This document discusses two theories on whether leaders are born or made:
1. Leadership trait theory suggests that leaders are born with certain innate qualities and traits. However, it does not account for how leadership may vary based on the situation.
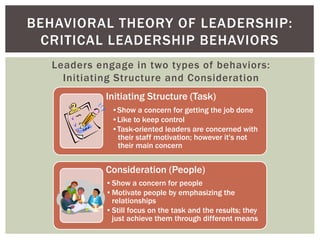
2. Behavioral theory of leadership proposes that anyone can become an effective leader through learning key behaviors, such as initiating structure and consideration. It is based on research finding that a leader's behavior best predicts their influence and success. However, no single leadership style is appropriate for all situations. The most effective leaders can adapt their behavior to different contexts.