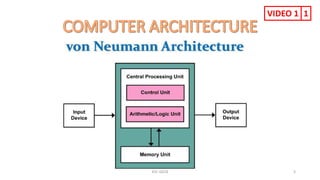
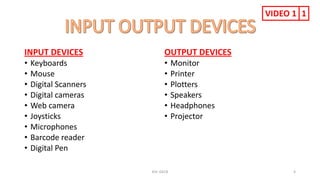
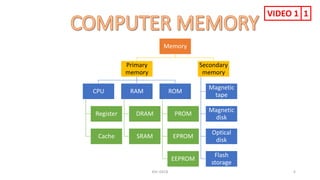
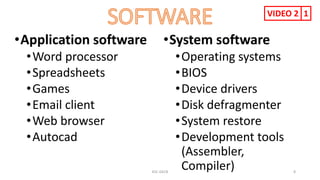
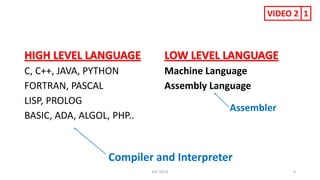
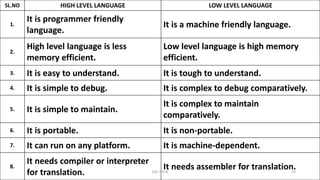
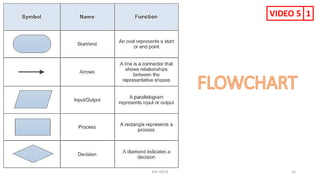
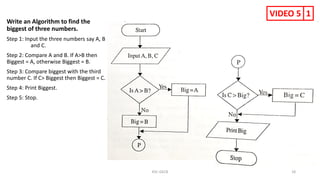
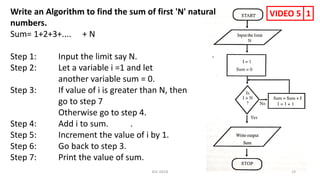
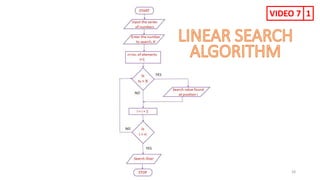
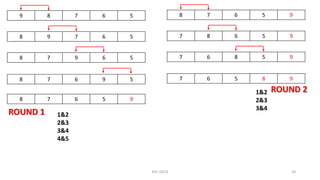
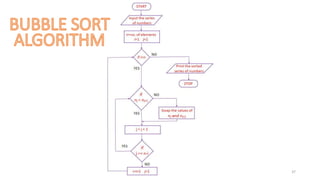
The document provides information about various computer components and concepts. It begins with a list of input and output devices for computers. It then discusses different types of computer memory, including primary memory (registers, cache, RAM, ROM) and secondary memory (magnetic tape, disk, optical disk, flash storage). The document also covers computer software categories like application software, system software, programming languages, and algorithms for simple problems. It includes pseudocode examples and diagrams explaining sorting and searching algorithms like bubble sort.