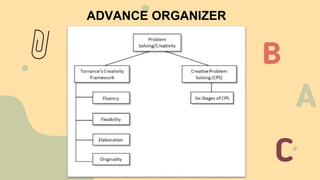
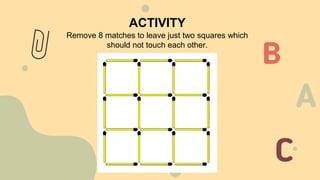
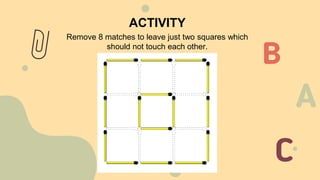
Edward Paul Torrance was known as the "Father of Creativity" for his nearly 60 years of research on creativity. He invented the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking, which helped establish creativity as an important aspect of intelligence. Torrance identified four dimensions of creativity: fluency, flexibility, elaboration, and originality. Creative Problem Solving is an intentional process for solving problems and identifying opportunities developed by Alex Osborn in the 1950s. It involves six stages: mess finding, data finding, problem finding, idea finding, solution finding, and acceptance finding.