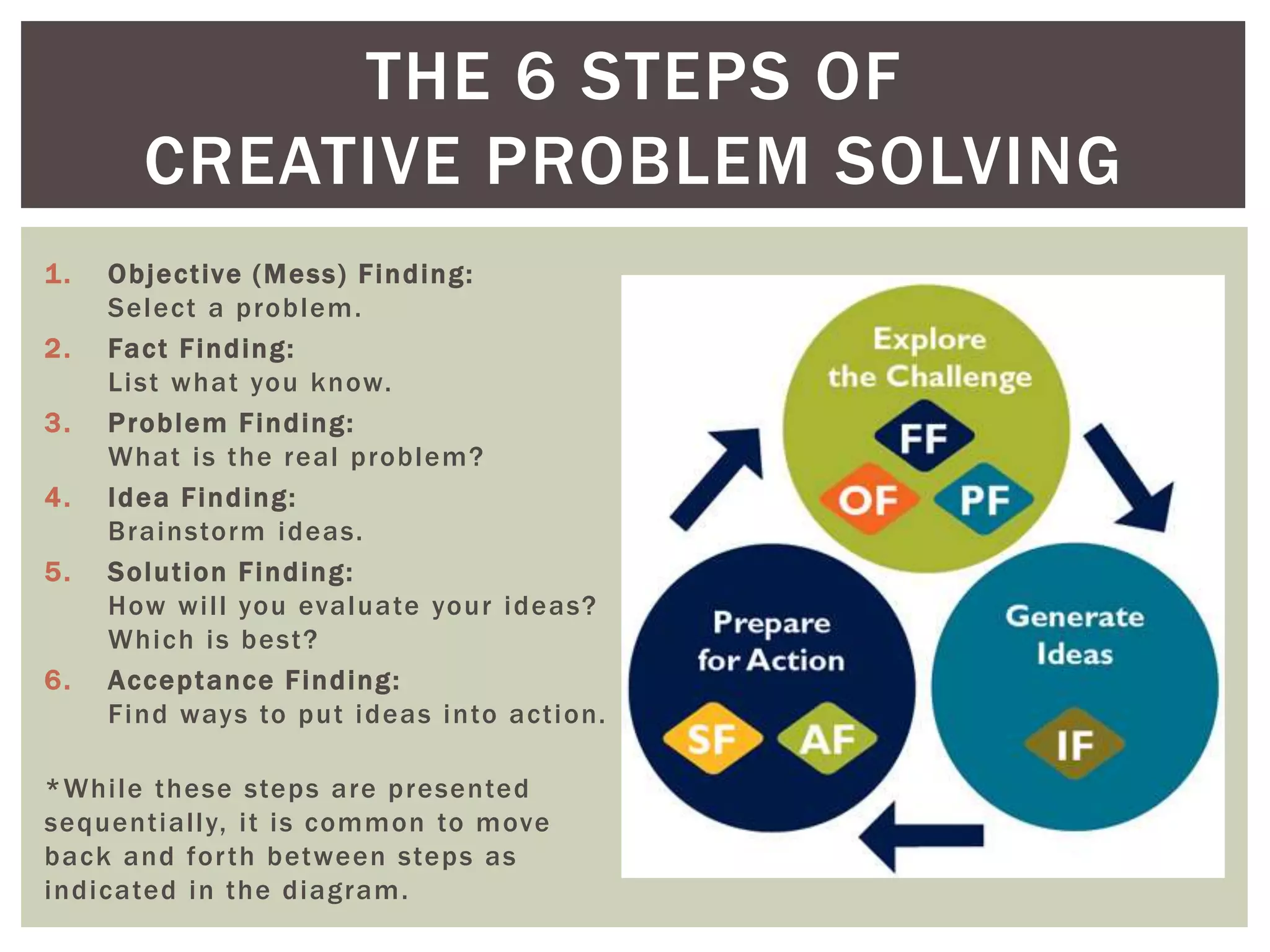
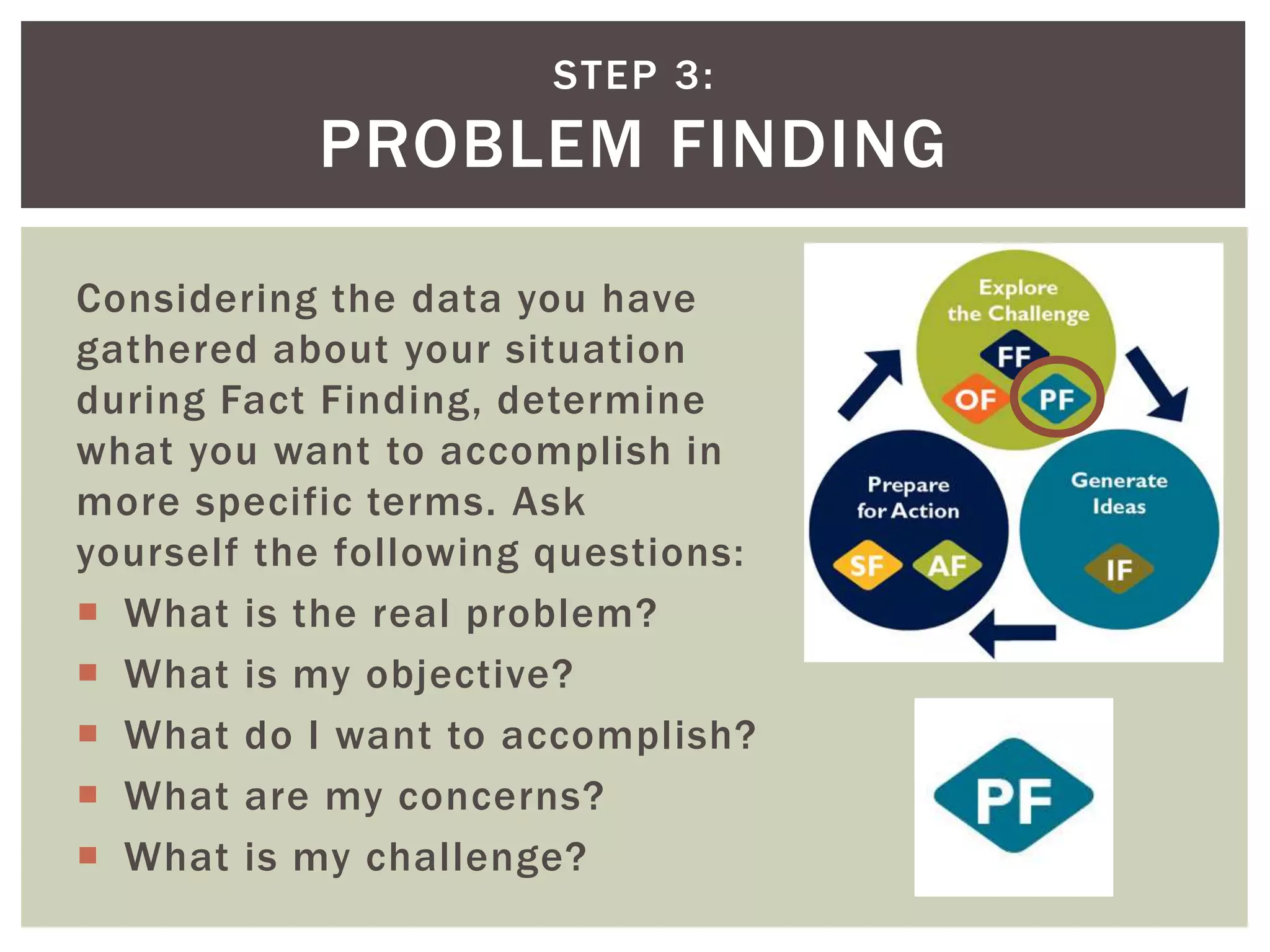
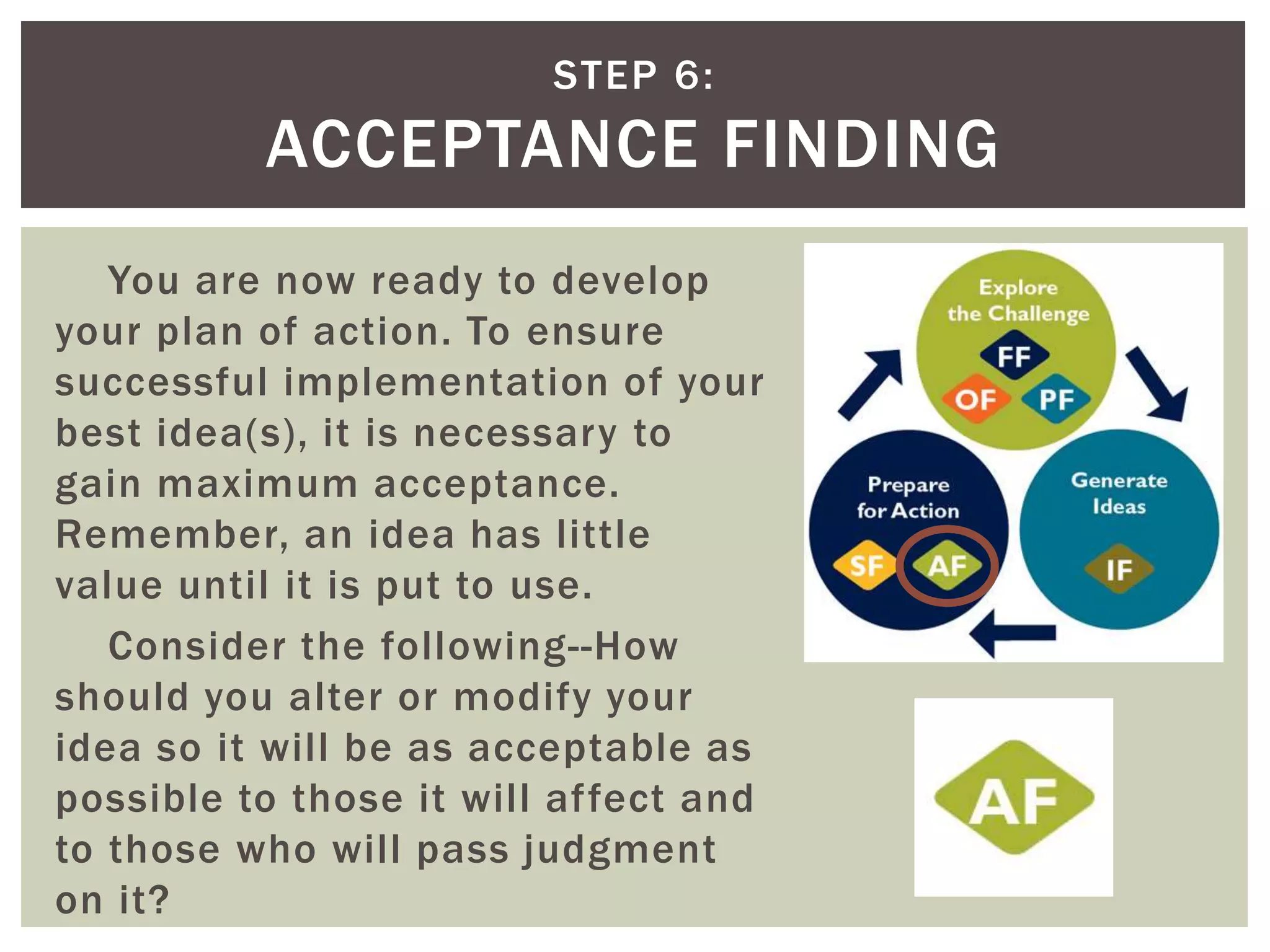
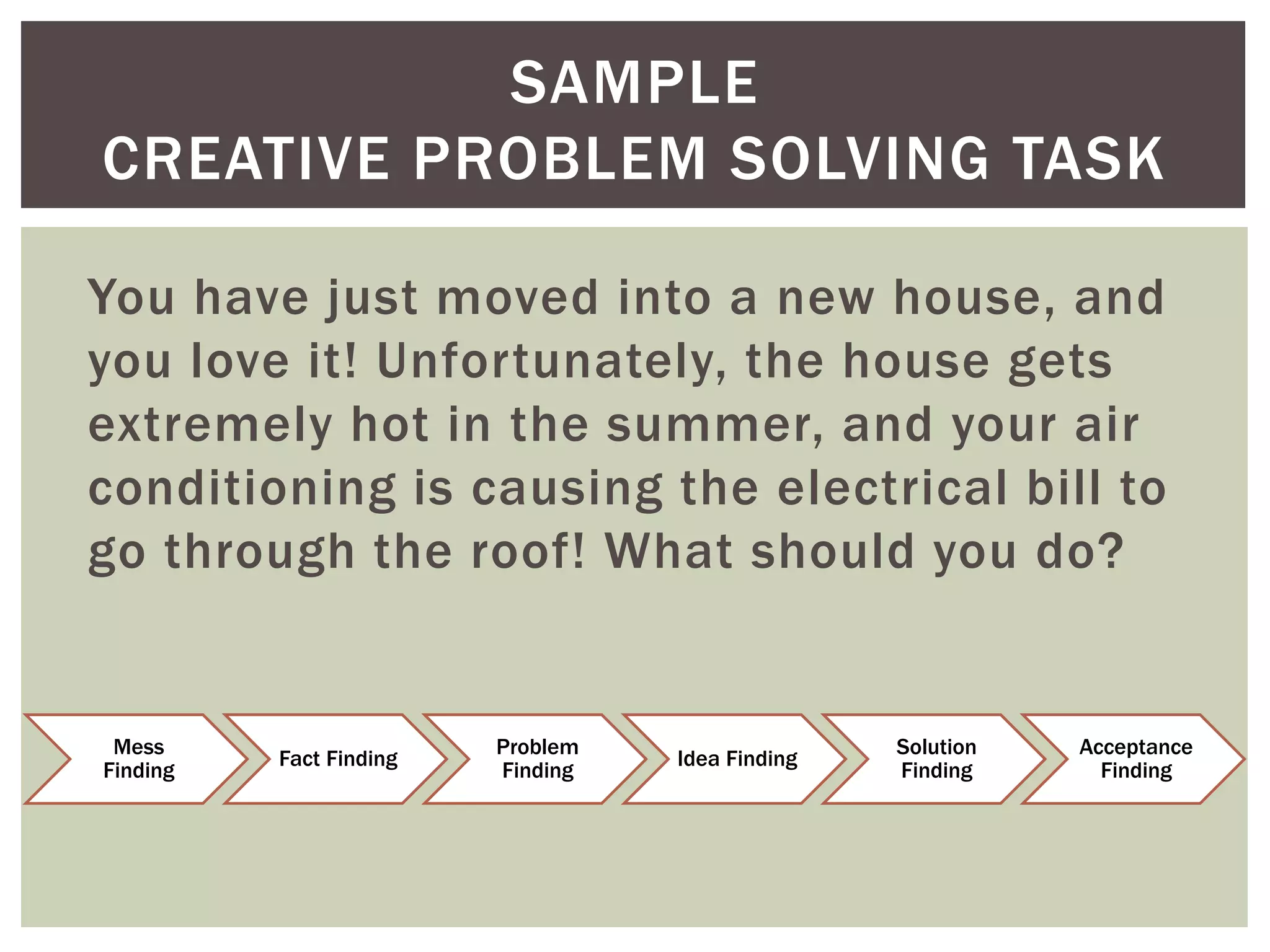
This document introduces the concept of Creative Problem Solving (CPS), which is a framework developed by Alex Osborn and Sidney Parnes to apply creative thinking processes to solve problems. The CPS method involves 6 sequential steps - objective finding, fact finding, problem finding, idea finding, solution finding, and acceptance finding - with an emphasis on divergent and convergent thinking. Examples of CPS tasks are provided to illustrate how it can be applied in classroom settings to teach both content and creative problem-solving skills.