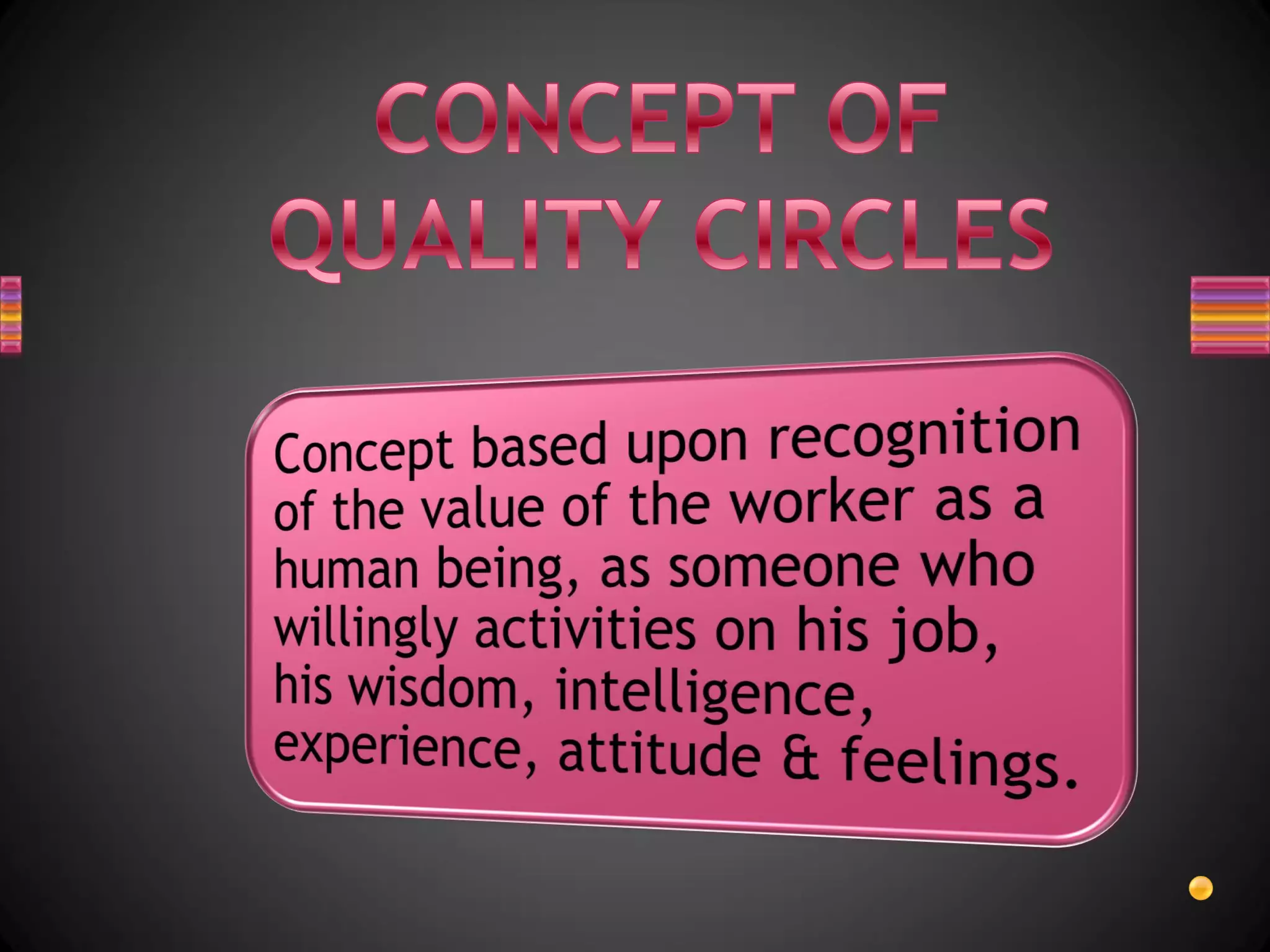
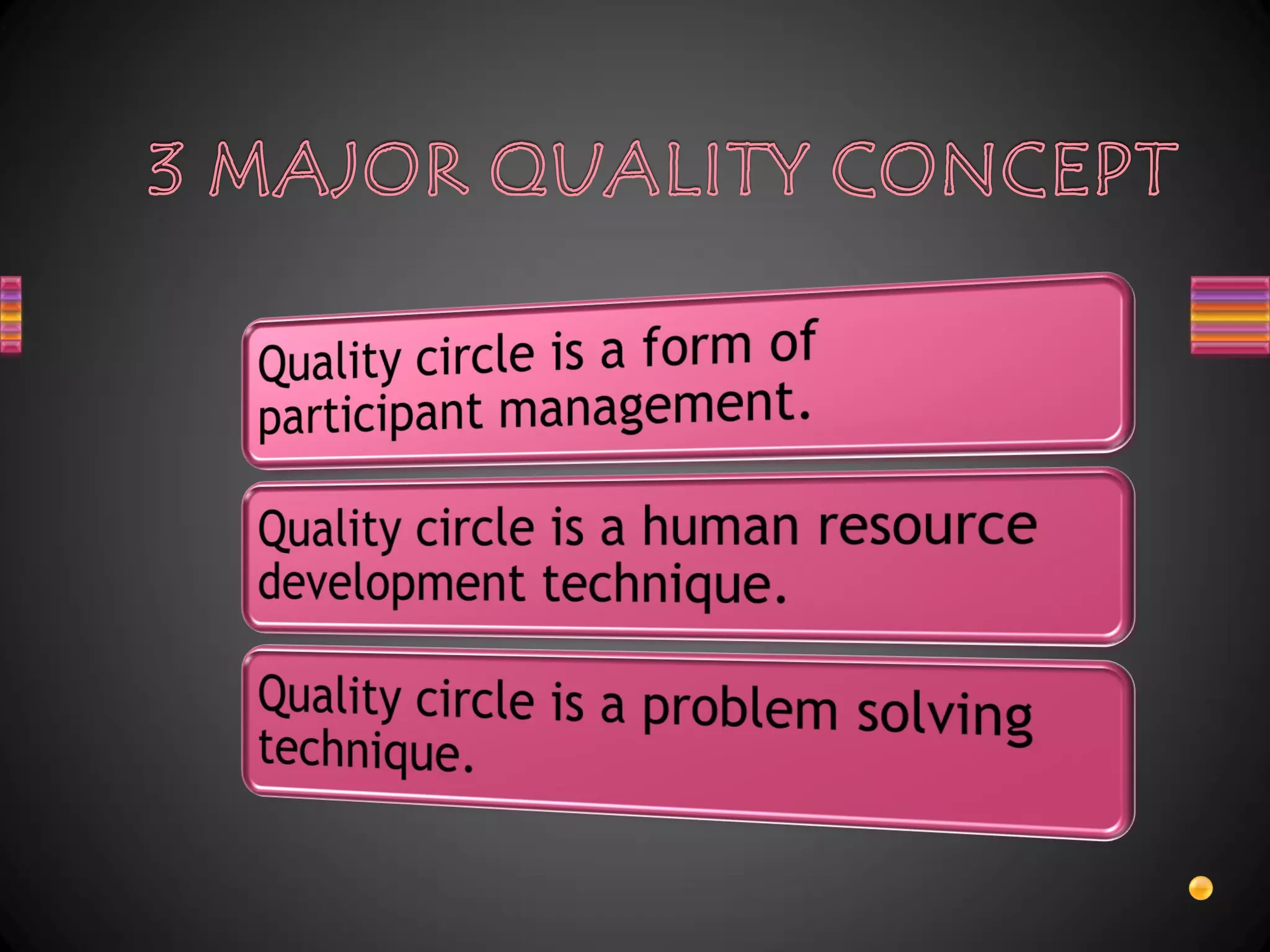
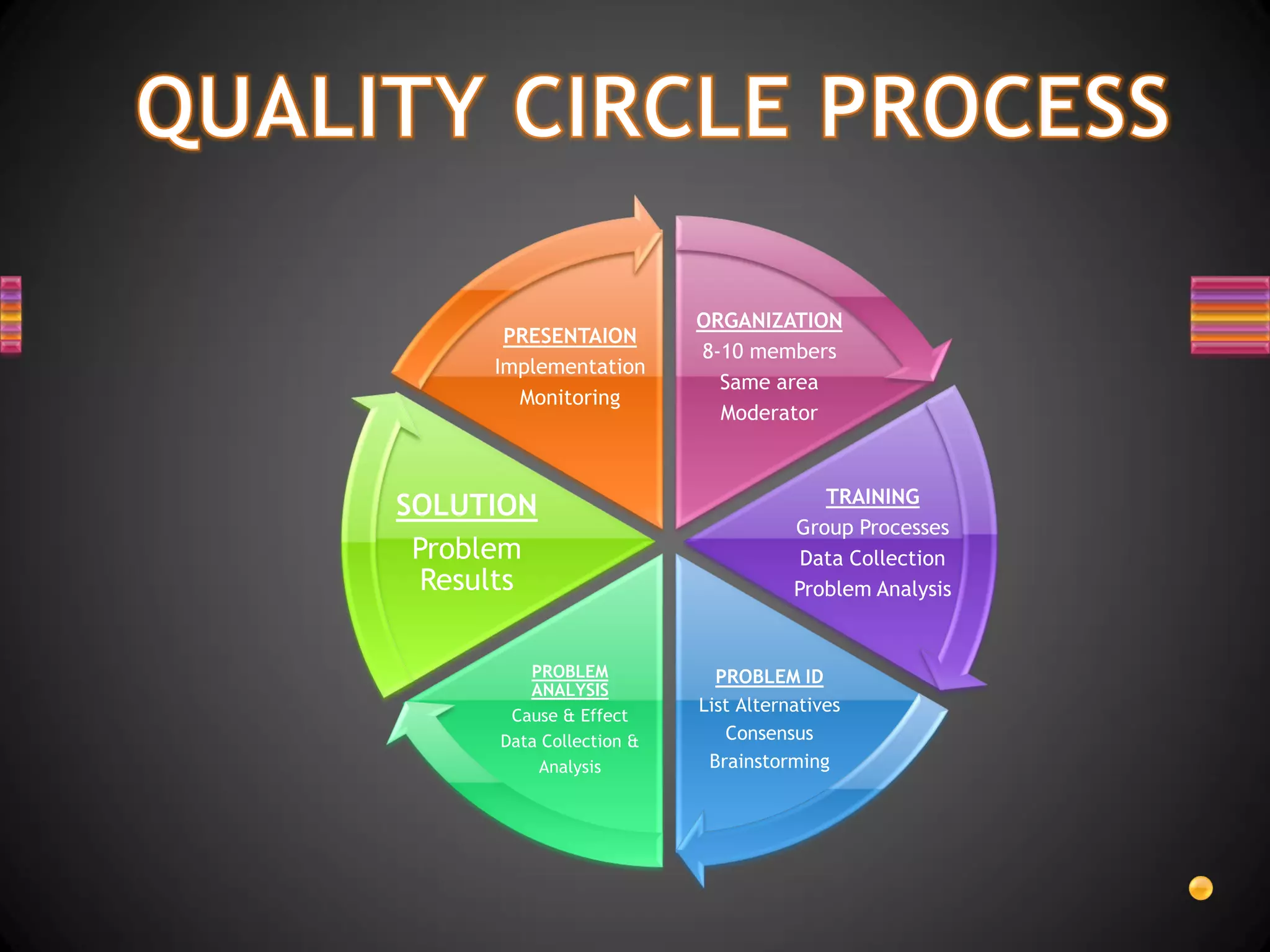
1. Quality circles are voluntary groups of 8-10 employees and supervisors that work on continuous process improvement in an organization.
2. Quality circles were first developed in Japan in the 1960s and have since spread to over 50 countries.
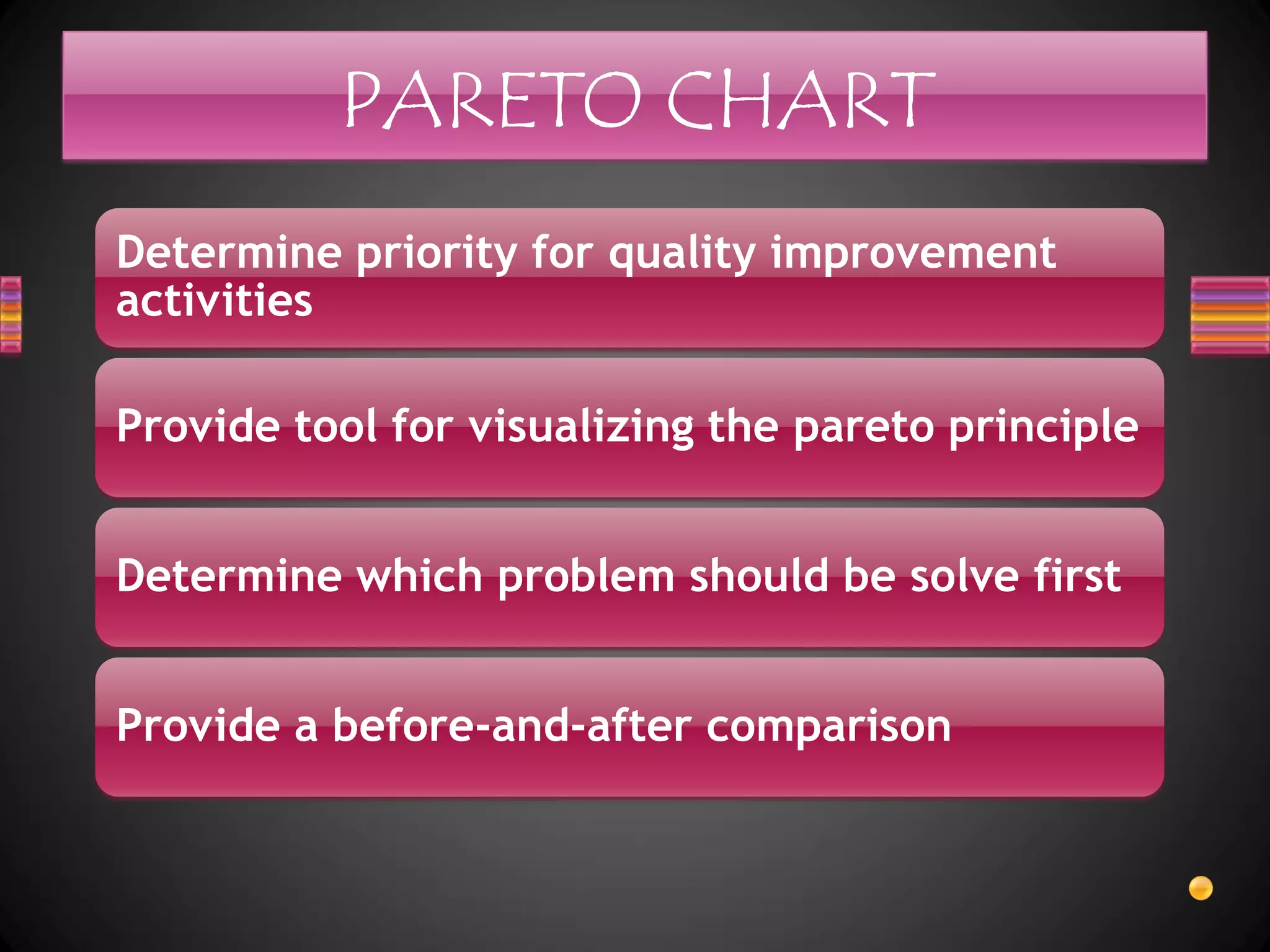
3. Advantages of quality circles include improving organization morale, promoting effective teamwork, personal development, cost reduction, and increasing employee motivation.