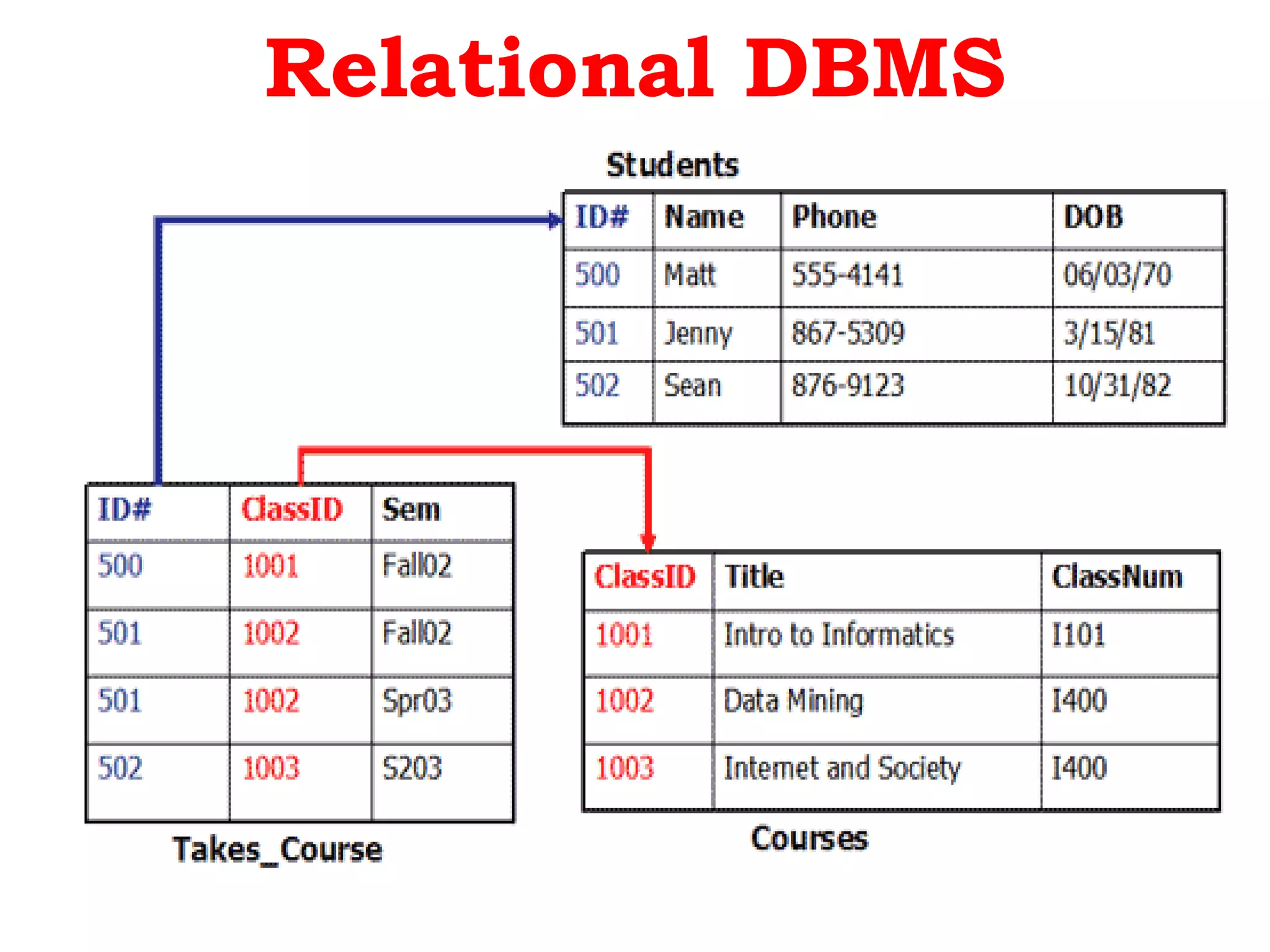
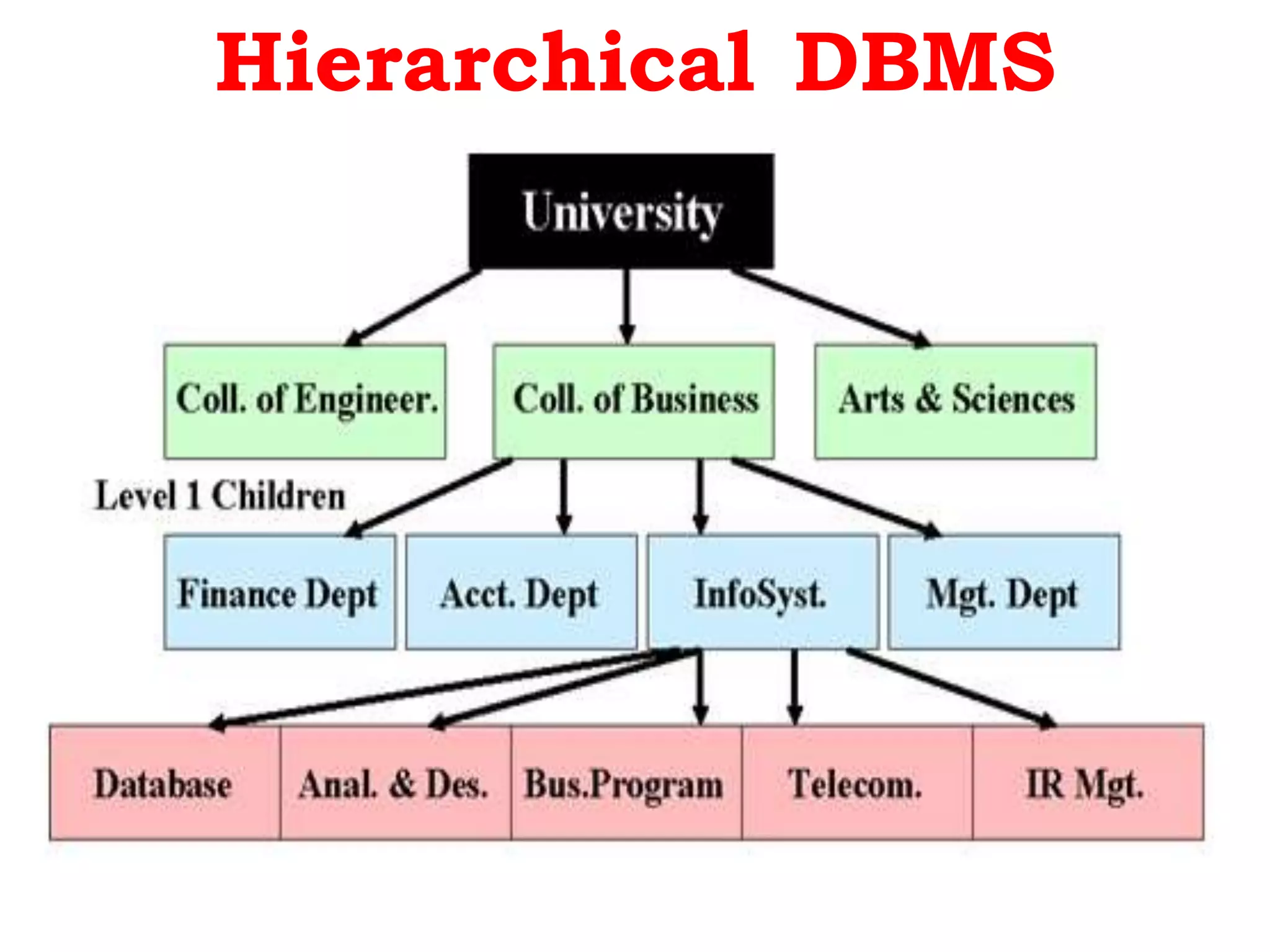
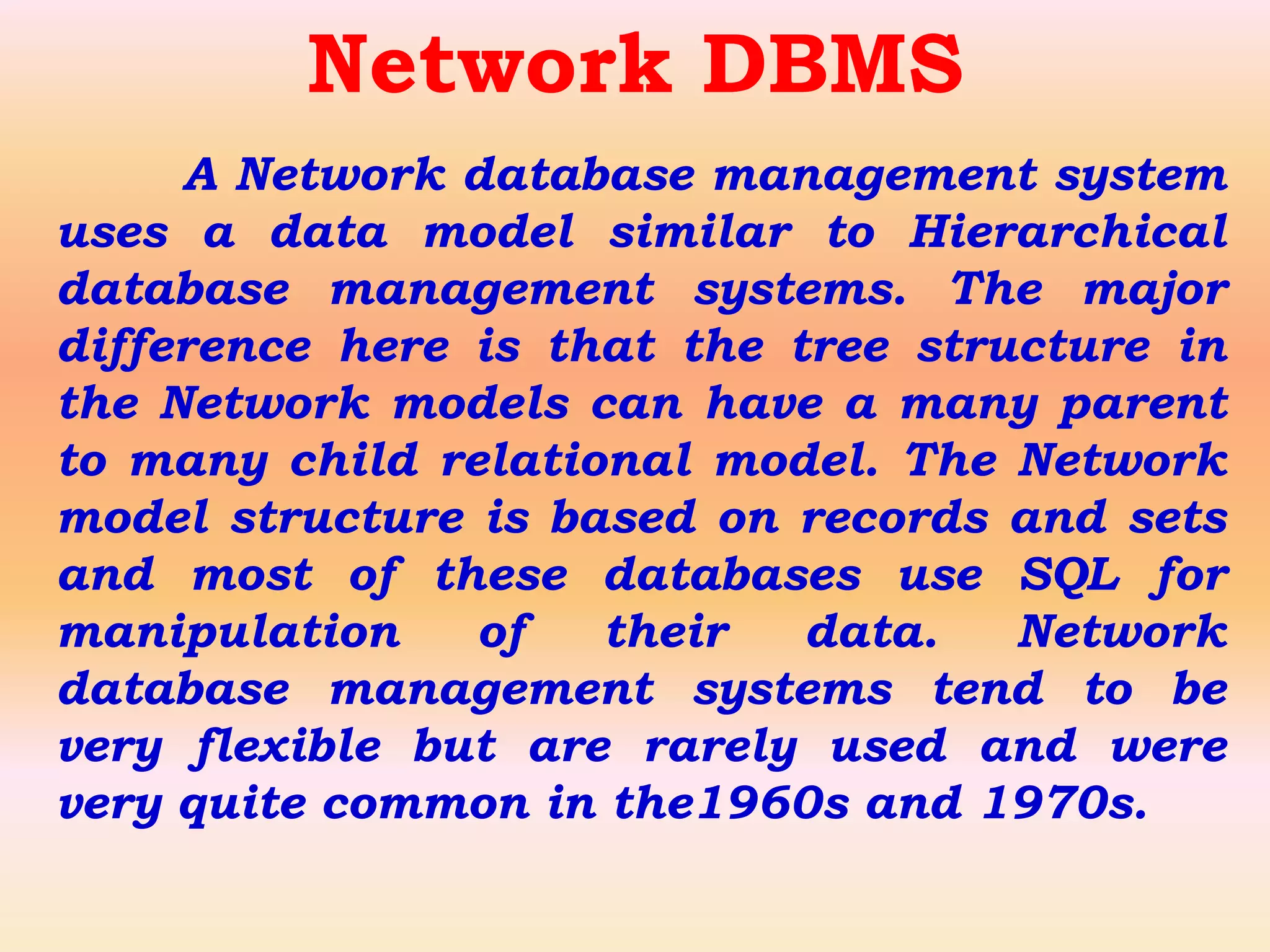
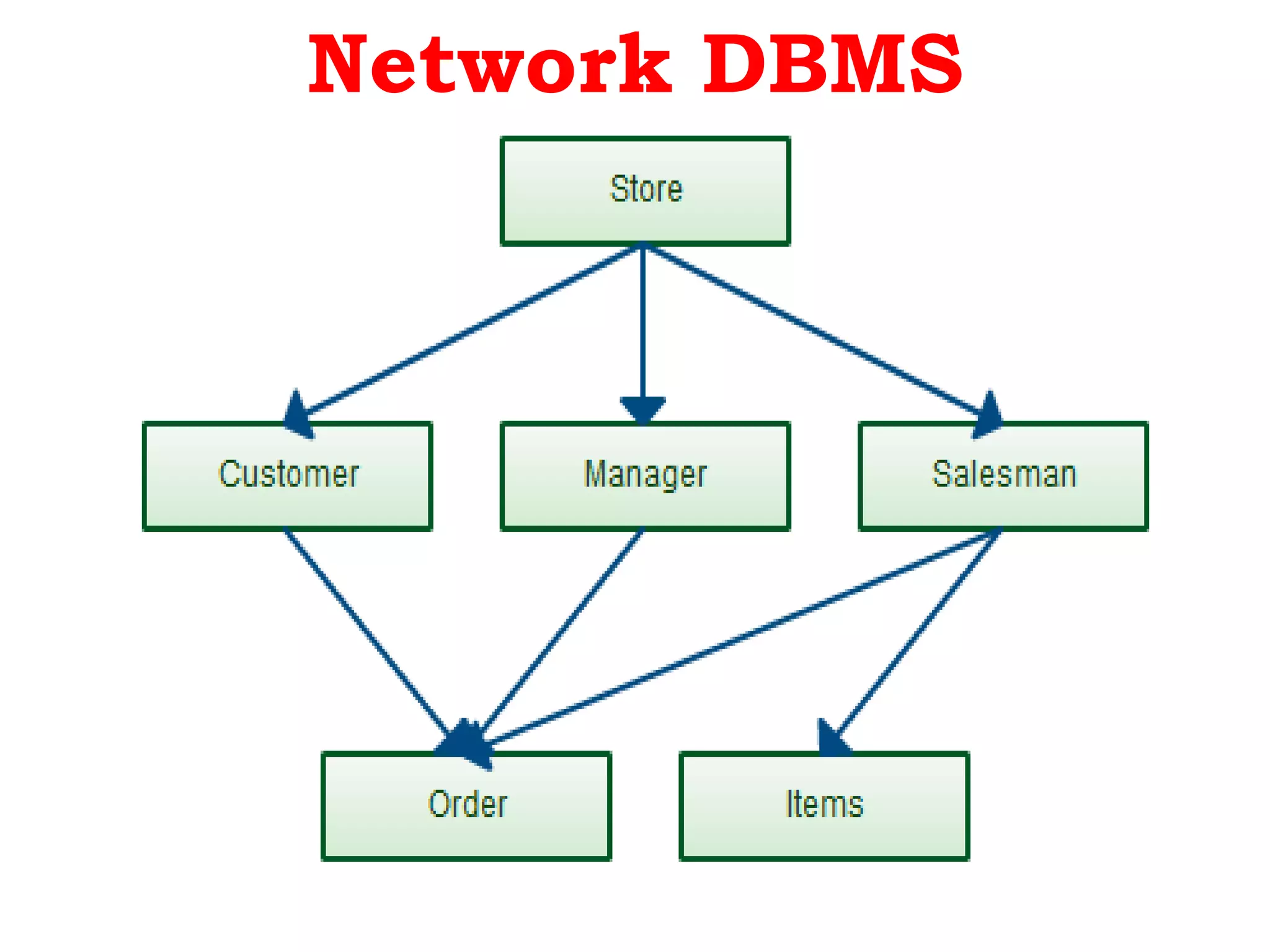
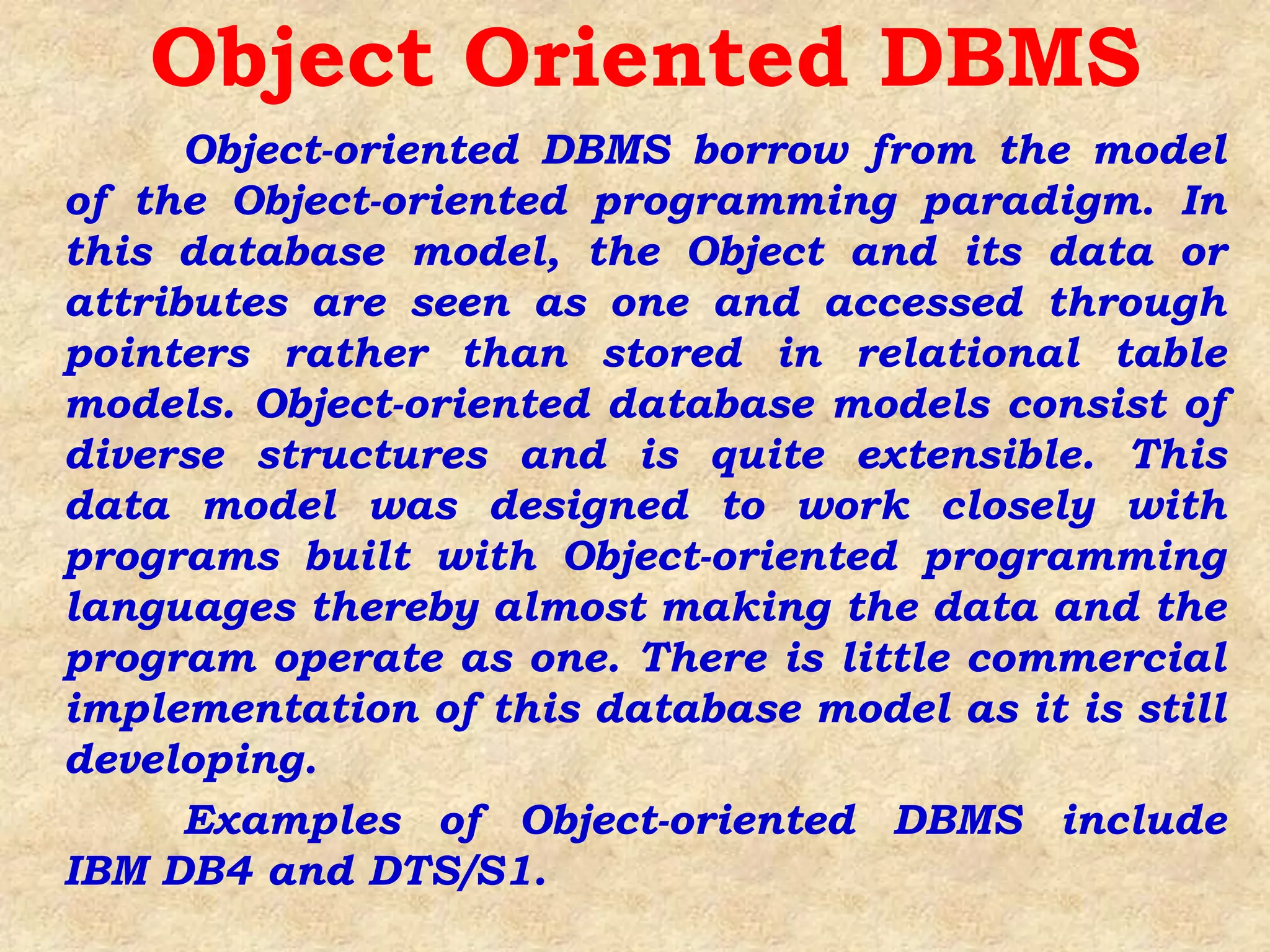
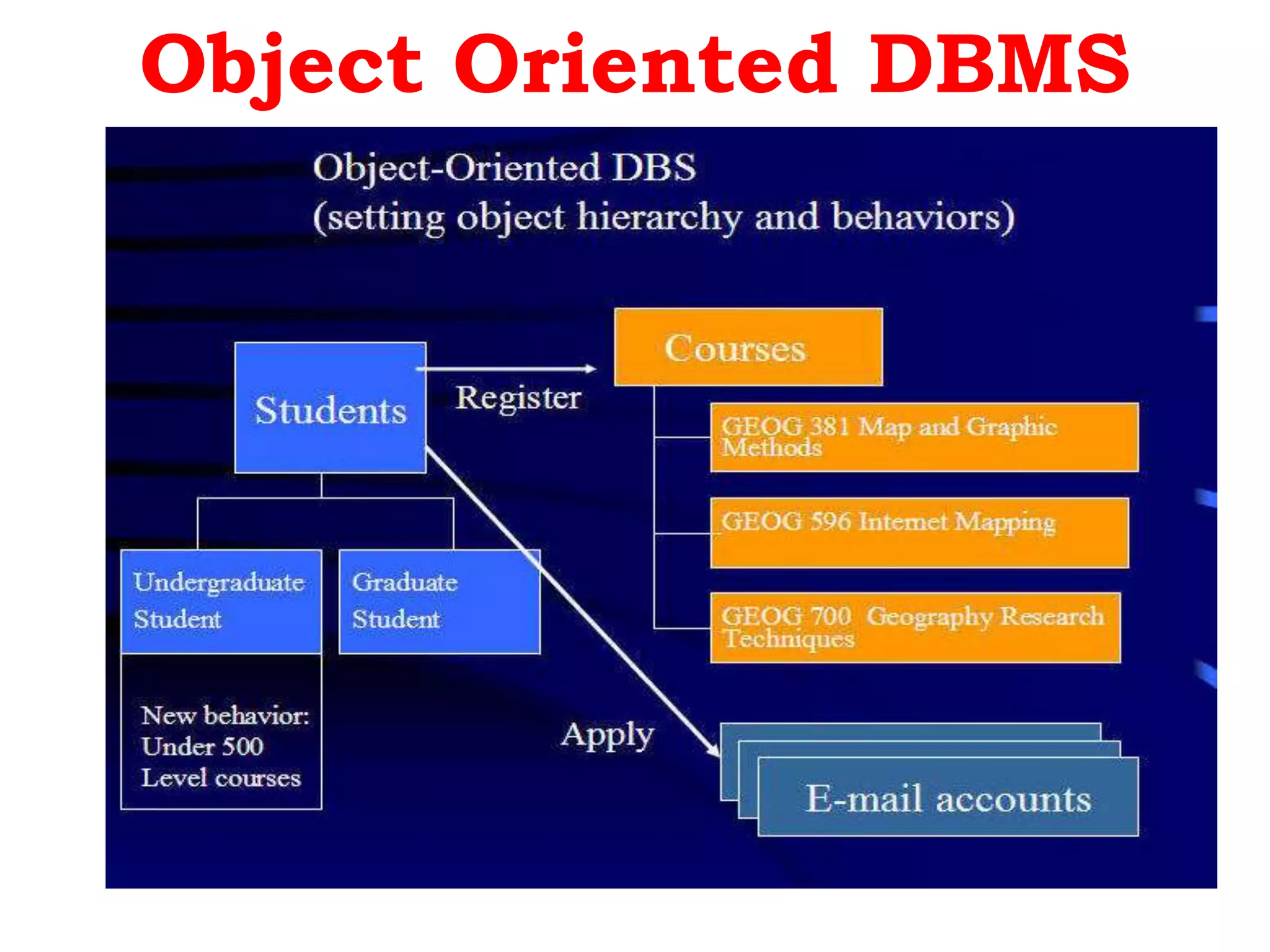
A database management system (DBMS) is system software that manages organization, storage, access, modification and integrity of data in a structured database. A DBMS allows end users to create, read, update and delete data systematically and serves as an interface between the database and end users. Common applications of DBMS include banking, airlines, universities, telecommunications, finance, sales, manufacturing and human resources. Popular DBMS software includes Oracle, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP Sybase ASE, Teradata, ADABAS, MySQL, FileMaker, Microsoft Access and Informix. Common types of DBMS are relational, hierarchical, network and object-oriented.