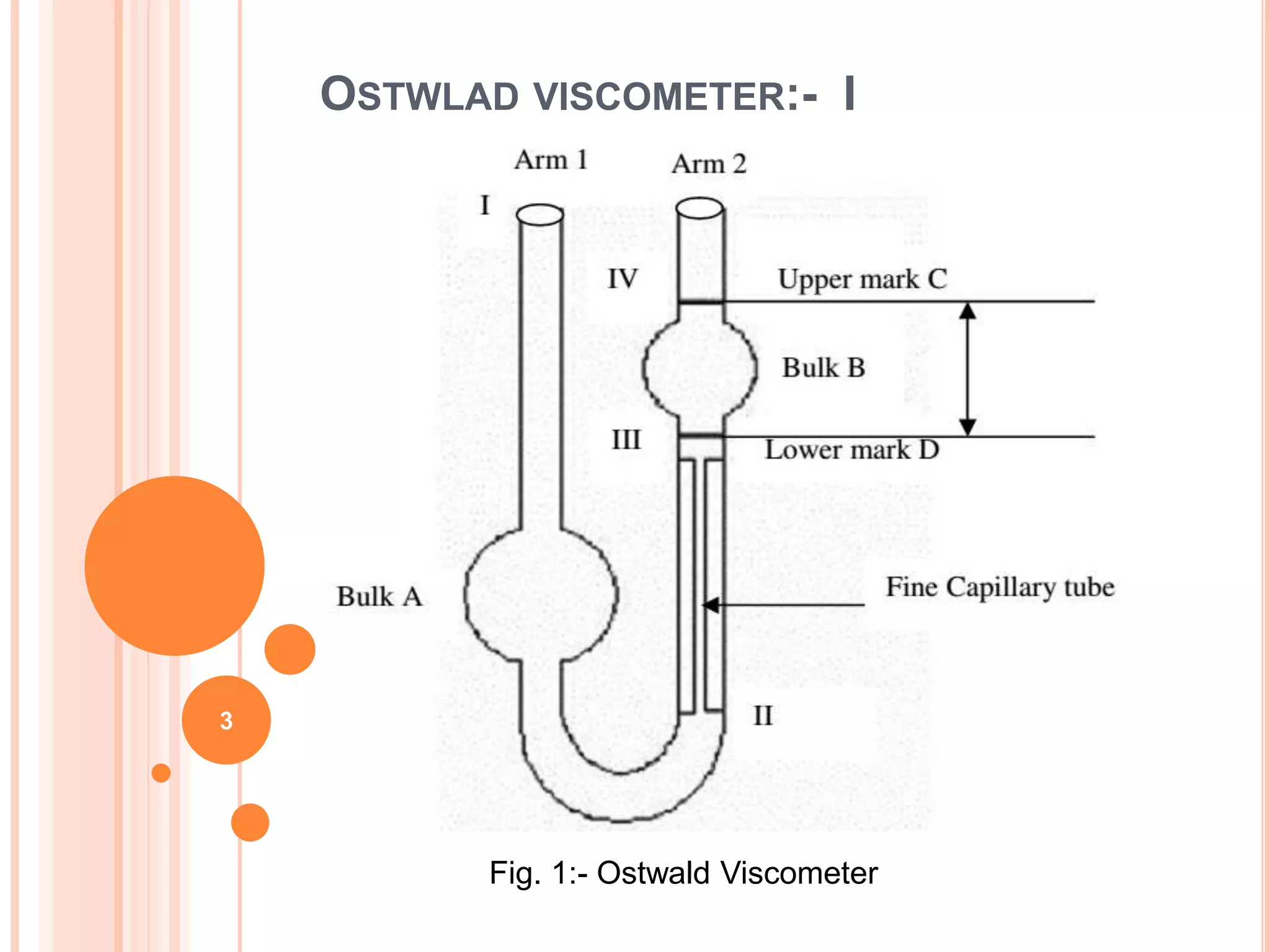
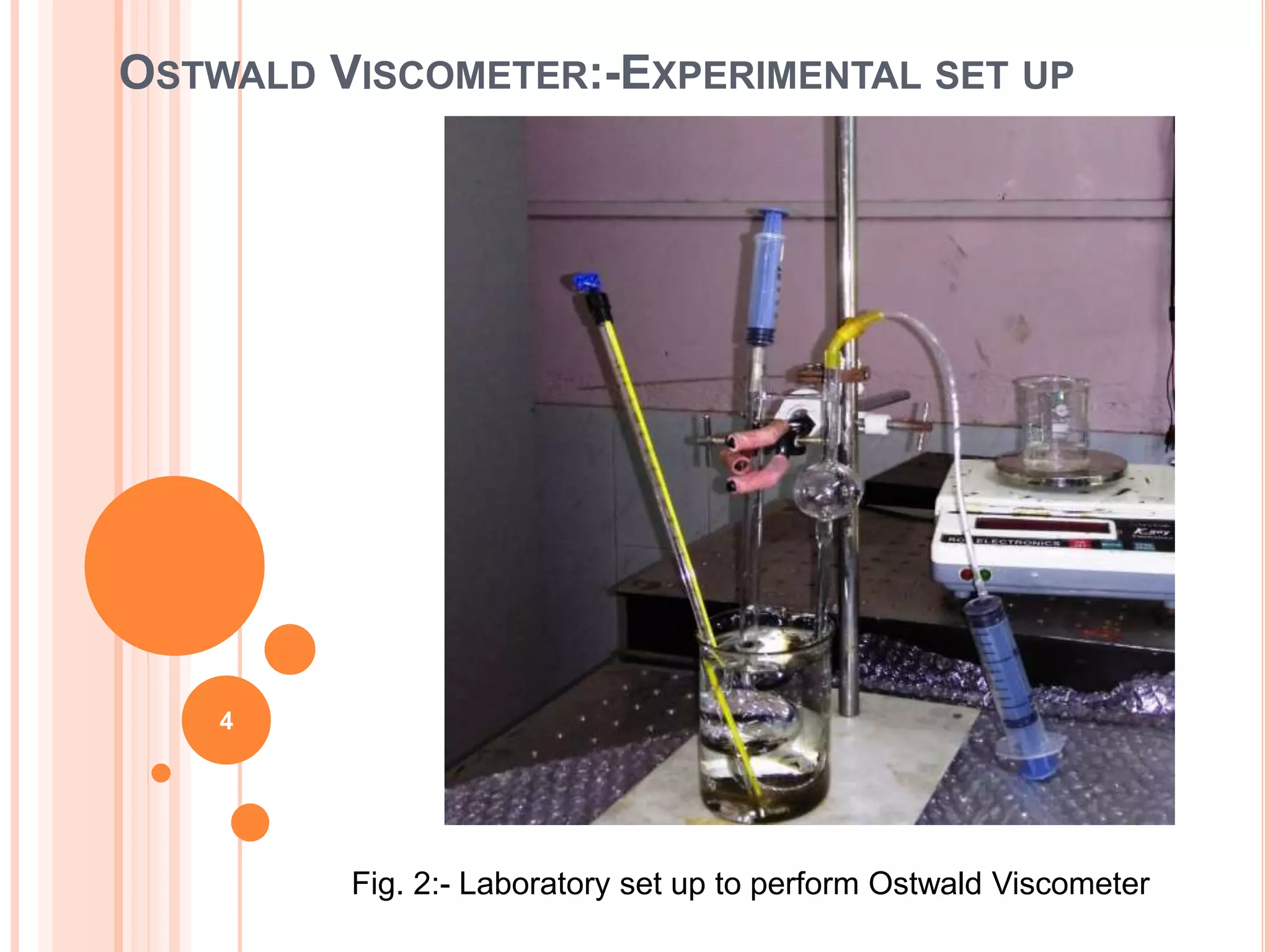
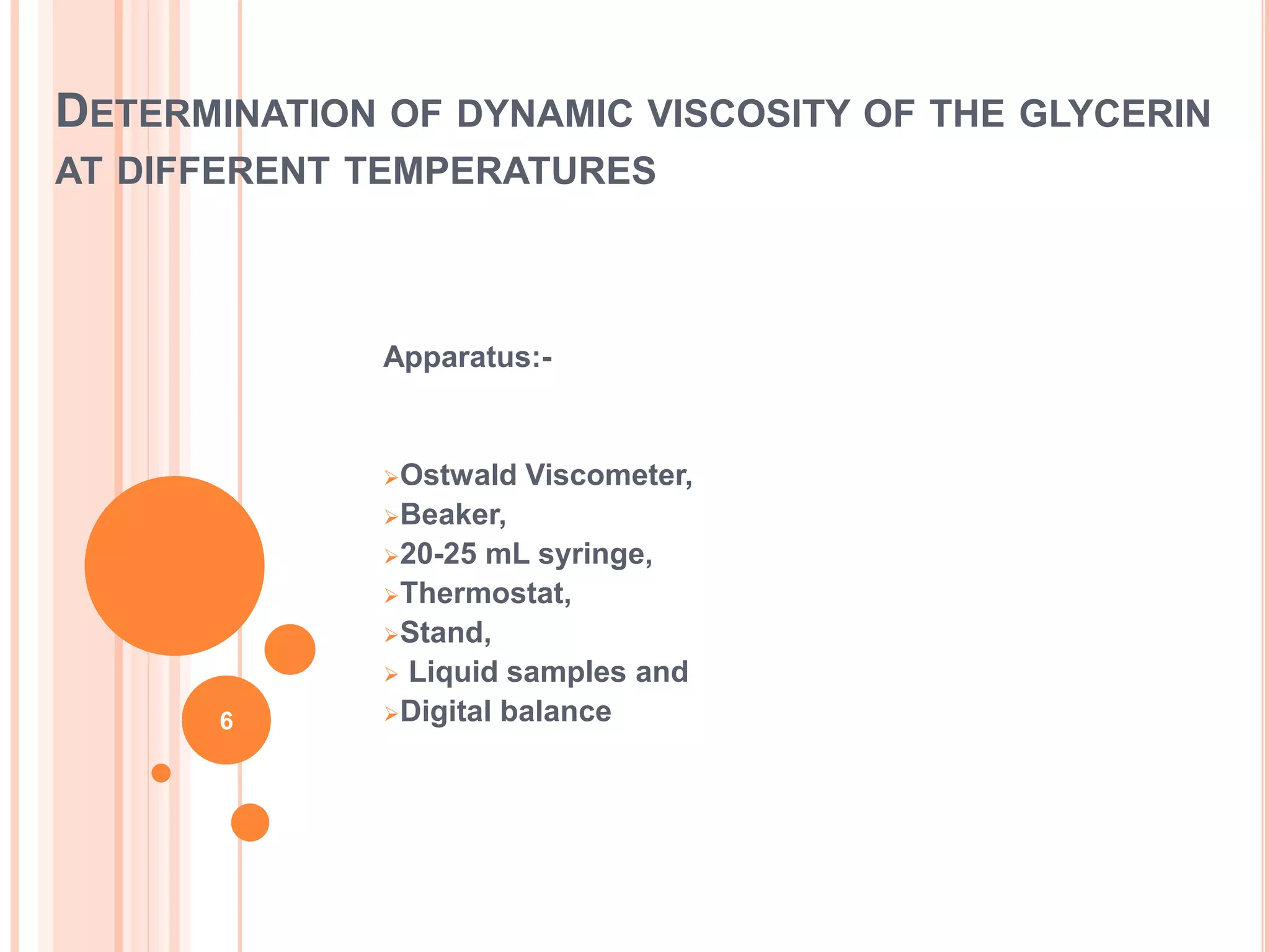
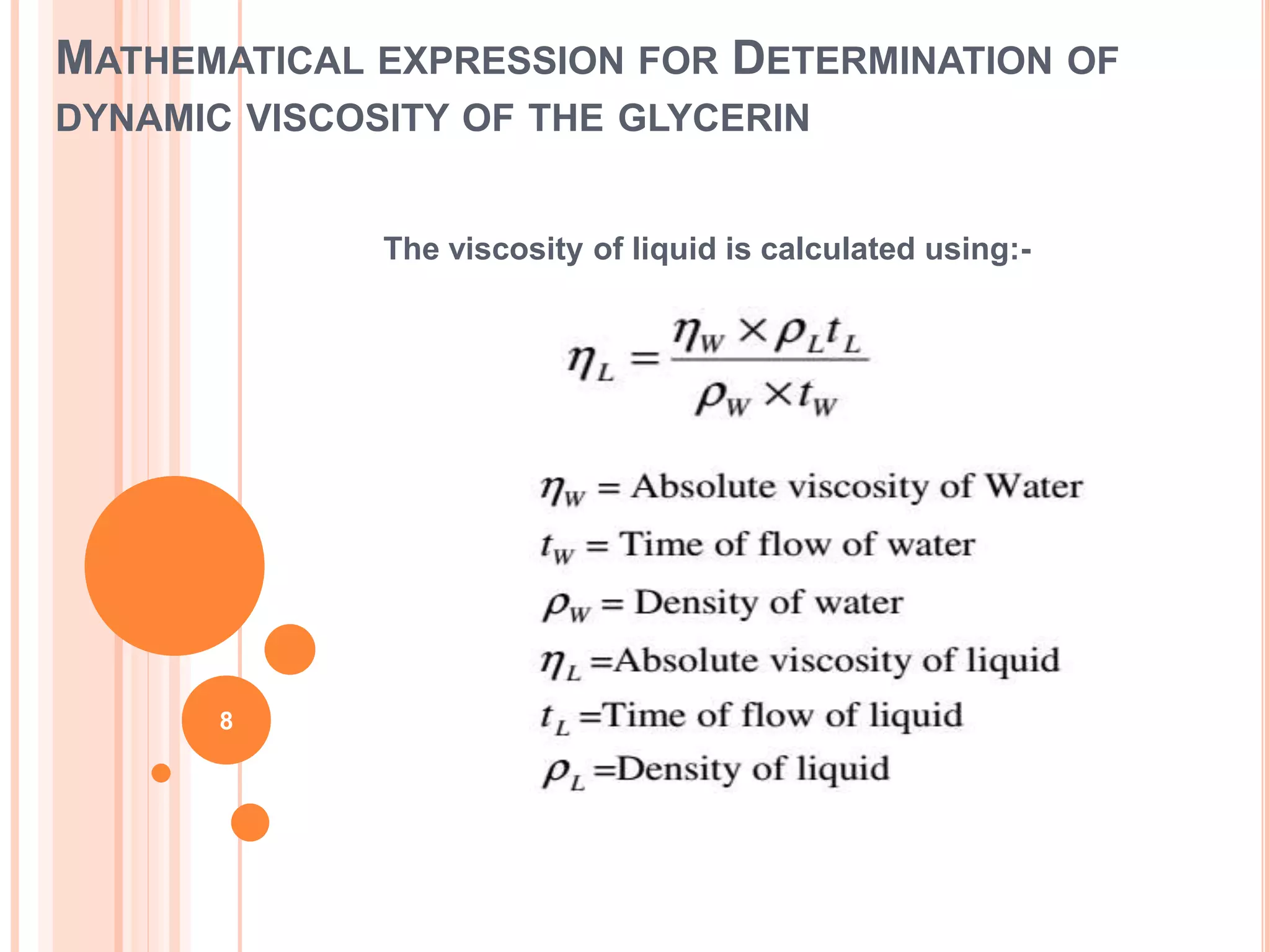
This document describes how to measure the dynamic viscosity of glycerin using an Ostwald viscometer at different temperatures. Key points:
- The Ostwald viscometer experiment involves measuring the flow rate of glycerin-water solutions through a capillary tube at controlled temperatures.
- Flow rate is measured by timing how long it takes the solution level to drop between marked intervals on the viscometer. Lower flow rates indicate higher viscosity.
- Dynamic viscosity is calculated using Poiseuille's law, which relates viscosity to factors like flow rate, capillary tube radius and length, pressure, and temperature.
- Glycerin-water solutions at varying concentrations are tested to obtain viscosity measurements