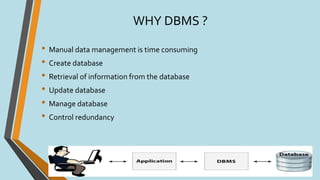
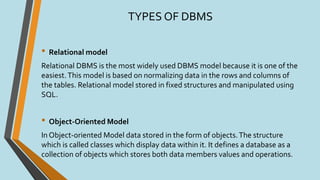
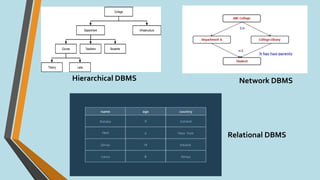
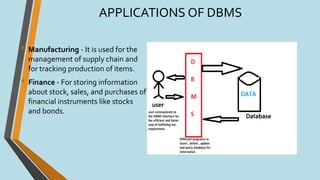
This document discusses database management systems (DBMS), defining databases as systematic collections of data and highlighting the importance of DBMS for efficient data management, including data creation, retrieval, and updates. It outlines various types of DBMS, such as hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented, as well as their applications across different industries. The advantages and disadvantages of DBMS are also covered, emphasizing security and efficiency against potential high costs and complexity.