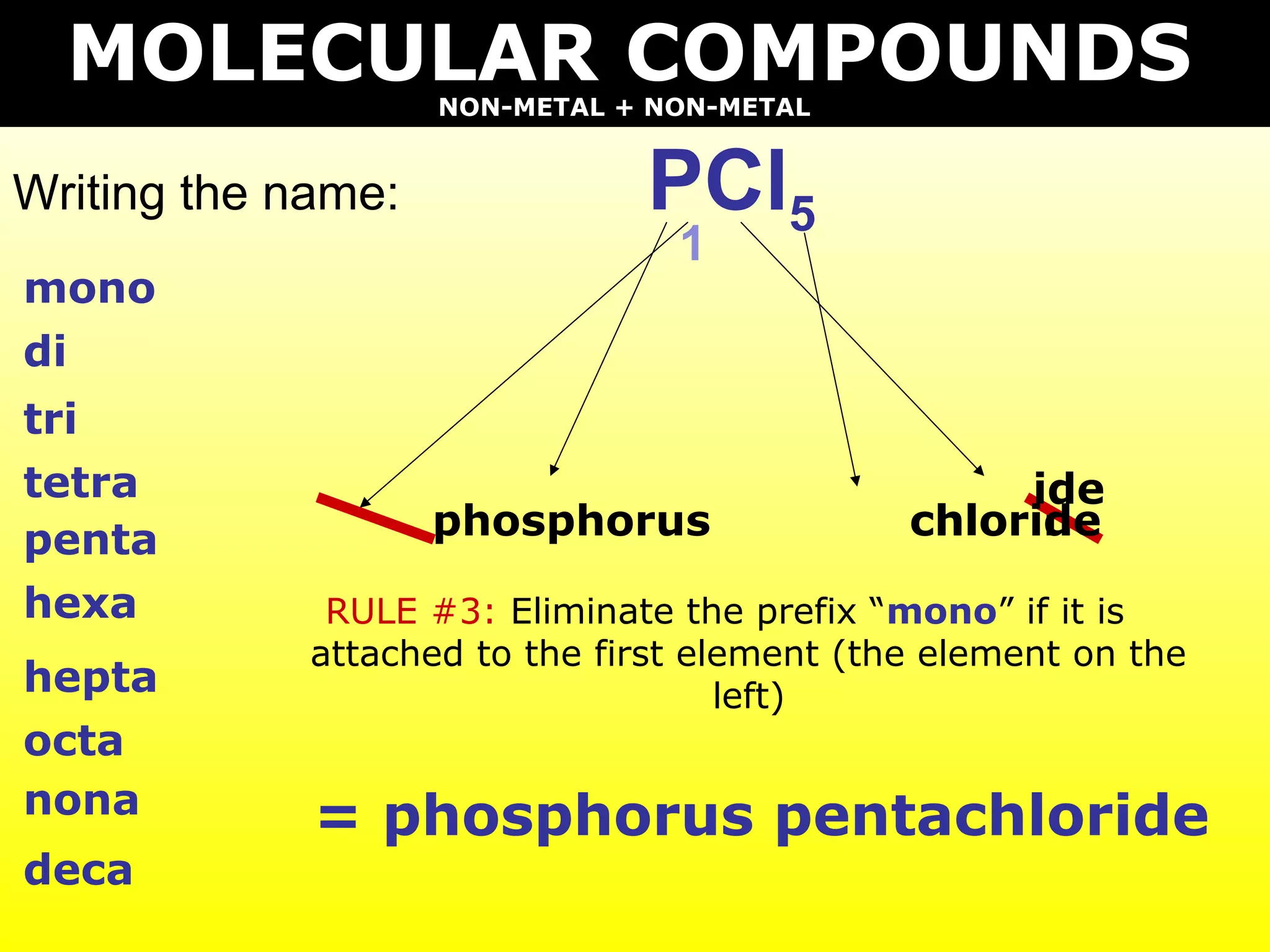
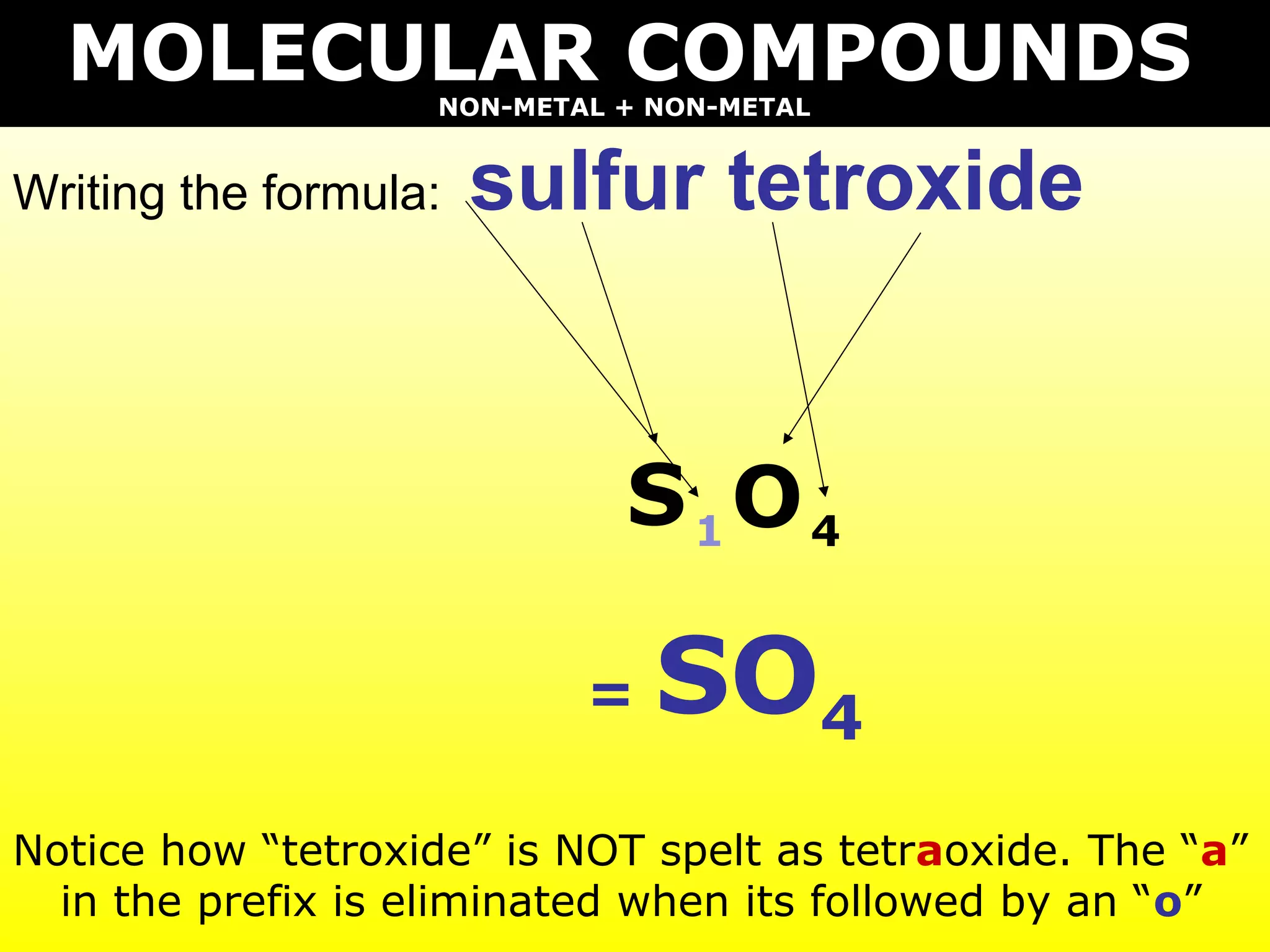
- Molecular compounds formed between two nonmetals using prefixes to indicate the number of each element and dropping "mono" if attached to the first element.
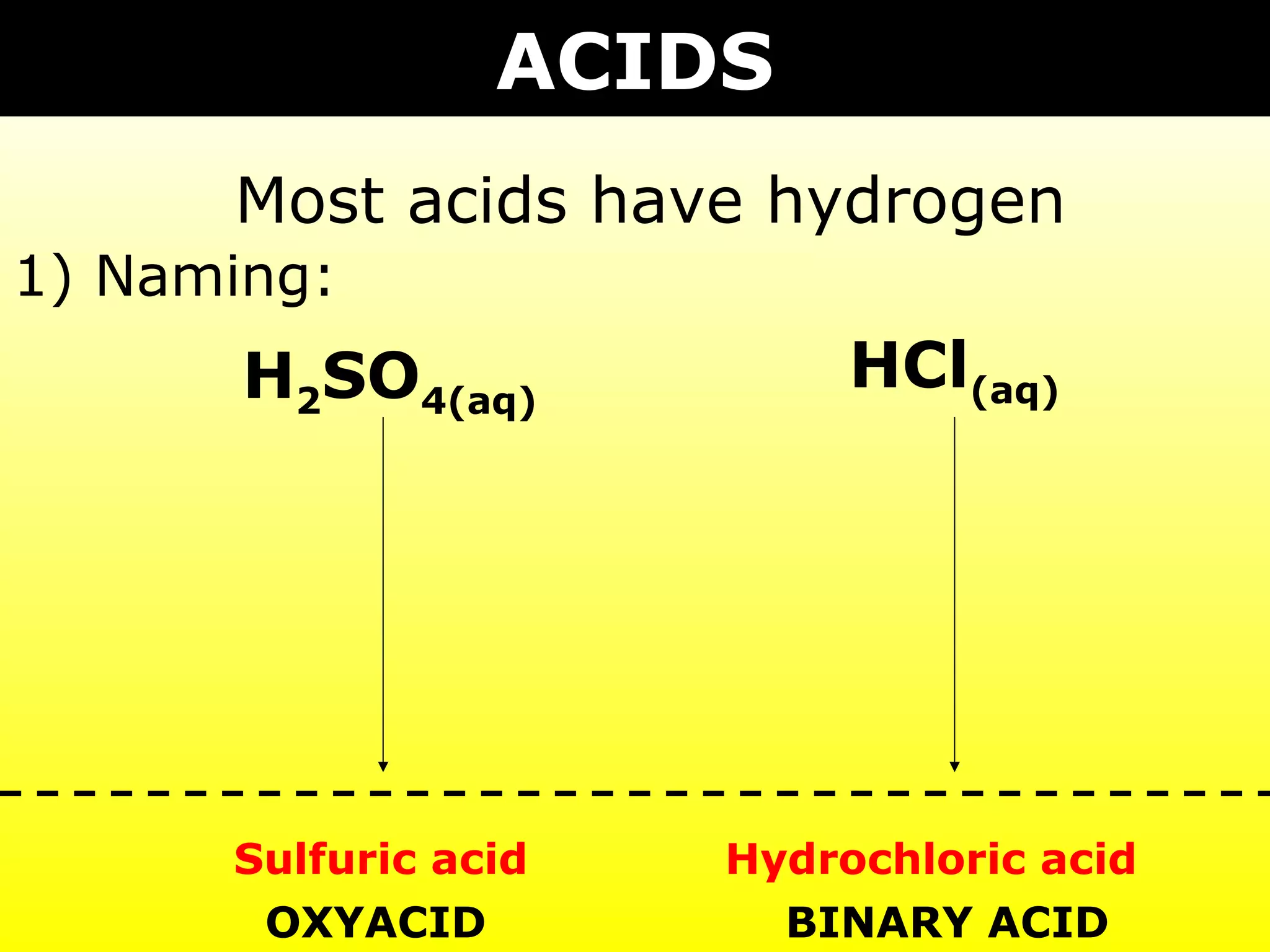
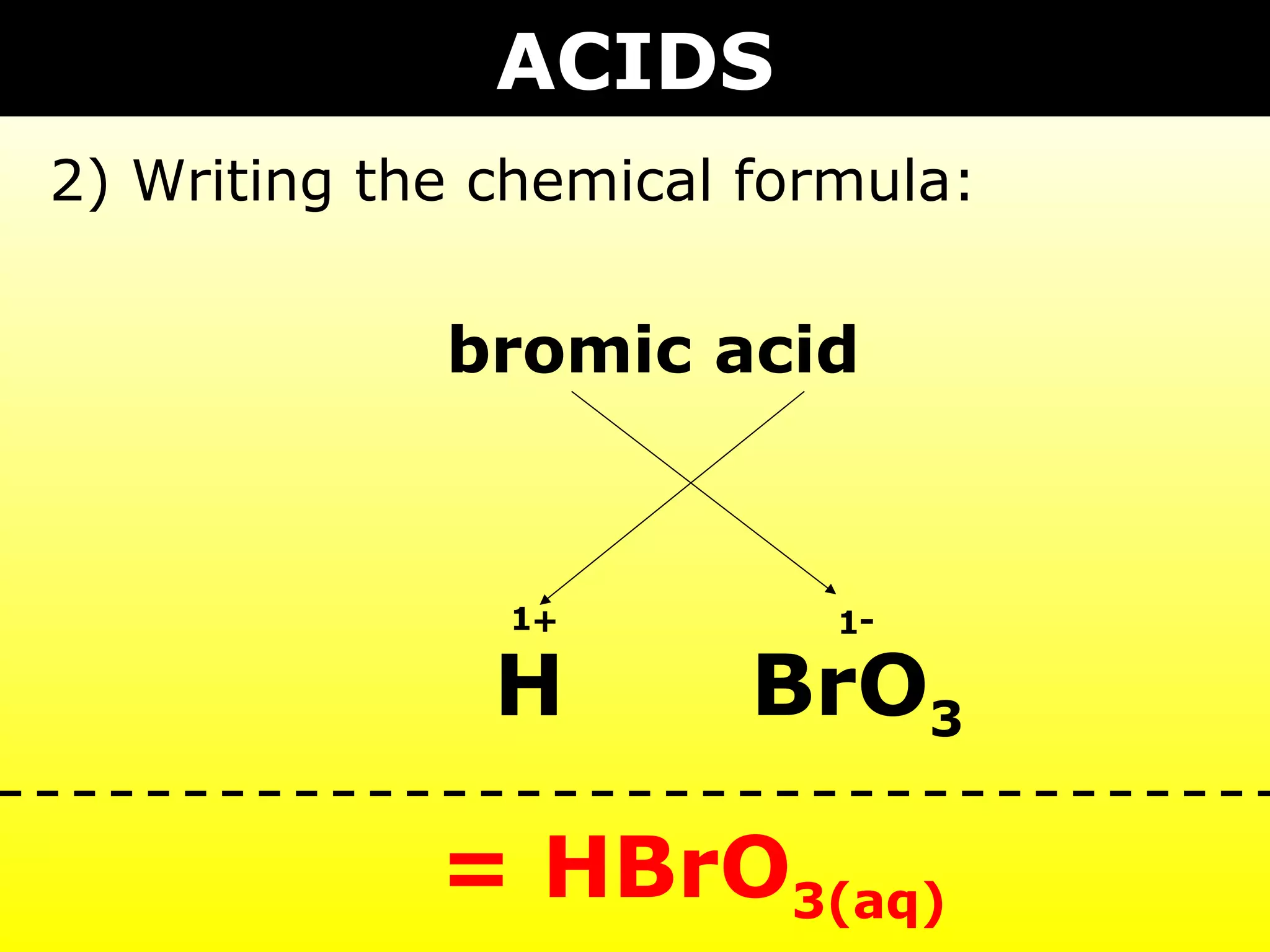
- Acids containing polyatomic ions that have modified names and gain hydrogen to become ionic in water.