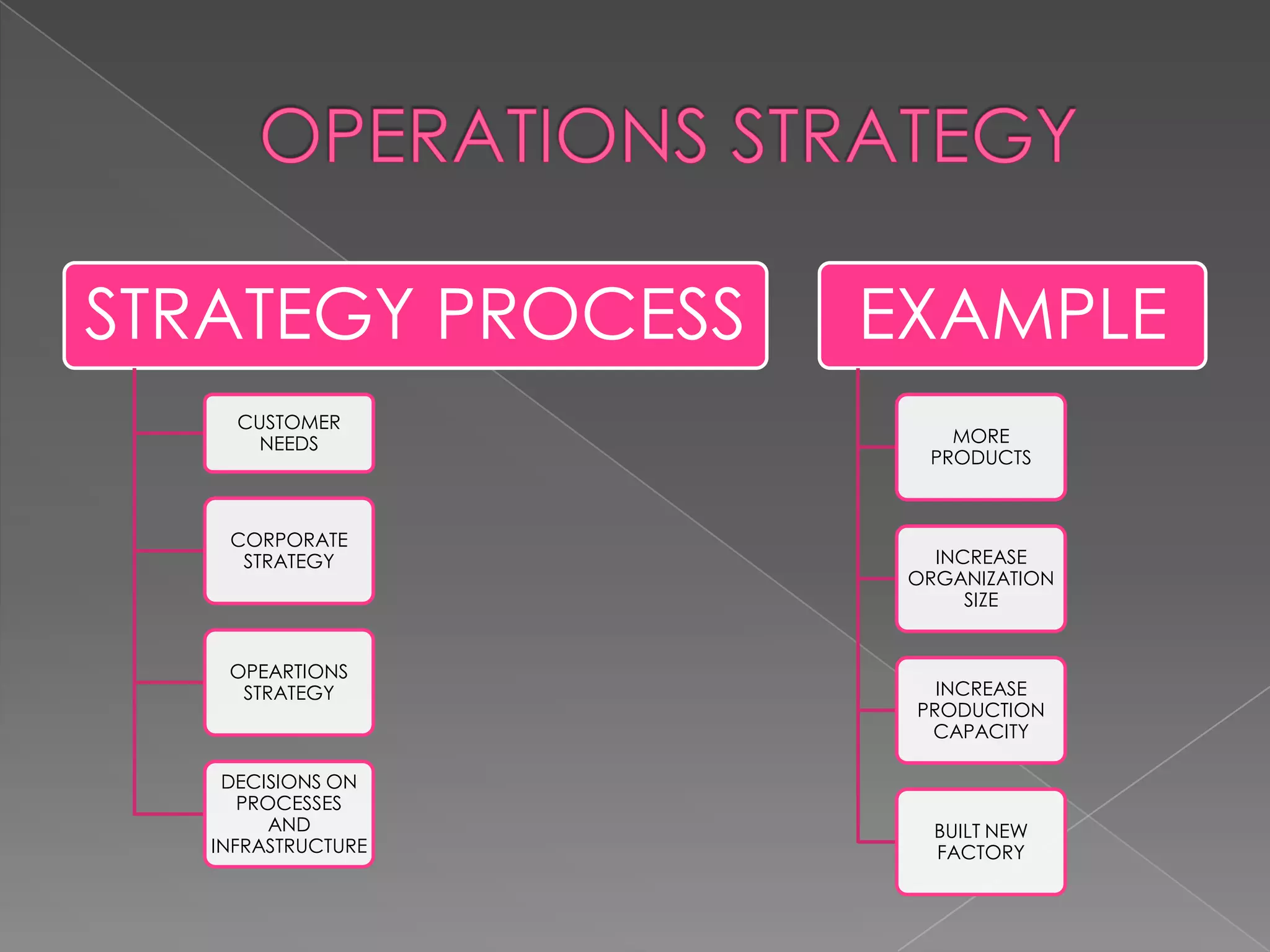
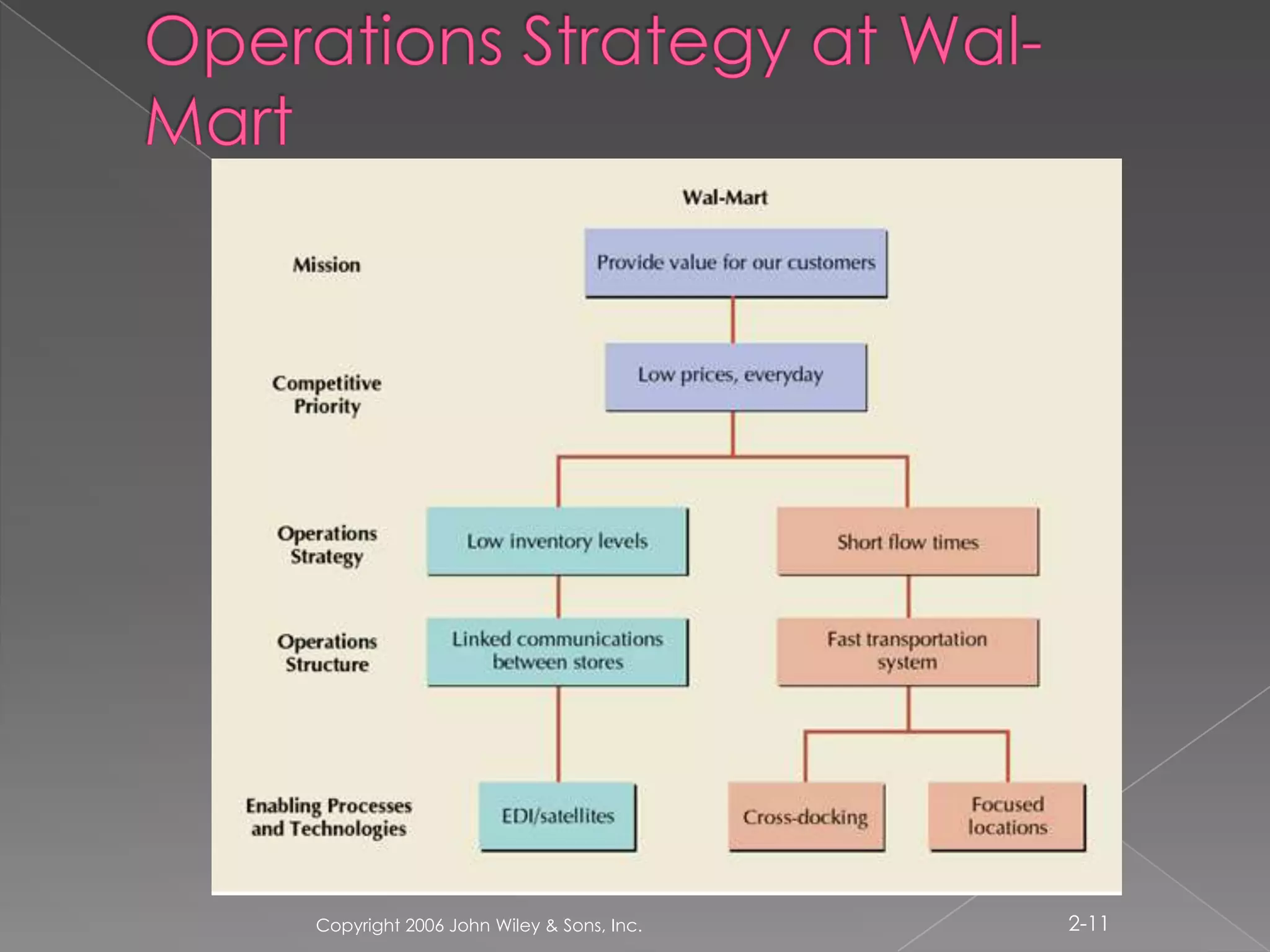
Operations managers must develop an operations strategy that is consistent with the firm's corporate strategy. An operations strategy involves key decisions such as which products to produce internally and which to purchase, how many facilities are needed and where to locate them, what processes and technologies to use, how to distribute products to customers, which suppliers to use and how much to source from them, what human resources and skills are required, and quality measures. The operations strategy provides support for the firm's overall differentiated strategy and competitive approach through efficient and effective execution of operations.