Embed presentation
Downloaded 51 times






![Intermediate Value TheoremIf the function is continuous from [a,b], then there must be a point c in the interval [a,b] and it must have a y-value that is between f(a) and f(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/limits-110606081824-phpapp01/75/Limits-17-2048.jpg)
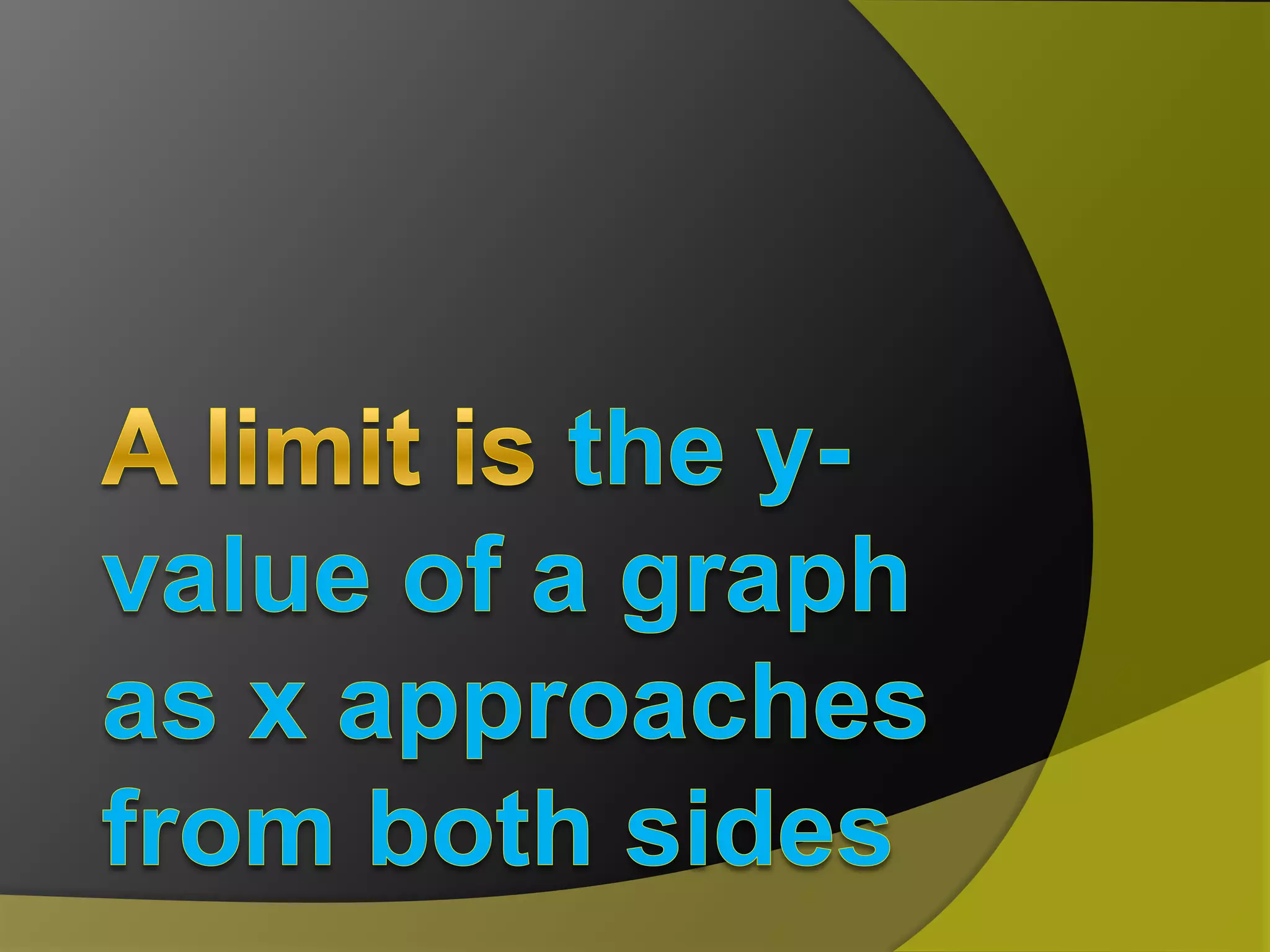
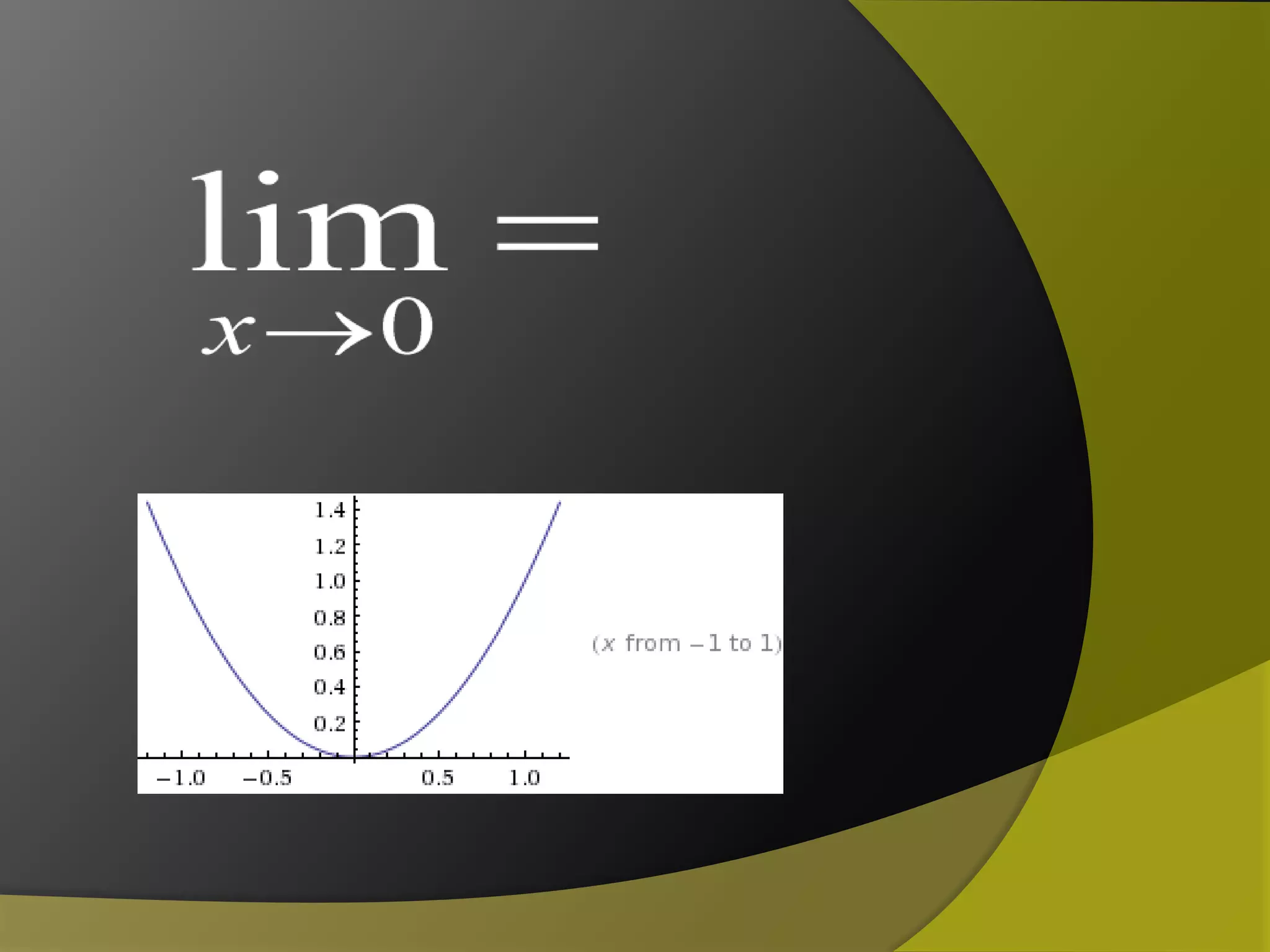
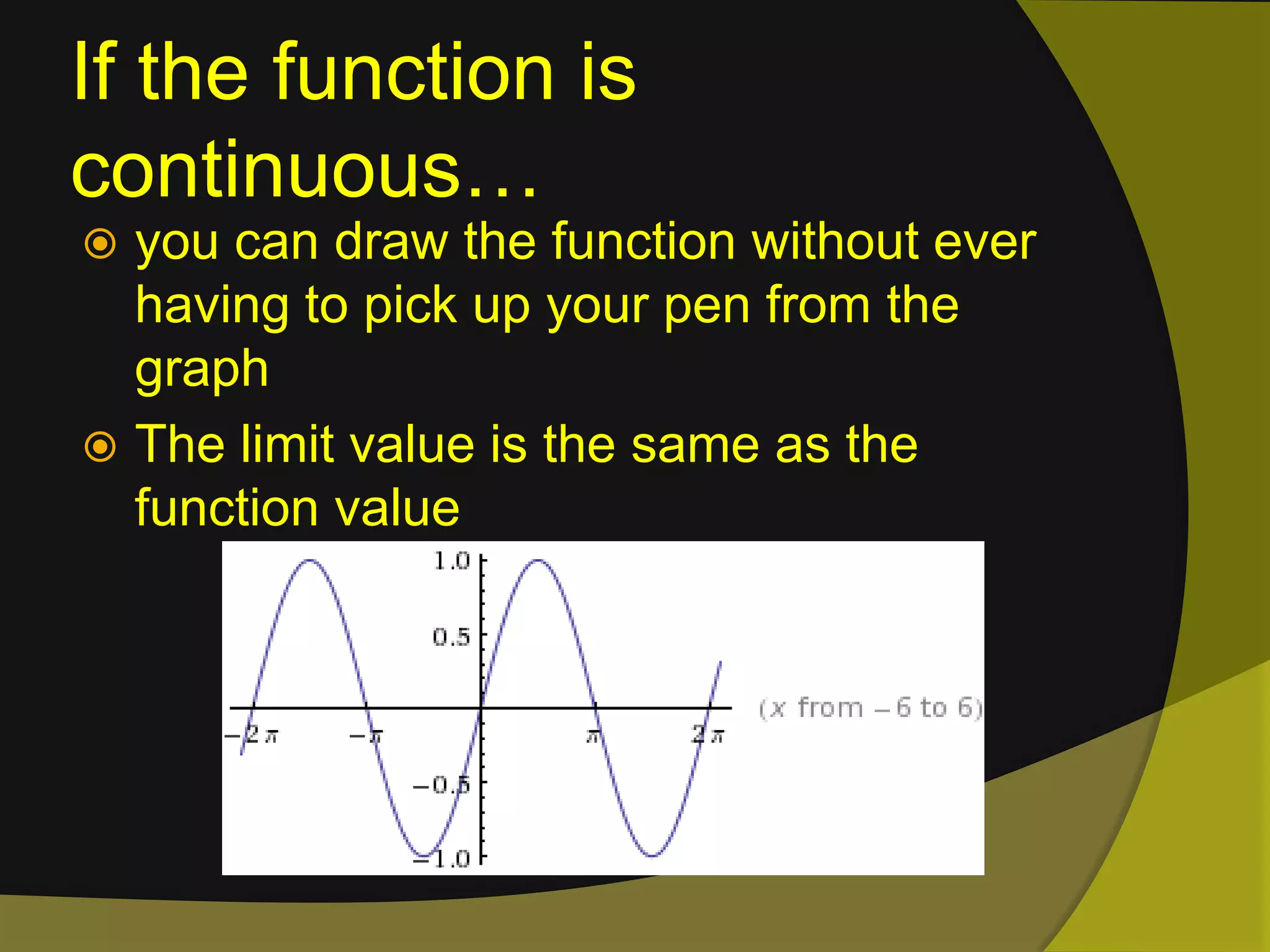
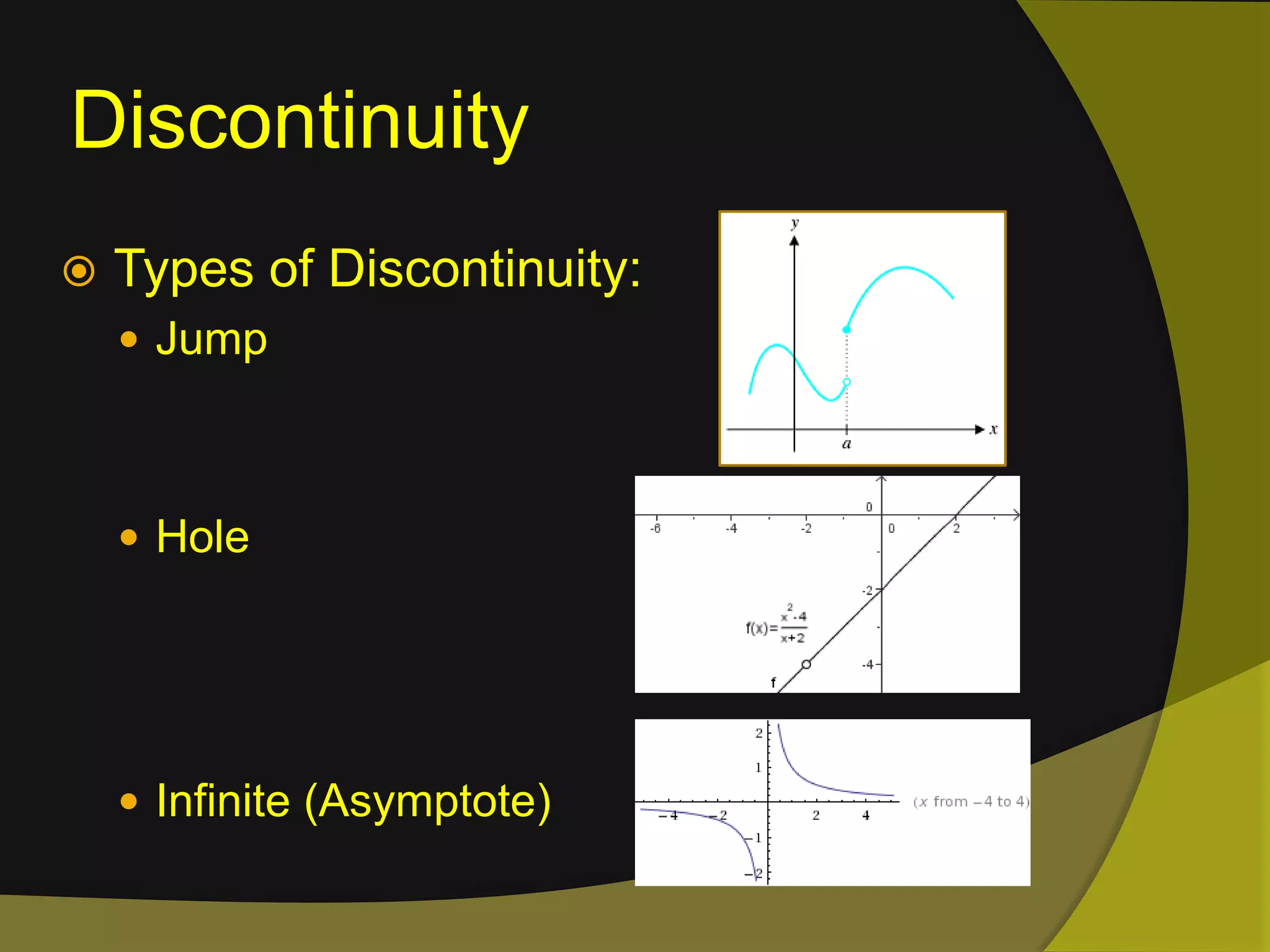
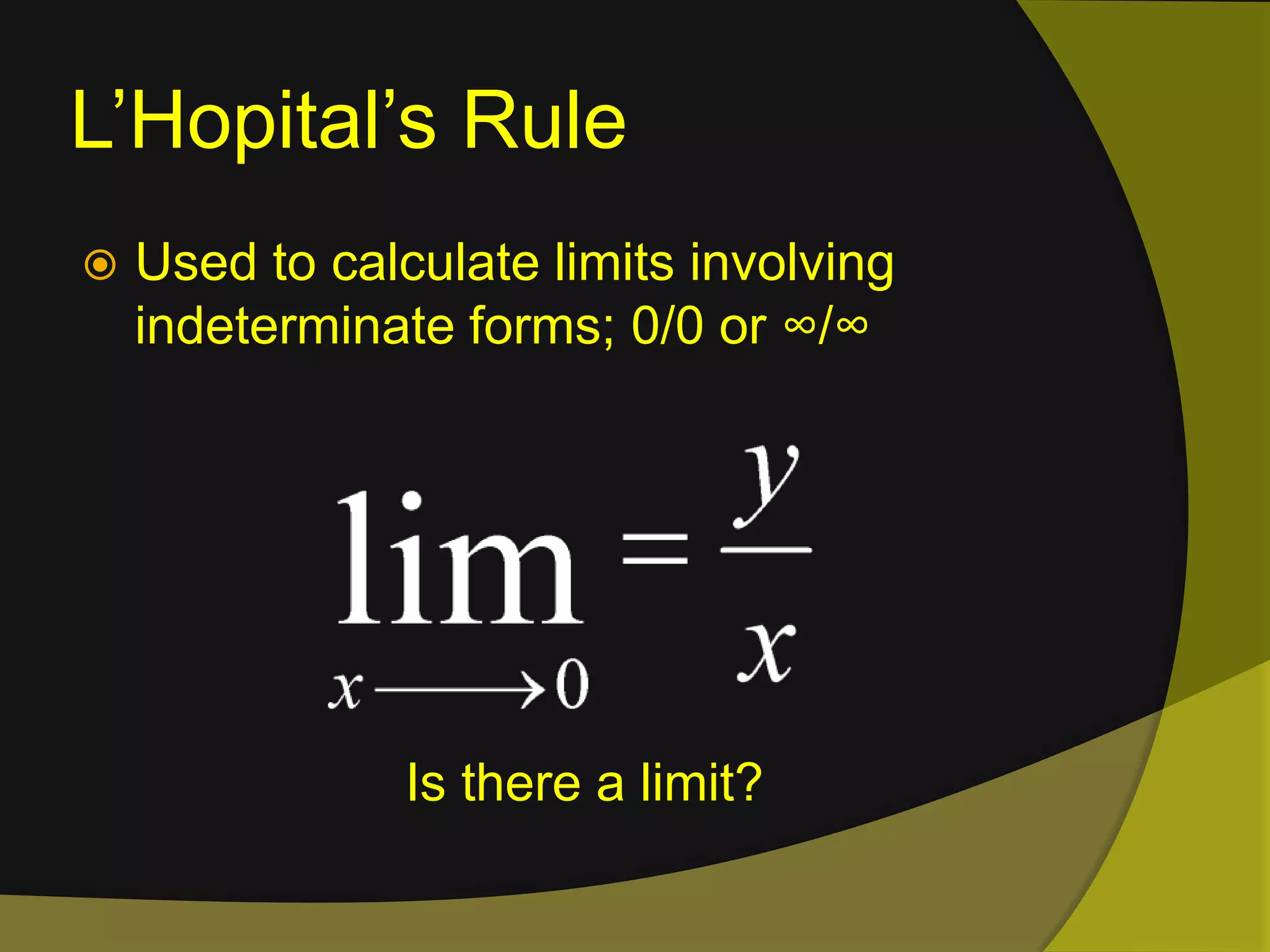
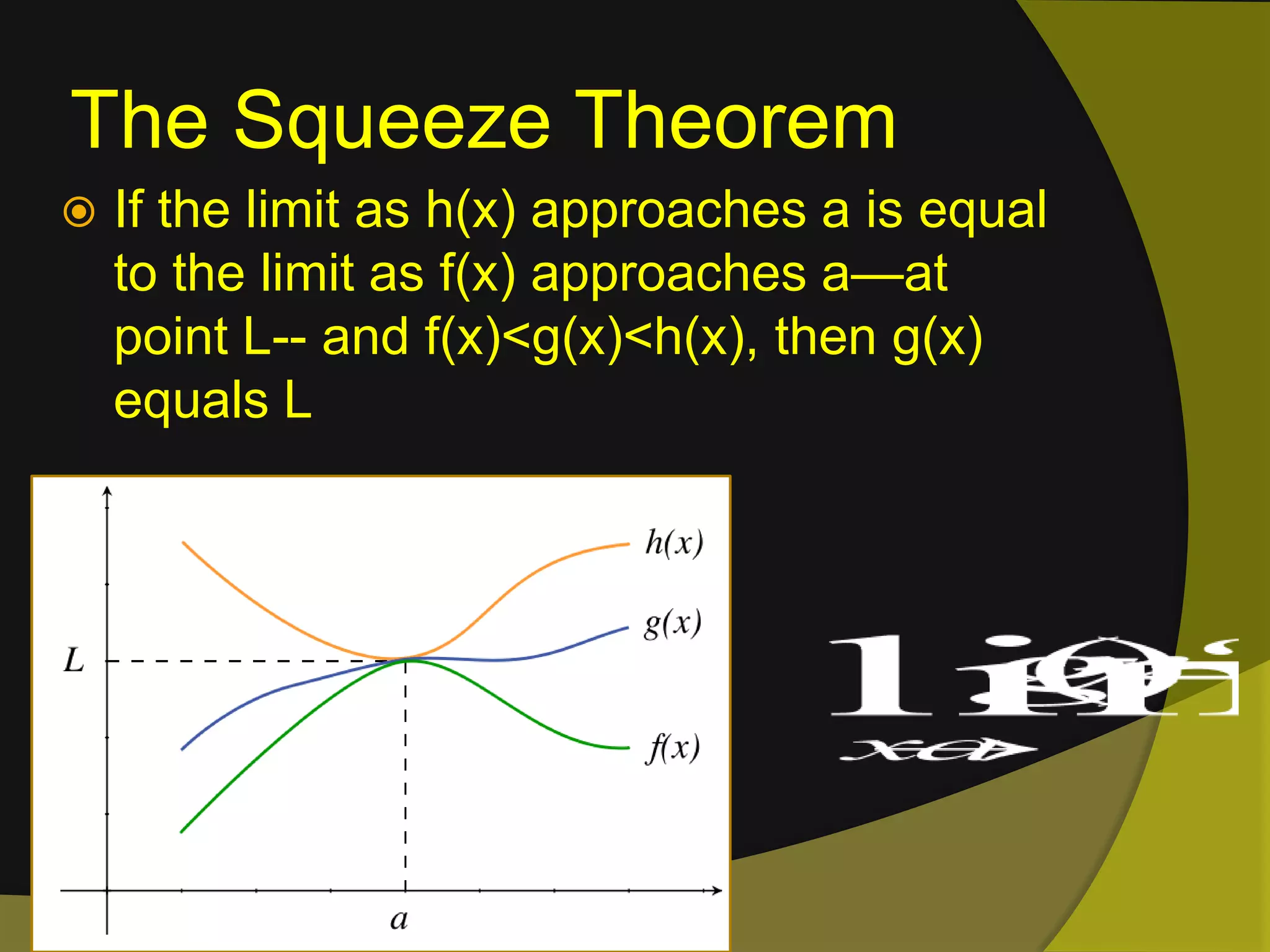
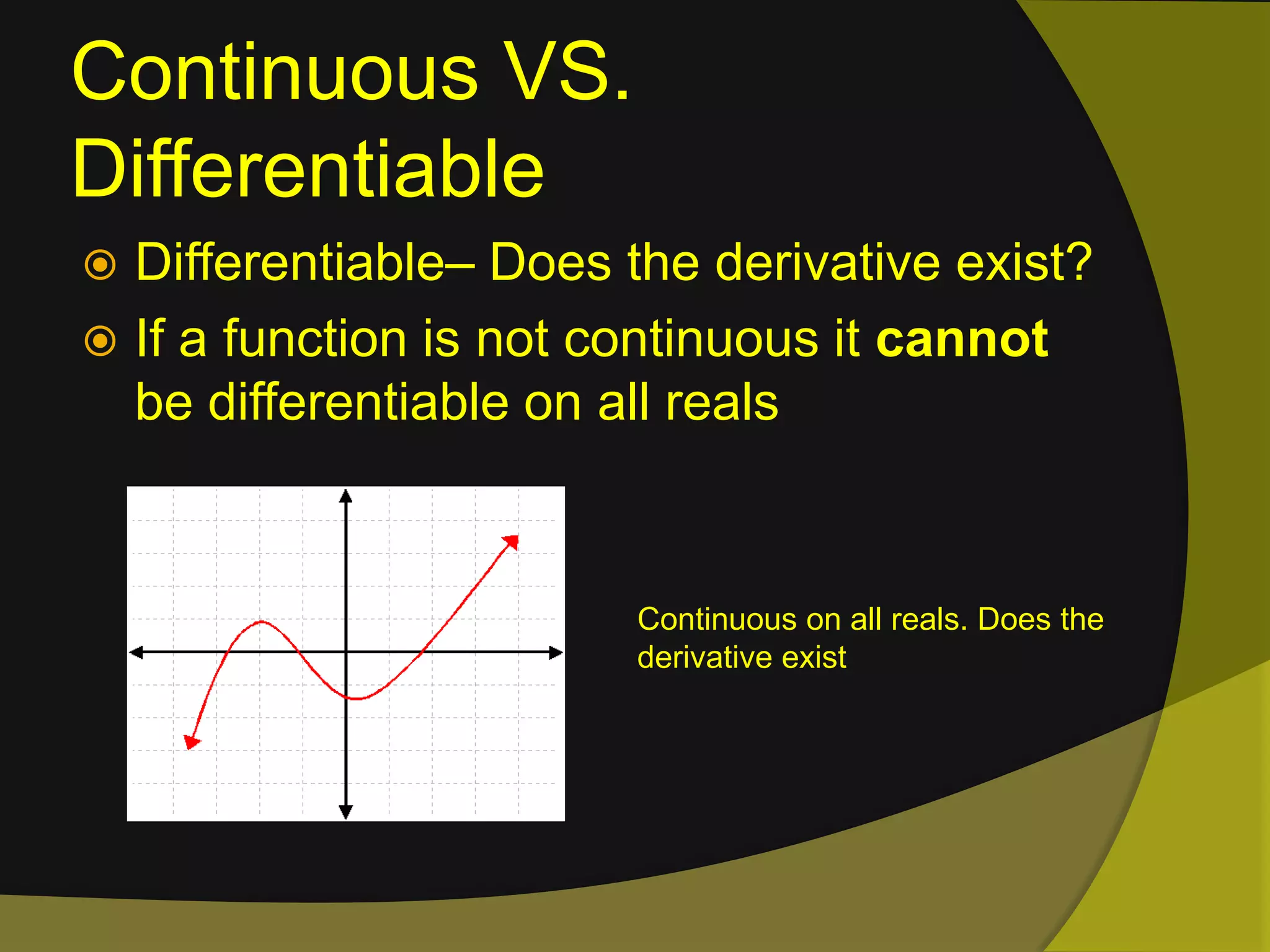
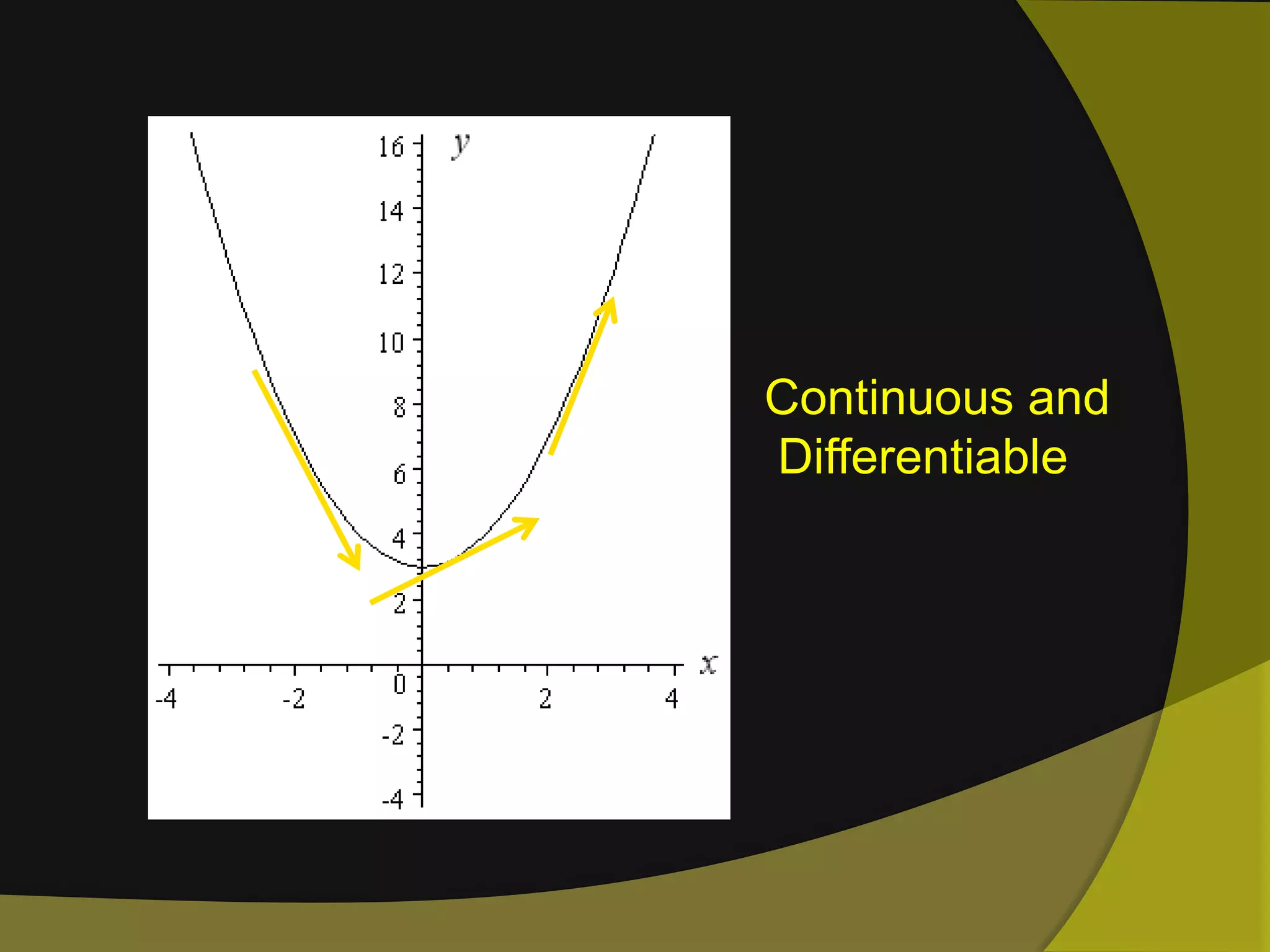
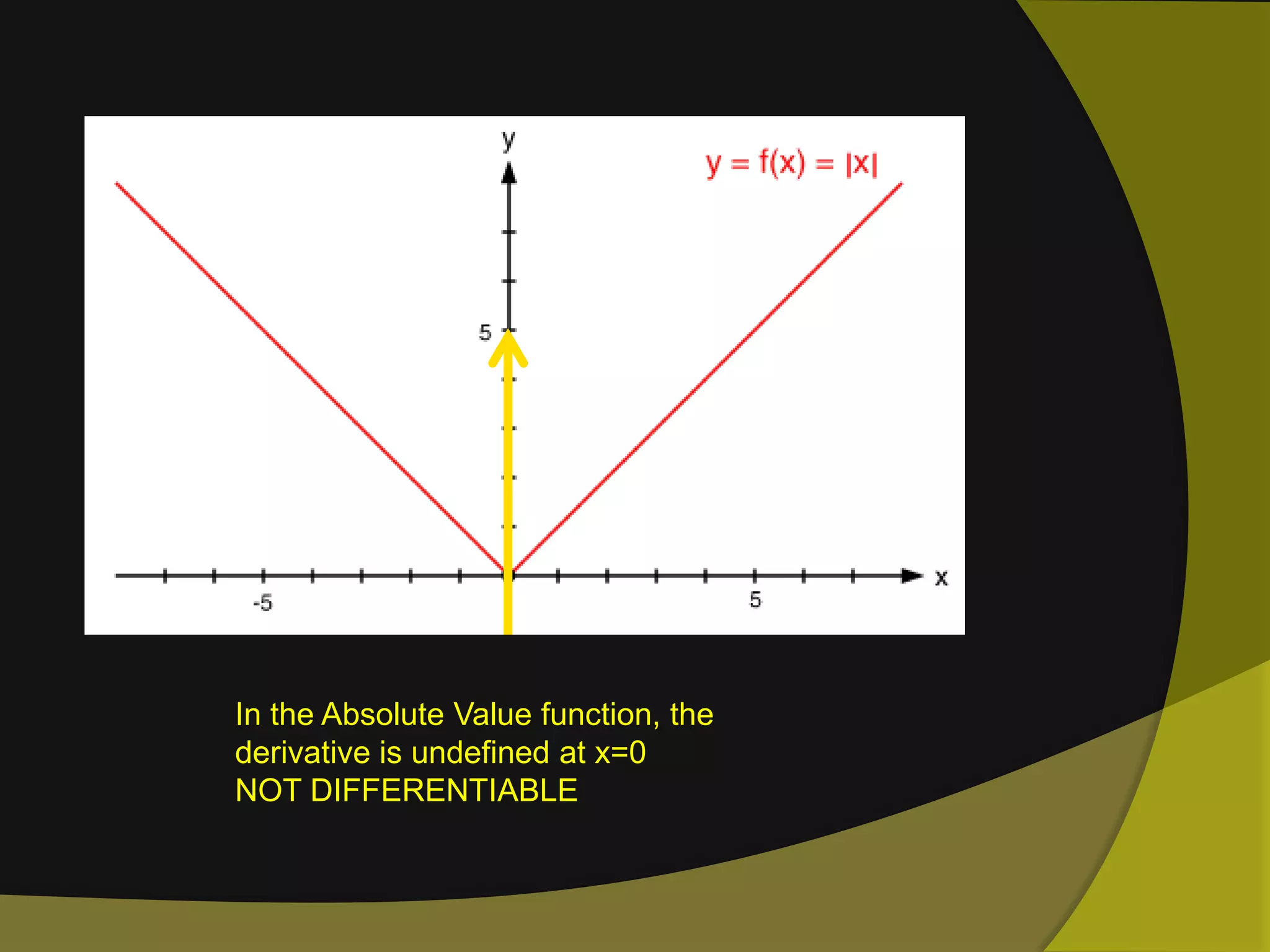
The document discusses limits and continuity in calculus. It defines a limit as the y-value of a graph as x approaches from both sides. It discusses different types of discontinuities such as jumps, holes, and asymptotes. It also discusses left-hand and right-hand limits, L'Hopital's Rule, the Squeeze Theorem, and the differences between continuous and differentiable functions. The Intermediate Value Theorem is also summarized as stating that if a function is continuous over an interval, there must exist a value within the interval.
















![Intermediate Value TheoremIf the function is continuous from [a,b], then there must be a point c in the interval [a,b] and it must have a y-value that is between f(a) and f(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/limits-110606081824-phpapp01/75/Limits-17-2048.jpg)