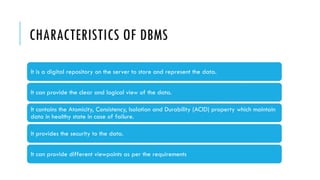
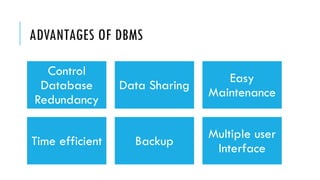
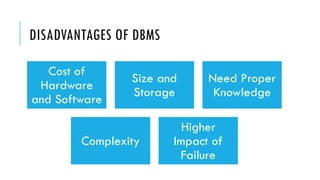
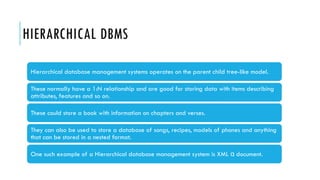
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that facilitates the organization, access, modification, and integrity of data within a structured database. It supports various applications across sectors such as banking, telecommunications, finance, and education while also having advantages like data sharing and easy maintenance, alongside disadvantages like cost and complexity. Types of DBMS include relational, hierarchical, network, and object-oriented models, each with unique structures and use cases.